What Is The Prime Factorization For 51
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 5 min read
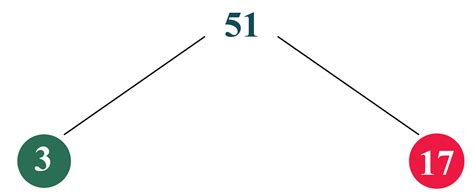
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization for 51? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization for 51?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the process and the underlying concepts of prime numbers and factorization is crucial for anyone seeking a deeper grasp of mathematics. This article will not only provide the answer but delve into the methods, significance, and broader implications of prime factorization, specifically focusing on the number 51.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 51, let's establish a firm understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 2 is unique as it's the only even prime number. All other even numbers are divisible by 2, and thus, not prime.
Key Characteristics of Prime Numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This was famously proven by Euclid.
- Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: Every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors). This theorem forms the bedrock of prime factorization.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that multiply together to make a specific number. It's like breaking down a number into its fundamental building blocks, which are its prime factors. This process is unique for every composite number (a number that is not prime).
Why is Prime Factorization Important?
Prime factorization has numerous applications across various mathematical fields and even in computer science, including:
- Cryptography: The security of many encryption algorithms relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
- Number Theory: Prime factorization is a cornerstone of many theorems and concepts in number theory.
- Modular Arithmetic: Understanding prime factorization aids in solving problems related to modular arithmetic, which is essential in cryptography and other areas.
- Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization has significant implications in abstract algebra, particularly in ring theory and field theory.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 51
Now, let's finally address the prime factorization of 51. We need to find the prime numbers that multiply together to equal 51. We can do this systematically:
- Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 51 is not divisible by 2 (it's odd).
- Try the next prime number, 3: 51 divided by 3 is 17.
- Check if 17 is prime: 17 is only divisible by 1 and 17, confirming it's a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 51 is 3 x 17. This means that 3 and 17 are the prime factors of 51. There are no other prime numbers that can be multiplied together to produce 51.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
Several methods can help determine the prime factorization of a number, especially for larger numbers. These include:
- Trial Division: This is the most basic method, involving successively dividing the number by prime numbers starting from 2. It's efficient for smaller numbers but becomes computationally expensive for very large numbers.
- Factor Trees: A visual method that breaks down a number into smaller factors until only prime numbers remain. It's a helpful tool for visualizing the process.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: A method to generate a list of prime numbers up to a specified limit. It's not directly used for factorization, but it can help identify potential prime factors.
- Advanced Algorithms: For extremely large numbers, specialized algorithms are employed, such as the General Number Field Sieve (GNFS), which are computationally intensive and require significant processing power.
The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic assures us that the prime factorization of any integer greater than 1 is unique (except for the order of the factors). This means that there's only one set of prime numbers that will multiply to give a particular composite number. This uniqueness is essential in various mathematical contexts and is a cornerstone of number theory.
For 51, this uniqueness is evident. There is no other combination of prime numbers that will multiply to equal 51 other than 3 x 17. This uniqueness is crucial for many mathematical operations and proofs.
Practical Applications of Prime Factorization
Beyond the theoretical realm, prime factorization finds practical application in various fields:
- Cryptography: RSA encryption, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of online transactions and sensitive data often depends on this cryptographic technique.
- Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a critical role in error-correcting codes, which are vital for reliable data transmission and storage.
- Hashing Algorithms: Prime numbers are frequently used in hashing algorithms to minimize collisions and ensure efficient data retrieval.
Conclusion: The Significance of Prime Factorization for 51 and Beyond
While the prime factorization of 51 might seem like a straightforward problem (3 x 17), it provides a glimpse into the elegant world of number theory. Understanding prime factorization is crucial not just for solving mathematical problems but also for appreciating its importance in various applications, from securing online transactions to ensuring reliable data transmission. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which underlies the uniqueness of prime factorization, is a foundational concept in mathematics with far-reaching consequences. This seemingly simple number, 51, therefore serves as a gateway to explore deeper mathematical concepts and their practical implications in the modern world. The exploration of prime factorization extends far beyond just finding the factors of a single number; it's a journey into the core principles that govern the structure of numbers and their significant role in our technological world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Is Blood Considered To Be A Connective Tissue
May 09, 2025
-
Name For A Group Of Penguins
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 1 Billion X 1 Trillion
May 09, 2025
-
Vinegar Is An Acid Or Base
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 3 Out Of 4 As A Percentage
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization For 51 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.