What Is The Prime Factorization For 66
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
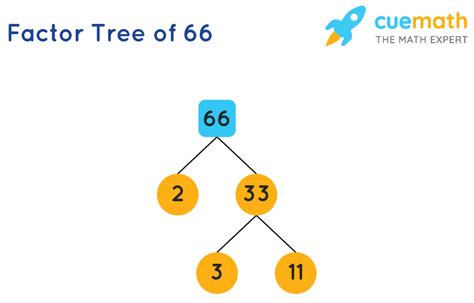
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization for 66? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Finding the prime factorization of a number might seem like a simple mathematical exercise, but it's a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications in number theory, cryptography, and computer science. This article will not only answer the question, "What is the prime factorization for 66?", but also explore the broader concepts of prime numbers, factorization, and their significance. We'll delve into the methods used to find prime factorizations, explore practical applications, and even touch upon some fascinating unsolved problems related to prime numbers.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 66, let's establish a solid understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In other words, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Note that 1 is not considered a prime number.
The fundamental theorem of arithmetic states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This unique representation is called the prime factorization of the number. This theorem forms the bedrock of many number-theoretic concepts.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 66
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 66. We can use a method called the factor tree. This involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until we are left with only prime numbers.
- Start with 66: 66 is an even number, so its smallest prime factor is 2.
- Divide by 2: 66 ÷ 2 = 33
- Consider 33: 33 is divisible by 3.
- Divide by 3: 33 ÷ 3 = 11
- Consider 11: 11 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 66 is 2 x 3 x 11. We can represent this as: 66 = 2 × 3 × 11
This means that 66 can only be expressed as the product of the prime numbers 2, 3, and 11. Any other factorization of 66 will ultimately reduce to this same set of prime factors.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
While the factor tree is a visually intuitive method, especially for smaller numbers, other methods exist for finding prime factorizations, particularly for larger numbers.
-
Trial Division: This method involves systematically testing each prime number as a potential divisor. We start with the smallest prime number (2) and continue until we've found all the prime factors. This method is straightforward but can become computationally expensive for very large numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It's efficient for generating a list of primes, which can then be used in trial division to find the prime factorization of a specific number.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: For extremely large numbers, more sophisticated algorithms like Pollard's Rho algorithm are necessary. These algorithms are probabilistic and rely on advanced mathematical concepts to efficiently find prime factors.
Significance and Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has profound implications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Many modern cryptographic systems, such as RSA encryption, rely heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of these systems hinges on the fact that while multiplying large prime numbers is relatively easy, factoring their product is computationally intractable for sufficiently large numbers.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is central to many branches of number theory, such as the study of modular arithmetic, Diophantine equations, and the distribution of prime numbers.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms related to prime factorization are used in various computer science applications, including hash table design, random number generation, and primality testing.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a crucial role in error-correcting codes, ensuring reliable data transmission and storage.
Exploring Unsolved Problems Related to Prime Numbers
Despite centuries of study, many mysteries surrounding prime numbers remain unsolved. Some notable examples include:
-
The Twin Prime Conjecture: This conjecture proposes that there are infinitely many pairs of twin primes (prime numbers that differ by 2, such as 3 and 5, or 11 and 13). While extensive computational evidence supports this conjecture, a rigorous mathematical proof remains elusive.
-
Goldbach's Conjecture: This conjecture states that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two prime numbers. This conjecture has also been extensively tested, but a formal proof is still lacking.
-
Riemann Hypothesis: This is arguably the most important unsolved problem in mathematics. It concerns the distribution of prime numbers and is deeply connected to the properties of the Riemann zeta function. A proof of the Riemann Hypothesis would have profound implications for our understanding of prime numbers and many other areas of mathematics.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization for 66?" opens the door to a vast and fascinating world of number theory and its applications. While the prime factorization of 66 itself is easily determined, the underlying concepts and their far-reaching implications are crucial to many fields. The ongoing research into prime numbers highlights the enduring mystery and mathematical elegance of these fundamental building blocks of arithmetic. Understanding prime factorization provides a foundation for appreciating the complexity and beauty inherent within the seemingly simple realm of numbers. The quest to understand the distribution and properties of prime numbers continues, driving innovation and progress across various scientific and technological disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Use Distributive Property To Simplify The Expression
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Items Are In A Gross
May 09, 2025
-
13 10 As A Mixed Number
May 09, 2025
-
Most Abundant Cartilage In The Body
May 09, 2025
-
2 Cubic Feet Equal How Many Quarts
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization For 66 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.