What Is The Prime Factorization Of 66
Juapaving
Mar 05, 2025 · 5 min read
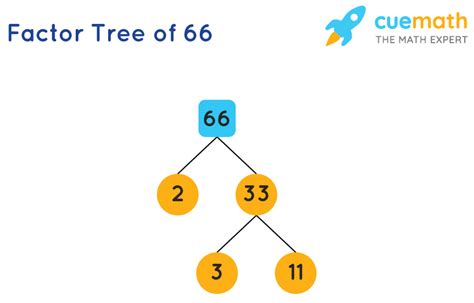
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 66? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 66?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the process reveals fundamental concepts crucial to understanding mathematics and computer science. This article will not only answer the question but will also delve into the underlying principles of prime numbers, prime factorization, and its applications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 66, let's establish a firm understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The sequence continues infinitely, a fact that has captivated mathematicians for centuries.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks in number theory. They are often referred to as the "atoms" of arithmetic because all other whole numbers (except 1) can be constructed by multiplying prime numbers together. This property is the cornerstone of prime factorization. Their unique properties also play a vital role in cryptography, ensuring the security of online transactions and data communication.
Identifying Prime Numbers
Determining whether a large number is prime can be computationally intensive. While simple methods exist for smaller numbers, sophisticated algorithms are required for larger numbers encountered in cryptography. The Sieve of Eratosthenes, a simple but effective ancient algorithm, is a classic method for finding prime numbers within a given range. Modern algorithms, like the Miller-Rabin primality test, provide probabilistic assessments of primality, offering a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency.
Prime Factorization: Breaking Down Numbers
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) as a product of its prime factors. This representation is unique for each composite number; meaning, there's only one way to express a composite number as a product of its prime factors (ignoring the order of the factors). This uniqueness is fundamental to many mathematical applications.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
This uniqueness is formally stated as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, a cornerstone of number theory. It asserts that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (up to the order of the factors). This theorem underpins many aspects of number theory and provides a solid foundation for various mathematical operations.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 66
Now, let's finally find the prime factorization of 66. We can do this using a method called the factor tree.
-
Start with the number 66: We begin by finding the smallest prime number that divides 66 evenly. That's 2.
-
Divide by the prime factor: 66 divided by 2 equals 33.
-
Continue the process: Now we look at 33. The smallest prime number that divides 33 is 3. 33 divided by 3 equals 11.
-
Identify the prime factors: We're left with 11, which is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 66 is 2 x 3 x 11. No other combination of prime numbers will multiply to give 66.
Alternative Methods
While the factor tree is visually intuitive, other methods exist for finding prime factorizations. One approach involves systematically dividing the number by progressively larger prime numbers until only prime factors remain.
Let's demonstrate this with 66:
- Divide 66 by 2: 66 / 2 = 33
- Divide 33 by 3: 33 / 3 = 11
- 11 is a prime number.
This method leads to the same result: 2 x 3 x 11.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple concept of prime factorization has profound implications across various fields:
Cryptography
Prime numbers and prime factorization are central to modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms rely on the difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components. The time it takes to factor a large number with hundreds of digits is computationally infeasible using current technology, making these systems secure. RSA encryption, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, heavily depends on this principle.
Computer Science
Prime factorization algorithms are used in computer science for various tasks, including:
- Hashing: Prime numbers are often used in hash table algorithms to reduce collisions and improve performance.
- Data Compression: Certain compression algorithms leverage the properties of prime numbers to optimize data representation.
Number Theory Research
Prime factorization continues to be a subject of active research in number theory. Open questions about the distribution of primes and the efficiency of factorization algorithms remain central to the field, driving ongoing mathematical inquiry. The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, directly relates to the distribution of prime numbers.
Beyond 66: Exploring Larger Numbers
Understanding the prime factorization of 66 provides a foundation for tackling larger numbers. The process remains the same: systematically divide by prime numbers until you reach only prime factors. For very large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are needed, as manual factorization becomes impractical.
Consider the number 100:
- 100 / 2 = 50
- 50 / 2 = 25
- 25 / 5 = 5
- 5 is prime.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 100 is 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 or 2² x 5².
Conclusion: The Importance of Fundamentals
The prime factorization of 66, seemingly a simple calculation, illustrates the power and elegance of fundamental mathematical concepts. The principles involved extend far beyond this specific example, impacting fields ranging from cryptography to computer science. By understanding prime numbers and prime factorization, we gain insight into the structure of numbers and their applications in a wide array of disciplines. This fundamental knowledge serves as a building block for more advanced mathematical explorations and technological advancements. The seemingly simple question of "What is the prime factorization of 66?" opens a gateway to a world of mathematical wonder and practical application.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Greatest Common Divisor Of 24 And 32
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Factor Of 44
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Sum Of The Interior Angles Of Hexagon
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Do The Arrows On A Food Chain Represent
Mar 05, 2025
-
Words With O I In Them
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 66 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
