What Is The Prime Factorization Of 46
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
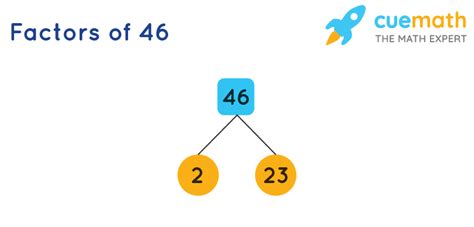
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 46? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 46?" opens a door to a fundamental concept in mathematics: prime numbers and their role in breaking down larger numbers. This exploration will go beyond simply providing the answer; we'll delve into the definition of prime numbers, the process of prime factorization, and the significance of this concept in various areas of mathematics and computer science.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 46, let's solidify our understanding of what constitutes a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In simpler terms, a prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself.
For example:
- 2 is a prime number (only divisible by 1 and 2).
- 3 is a prime number (only divisible by 1 and 3).
- 5 is a prime number (only divisible by 1 and 5).
- 7 is a prime number (only divisible by 1 and 7).
Conversely, numbers that are not prime are called composite numbers. Composite numbers can be expressed as the product of two or more prime numbers. For example, 6 (2 x 3), 12 (2 x 2 x 3), and 15 (3 x 5) are all composite numbers. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The cornerstone of our exploration is the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This theorem underpins the importance of prime factorization; it guarantees that there's only one way to break down any number into its prime components.
This uniqueness is crucial in various mathematical applications, ensuring consistency and predictability in calculations and algorithms.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 46
Now, let's apply our understanding to find the prime factorization of 46. The process involves systematically dividing the number by prime numbers until we are left with only prime numbers as factors.
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 46 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 46 ÷ 2 = 23.
-
Examine the resulting quotient: The quotient is 23.
-
Check if 23 is prime: 23 is only divisible by 1 and 23, making it a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 46 is 2 x 23. We've successfully broken down 46 into its unique prime components.
Methods for Prime Factorization
While the prime factorization of 46 was relatively straightforward, larger numbers might require more systematic approaches. Here are some common methods:
1. Factor Tree Method
This visual method involves branching out from the original number, repeatedly dividing by prime numbers until only prime numbers remain at the ends of the branches. For 46:
46
/ \
2 23
The prime factors at the end of the branches (2 and 23) give us the prime factorization: 2 x 23.
2. Repeated Division Method
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly until the quotient is 1. The prime numbers used in the divisions constitute the prime factorization. For 46:
- 46 ÷ 2 = 23
- 23 ÷ 23 = 1
The prime factors are 2 and 23.
3. Using Algorithms (for larger numbers)
For extremely large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are employed. These algorithms often utilize probabilistic methods to efficiently find prime factors. One such algorithm is the Pollard rho algorithm, which is a probabilistic algorithm that is relatively efficient for finding small prime factors. Other algorithms, such as the general number field sieve, are designed for factoring very large numbers, often used in cryptography. These algorithms are beyond the scope of this basic explanation but highlight the complexities involved in factoring large numbers.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple task of finding the prime factorization of a number has far-reaching consequences in various fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime factorization is the cornerstone of many modern encryption methods. The difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components forms the basis of the security of RSA encryption, widely used in secure online communication, e-commerce, and digital signatures. The strength of RSA encryption relies on the computational difficulty of factoring the product of two very large prime numbers.
2. Number Theory
Prime factorization plays a vital role in number theory, a branch of mathematics focused on the properties of integers. Concepts like modular arithmetic, congruences, and Diophantine equations heavily rely on the properties of prime numbers and their factorization.
3. Abstract Algebra
Prime numbers and their factorization find applications in abstract algebra, particularly in ring theory and field theory. Prime ideals, a concept in ring theory, are directly related to the prime factorization of elements within the ring.
4. Computer Science
Algorithms for prime factorization are crucial in computer science, especially in areas related to cryptography and computational number theory. The efficiency of these algorithms impacts the security and performance of various systems. Furthermore, understanding prime factorization aids in designing efficient data structures and algorithms for handling large numbers.
Beyond 46: Exploring Other Factorizations
Let's briefly explore the prime factorization of some related numbers to illustrate the concept further:
- 47: 47 is a prime number; its prime factorization is simply 47.
- 48: 48 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 2⁴ x 3
- 49: 49 = 7 x 7 = 7²
- 50: 50 = 2 x 5 x 5 = 2 x 5²
These examples demonstrate the diverse ways numbers can be broken down into their prime components, highlighting the fundamental nature of prime numbers in mathematics.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple task of finding the prime factorization of 46 – which we determined to be 2 x 23 – serves as a gateway to understanding the profound importance of prime numbers in mathematics and computer science. From the fundamental theorem of arithmetic to its crucial role in cryptography and other fields, prime factorization continues to be a topic of intense study and application. The simplicity of the concept belies its far-reaching implications, showcasing the beauty and power of fundamental mathematical ideas. The continued exploration and refinement of prime factorization algorithms will remain essential for maintaining the security of our digital world and advancing our understanding of the intricate world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Big Is 6 Inches In Cm
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 85 Inches
May 09, 2025
-
Does The Diagonals Of A Parallelogram Bisect Each Other
May 09, 2025
-
Is 88 A Prime Or Composite Number
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Bonds Is The Weakest
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 46 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.