What Is The Square Root Of 29
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
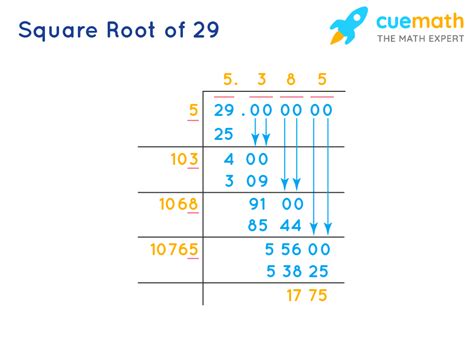
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 29? A Deep Dive into Irrational Numbers
The seemingly simple question, "What is the square root of 29?" opens a fascinating exploration into the world of mathematics, specifically the realm of irrational numbers. While a calculator readily provides a decimal approximation, understanding the true nature of √29 requires a deeper delve into its properties and implications. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the broader mathematical concepts surrounding it.
Understanding Square Roots
Before tackling √29, let's establish a foundational understanding of square roots. The square root of a number, x, is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals x. In simpler terms, it's the inverse operation of squaring a number. For example:
- The square root of 9 (√9) is 3, because 3 x 3 = 9.
- The square root of 16 (√16) is 4, because 4 x 4 = 16.
This concept is straightforward for perfect squares – numbers that are the result of squaring whole numbers. However, things become more interesting when we deal with numbers that aren't perfect squares.
The Irrational Nature of √29
29 is not a perfect square. There is no whole number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 29. This means √29 is an irrational number. Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Their decimal representation continues infinitely without repeating. This is a fundamental difference from rational numbers, such as 1/2 (0.5) or 2/3 (0.666...).
This characteristic of irrationality makes finding the exact value of √29 impossible. We can only approximate it. Calculators typically provide a decimal approximation, such as 5.3851648... However, this is only a truncated representation; the true value extends infinitely.
Approximating √29: Different Methods
While we cannot find the exact value, we can approximate √29 using several methods:
1. Using a Calculator: The Easiest Method
The simplest method is using a calculator. Most calculators have a square root function (√) that directly provides a decimal approximation. This is the most practical method for everyday calculations. The accuracy depends on the calculator's precision.
2. The Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): An Iterative Approach
The Babylonian method is an iterative algorithm that refines an initial guess to progressively closer approximations of the square root. The formula is:
x<sub>n+1</sub> = ½ (x<sub>n</sub> + a/x<sub>n</sub>)
Where:
- x<sub>n</sub> is the current approximation.
- x<sub>n+1</sub> is the next, improved approximation.
- 'a' is the number whose square root we are seeking (in our case, 29).
Let's illustrate this with an initial guess of 5:
- Iteration 1: x<sub>1</sub> = ½ (5 + 29/5) = 5.4
- Iteration 2: x<sub>2</sub> = ½ (5.4 + 29/5.4) ≈ 5.385
- Iteration 3: x<sub>3</sub> = ½ (5.385 + 29/5.385) ≈ 5.38516
As you can see, each iteration brings us closer to the actual value. This method is relatively simple and converges quickly to a good approximation.
3. Linear Approximation: A Simpler, Less Accurate Method
A simpler, albeit less accurate, method involves linear approximation. This involves finding the nearest perfect squares and using their distance to estimate the square root. Since 29 lies between 25 (5²) and 36 (6²), we can say √29 is somewhere between 5 and 6. A crude approximation could be obtained by considering the proportional distance:
29 is 4 units away from 25 and 7 units away from 36. This suggests a value closer to 5 than 6. A very rough estimate would be around 5.3 or 5.4. This method, however, lacks precision compared to the Babylonian method.
4. Using Continued Fractions: A More Advanced Approach
Continued fractions offer a more sophisticated way to represent irrational numbers. They provide a sequence of increasingly accurate rational approximations. The continued fraction representation of √29 is complex and requires a deeper understanding of number theory. However, its use provides a very precise approximation.
The Significance of Irrational Numbers
The existence of irrational numbers like √29 has profound implications in mathematics and beyond:
- Geometry: The discovery of irrational numbers, particularly √2, was a significant milestone in the development of geometry, challenging the then-prevalent belief that all numbers could be expressed as ratios. The diagonal of a square with side length 1 is precisely √2.
- Calculus: Irrational numbers play a crucial role in calculus, forming the basis for many calculations involving curves and areas.
- Physics and Engineering: Many physical constants and measurements involve irrational numbers, highlighting their presence in the real world.
Practical Applications of √29
While √29 might not seem to have immediate practical applications in everyday life like other numbers, its calculation principles apply widely. These include:
- Computer programming: Algorithms for calculating square roots are fundamental in various programming applications, from game development to scientific simulations.
- Engineering calculations: Many engineering problems involving geometry and trigonometry require the calculation of square roots.
- Financial modeling: Interest rate calculations and other financial models often use mathematical functions involving square roots.
Conclusion: Beyond the Decimal Approximation
The square root of 29 is an irrational number, meaning its exact value cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. While we can approximate it using various methods, from simple calculator functions to more complex algorithms like the Babylonian method or continued fractions, understanding its irrational nature is crucial. This seemingly simple number opens doors to a rich mathematical landscape, illustrating the beauty and complexity of numbers beyond the realm of simple integers and fractions. The exploration of √29 provides a valuable learning opportunity to comprehend the fundamental properties of numbers and their application in diverse fields. The more we understand its nature, the better equipped we are to approach more complex mathematical problems and to appreciate the elegance of mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 56 Inches
Mar 12, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 13 Centimeters
Mar 12, 2025
-
12 Is What Percent Of 80
Mar 12, 2025
-
How Many Legs Does The Ant Have
Mar 12, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Ending In An
Mar 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Square Root Of 29 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
