What Is The Prime Factorization Of 14
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
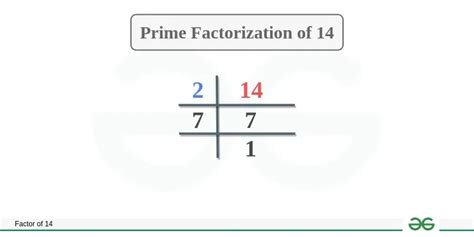
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 14? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 14?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, exploring fundamental concepts like prime numbers, factorization, and their applications in various fields of mathematics and computer science. This article will not only answer the question directly but will also delve into the underlying principles, providing a comprehensive understanding of prime factorization and its significance.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before diving into the prime factorization of 14, let's establish a solid understanding of what constitutes a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's a number that can only be divided evenly by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number. The reason for this exclusion is primarily to maintain the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers. If 1 were considered prime, this uniqueness would be lost.
Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other numbers, forming the foundation of number theory. Their distribution among integers is a subject of ongoing mathematical research, with conjectures like the Riemann Hypothesis focusing on the intricate patterns of primes.
What is Factorization?
Factorization, in its simplest form, is the process of breaking down a number into its constituent factors, which are numbers that divide the original number evenly. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Notice that each factor divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Factorization is crucial in many areas of mathematics. It is used in simplifying algebraic expressions, solving equations, and working with fractions. Understanding factorization is essential for a firm grasp of higher-level mathematical concepts.
Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
Prime factorization is a special type of factorization where a number is expressed as a product of only prime numbers. This process is also known as prime decomposition. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic guarantees that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is a cornerstone of many mathematical proofs and algorithms.
For instance, consider the number 12. Its prime factorization is 2 x 2 x 3, or 2² x 3. No other combination of prime numbers will yield 12. This unique decomposition is what makes prime factorization so important.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 14
Now, let's address the original question: What is the prime factorization of 14?
To find the prime factorization of 14, we need to identify the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal 14. We can start by checking the smallest prime number, 2. 14 is an even number, so it is divisible by 2.
14 ÷ 2 = 7
The result is 7, which is also a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
There are several methods for determining the prime factorization of a number. Let's explore a few common approaches:
1. The Factor Tree Method
The factor tree method is a visual approach that helps break down a number into its prime factors step-by-step. You start by finding any two factors of the number. Then, you continue to find factors for each of those factors until all factors are prime numbers.
For example, let's use the factor tree method for the number 14:
14
/ \
2 7
Both 2 and 7 are prime numbers, so the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7.
2. Repeated Division Method
The repeated division method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly. You continue this process until the result is 1.
Let's use this method for 14:
- Divide 14 by 2: 14 ÷ 2 = 7
- Divide 7 by 7: 7 ÷ 7 = 1
The prime factors are 2 and 7. Therefore, the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7.
3. Using Algorithms (for larger numbers)
For larger numbers, manual methods can become tedious. Computer algorithms, such as the trial division algorithm or the sieve of Eratosthenes, are used to efficiently find prime factorizations. These algorithms optimize the search for prime factors, making the process significantly faster for very large numbers.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, though seemingly a simple concept, finds applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Many cryptographic systems, such as RSA encryption, rely heavily on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The security of these systems depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring such numbers in a reasonable timeframe.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a crucial role in error-correcting codes, used in data transmission and storage to detect and correct errors introduced during transmission.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization is fundamental in abstract algebra, forming the basis for understanding concepts like modular arithmetic and rings.
-
Number Theory Research: Prime numbers and their distribution are active areas of mathematical research, with many unsolved problems and conjectures remaining.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms related to prime factorization are used in various computer science applications, such as primality testing and cryptography.
Conclusion
The prime factorization of 14, 2 x 7, is a simple example that unveils the deeper concepts of prime numbers and factorization. Understanding these concepts is crucial for comprehending more advanced mathematical topics and for appreciating the role of prime numbers in various scientific and technological applications. From the security of online transactions to the underlying structure of numbers themselves, prime factorization forms an essential part of the mathematical landscape. The simplicity of finding the prime factors of 14 belies the profound implications and complexities of the broader field of number theory, highlighting the importance of these seemingly simple building blocks of arithmetic.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 4 7 As A Percentage
Mar 05, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 12 And 7
Mar 05, 2025
-
Is 37 A Composite Or Prime Number
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Does Xxx Mean In Roman Numerals
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Are The Square Roots Of 196
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
