What Is The Prime Factorization Of 100
Juapaving
Mar 05, 2025 · 5 min read
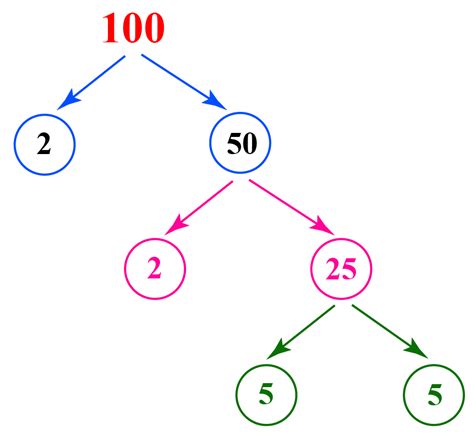
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 100? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 100?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, exploring fundamental concepts like prime numbers, factorization, and their significance in mathematics and beyond. This comprehensive guide will not only answer this specific question but also provide a robust understanding of the underlying principles. We'll delve into practical methods for finding prime factorizations and explore the broader implications of this concept.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before diving into the prime factorization of 100, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Key Characteristics of Prime Numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This is a fundamental theorem in number theory.
- Building Blocks: Prime numbers are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other integers.
What is Factorization?
Factorization is the process of breaking down a composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) into its prime number components. This process is crucial in various mathematical operations and has practical applications in cryptography and computer science. Every composite number can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers, a fact known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 100: Methods and Approaches
There are several ways to determine the prime factorization of 100. Let's explore the most common approaches:
Method 1: The Factor Tree
The factor tree is a visual method that systematically breaks down a number into its factors until only prime numbers remain.
-
Start with 100: We begin with the number 100.
-
Find a pair of factors: We can easily see that 100 = 10 × 10.
-
Branch out: We create two branches from 100, one for 10 and another for 10.
-
Continue factoring: Each 10 can be factored further: 10 = 2 × 5.
-
Prime factorization: We continue until all branches end in prime numbers. In this case, we arrive at 2, 2, 5, and 5.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 100 using the factor tree method is 2 × 2 × 5 × 5, or 2² × 5².
Method 2: Repeated Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible until we reach 1.
-
Start with 100: We begin with the number 100.
-
Divide by 2: 100 ÷ 2 = 50
-
Divide by 2 again: 50 ÷ 2 = 25
-
Divide by 5: 25 ÷ 5 = 5
-
Divide by 5 again: 5 ÷ 5 = 1
The prime numbers used in the division are 2, 2, 5, and 5. Therefore, the prime factorization of 100 is 2 × 2 × 5 × 5, or 2² × 5².
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number isn't just a mathematical exercise; it holds significant importance across various fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime numbers form the bedrock of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is the basis of the security of these systems. RSA encryption, for instance, heavily relies on the complexity of factoring the product of two large prime numbers.
2. Number Theory
Prime factorization is fundamental in number theory, providing insights into the structure and properties of integers. Concepts like modular arithmetic, congruences, and Fermat's Little Theorem are deeply connected to prime factorization.
3. Computer Science
Algorithms for prime factorization are extensively studied in computer science. Efficient algorithms are crucial for various applications, including cryptography and data compression.
4. Abstract Algebra
Prime factorization plays a crucial role in abstract algebra, specifically in ring theory and ideal theory. The unique factorization property is a defining characteristic of many important algebraic structures.
Exploring Related Concepts: Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Understanding prime factorization allows us to efficiently calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers.
-
GCD: The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder. Using prime factorization, we identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers to find the GCD.
-
LCM: The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers. Using prime factorization, we identify all prime factors and their highest powers to determine the LCM.
For example, let's find the GCD and LCM of 100 and 150.
Prime factorization of 100: 2² × 5² Prime factorization of 150: 2 × 3 × 5²
-
GCD(100, 150): The common prime factors are 2 and 5². The lowest power of 2 is 2¹, and the lowest power of 5 is 5². Therefore, GCD(100, 150) = 2 × 5² = 50.
-
LCM(100, 150): All prime factors are 2, 3, and 5. The highest power of 2 is 2², the highest power of 3 is 3¹, and the highest power of 5 is 5². Therefore, LCM(100, 150) = 2² × 3 × 5² = 300.
Beyond 100: Exploring Larger Numbers and Advanced Techniques
While the prime factorization of 100 is relatively straightforward, finding the prime factorization of significantly larger numbers becomes computationally challenging. Advanced algorithms, like the general number field sieve, are employed for factoring very large numbers, crucial in cryptography. These algorithms are far beyond the scope of this introductory discussion, but they highlight the ongoing research and importance of prime factorization in various fields.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple question of the prime factorization of 100 unveils a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From understanding prime numbers and factorization methods to appreciating its significance in cryptography and computer science, this exploration underscores the fundamental role of prime numbers in mathematics and the broader world. The seemingly simple act of breaking down a number into its prime components holds profound implications for fields as diverse as secure communication and the theoretical understanding of numbers themselves. The journey from 100 to 2² × 5² is a journey into the heart of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 3 10 As A Percent
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Many Chambers Does The Heart Of A Frog Have
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Gcf Of 42 And 28
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Division Of The Nucleus Is Called
Mar 06, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 8 And 16
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 100 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
