What Is The Prime Factorization For 14
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
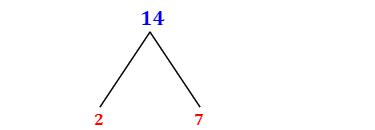
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization for 14? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization for 14?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the underlying concepts of prime numbers and factorization provides a robust understanding of fundamental mathematical principles. This article will delve into the prime factorization of 14, explaining the process step-by-step and broadening the scope to encompass related topics and their significance in mathematics and computer science.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 14, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder.
Some examples of prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number, while numbers like 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), and 9 (3 x 3) are not prime because they have divisors other than 1 and themselves. The infinitude of prime numbers is a fundamental theorem in number theory, meaning there are infinitely many prime numbers.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Greater than 1: 1 is not a prime number.
- Fundamental Building Blocks: All other integers (excluding 1) can be expressed as a product of prime numbers.
What is Factorization?
Factorization, in the context of number theory, is the process of breaking down a composite number (a number that is not prime) into its prime number factors. This process is unique for every composite number; meaning every composite number has only one unique prime factorization. This uniqueness is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic states that every integer greater than 1 is either a prime number itself or can be represented as a unique product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. For example, the number 12 can be factored as 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3), and this is the only possible prime factorization of 12.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 14
Now, let's address the original question: What is the prime factorization of 14?
We start by finding the smallest prime number that divides 14. That number is 2.
14 ÷ 2 = 7
The result, 7, is also a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7. We can't break it down any further into smaller prime numbers. This fulfills the criteria of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
While the prime factorization of 14 was relatively simple, larger numbers require more systematic approaches. Here are a few common methods:
1. Factor Tree Method
The factor tree is a visual method. You start with the original number and repeatedly branch out, dividing by the smallest prime number possible until you're left with only prime numbers at the end of each branch.
For example, let's find the prime factorization of 60 using a factor tree:
60
/ \
2 30
/ \
2 15
/ \
3 5
This shows that the prime factorization of 60 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 5, or 2² x 3 x 5.
2. Repeated Division Method
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number until you reach 1. Keep track of the prime divisors you used.
Let's factor 60 using repeated division:
- 60 ÷ 2 = 30
- 30 ÷ 2 = 15
- 15 ÷ 3 = 5
- 5 ÷ 5 = 1
The prime factors are 2, 2, 3, and 5. Therefore, the prime factorization of 60 is 2² x 3 x 5.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, despite its seemingly simple nature, has profound applications across various fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime numbers are the foundation of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors is the basis of the security of RSA cryptography, a widely used public-key cryptosystem used to secure online transactions and communications. The larger the prime numbers used, the more secure the encryption becomes.
2. Computer Science
Prime factorization plays a role in algorithms for efficient computation and data structures. Understanding prime numbers is crucial in the design of hash tables and other data structures that rely on efficient distribution of data.
3. Number Theory Research
Prime numbers are a central topic of ongoing research in number theory. Open problems such as the Riemann Hypothesis, which deals with the distribution of prime numbers, are of immense interest to mathematicians worldwide. The search for larger and larger prime numbers continues to push the boundaries of computational power.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding prime factorization opens doors to more advanced concepts in number theory:
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): Finding the greatest common divisor of two or more numbers involves finding their prime factorizations and identifying the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The least common multiple is found by identifying all prime factors present in the numbers, raised to the highest power.
- Modular Arithmetic: This branch of number theory deals with remainders after division and is crucial in cryptography.
- Diophantine Equations: These are algebraic equations where only integer solutions are sought. Prime factorization is often helpful in solving certain types of Diophantine equations.
Conclusion: The Significance of Prime Factorization of 14 and Beyond
The seemingly simple prime factorization of 14 – 2 x 7 – provides a launching point for exploring the rich world of prime numbers and factorization. This fundamental concept underlies numerous advanced mathematical principles and has significant practical applications in computer science and cryptography. Understanding prime numbers and factorization is not just about solving mathematical problems; it's about appreciating the elegant structure and profound implications of a fundamental concept in mathematics. The journey from understanding the prime factorization of 14 to grasping its broader significance is a testament to the power and beauty of mathematics itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Verbs That Start With A Y
May 09, 2025
-
Which One Of The Following Is A Pure Substance
May 09, 2025
-
What Is Lcm Of 3 And 4
May 09, 2025
-
3 Main Parts Of A Nucleotide
May 09, 2025
-
Why Is Blood Considered To Be A Connective Tissue
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization For 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.