What Is The Prime Factor Of 300
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
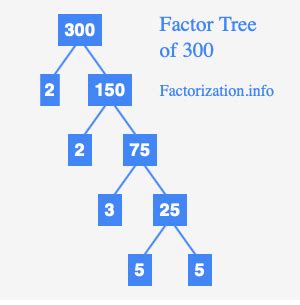
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 300? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 300?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers. Understanding prime factorization is crucial not only for solving mathematical problems but also for appreciating the fundamental building blocks of numbers and their applications in cryptography and computer science. Let's delve into the concept of prime numbers, factorization, and then unravel the prime factorization of 300.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 300, it's essential to understand what prime numbers are. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's a number that cannot be divided evenly by any other number except 1 and itself.
Some examples of prime numbers include: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number, and neither are numbers that are divisible by numbers other than 1 and themselves (e.g., 4 is divisible by 2, so it's not prime).
The prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all whole numbers greater than 1. This fundamental property forms the bedrock of prime factorization.
The Sieve of Eratosthenes: A Method for Finding Prime Numbers
One efficient method for finding prime numbers is the Sieve of Eratosthenes. This ancient algorithm works by iteratively marking the multiples of prime numbers, leaving only the prime numbers unmarked.
Imagine listing all numbers from 2 onwards. We start by marking 2 as prime. Then, we mark all multiples of 2 (4, 6, 8, etc.). Next, we find the next unmarked number (which is 3) and mark it as prime. Then, we mark all multiples of 3 (6, 9, 12, etc.). We continue this process, moving to the next unmarked number and marking its multiples. The unmarked numbers remaining are the prime numbers within the range we considered.
Understanding Factorization
Factorization is the process of breaking down a composite number (a number that is not prime) into its smaller component factors. These factors, when multiplied together, give the original number. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
The Importance of Prime Factorization
While we can factor a number in many ways, there's a unique way to express it using only prime numbers. This is known as prime factorization. It's unique because the prime factors, and their exponents, are always the same, regardless of the order in which you find them. This uniqueness is what makes prime factorization so important in mathematics and computer science.
Prime factorization allows us to simplify complex mathematical expressions, solve equations, and understand the underlying structure of numbers. It also plays a vital role in cryptography, where the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors forms the basis of many encryption algorithms.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 300
Now, let's finally find the prime factorization of 300. We can use a method called the factor tree. We begin by finding any two factors of 300. A good starting point is often to divide by 2 if the number is even:
300 = 2 x 150
Now, we continue factoring each branch of the tree:
150 = 2 x 75
75 = 3 x 25
25 = 5 x 5
We've now reached all prime numbers at the end of each branch. Therefore, the prime factorization of 300 is:
2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 5 = 2² x 3 x 5²
This means that 300 can be expressed as the product of the prime numbers 2, 3, and 5, with 2 appearing twice and 5 appearing twice. This representation is unique to 300. No other set of prime numbers multiplied together will equal 300.
Alternative Methods for Prime Factorization
While the factor tree method is visually intuitive, other methods can also determine the prime factorization of a number. One such method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number that divides it evenly. Let's illustrate this with 300:
- Divide 300 by 2 (the smallest prime): 300 / 2 = 150
- Divide 150 by 2: 150 / 2 = 75
- 75 is not divisible by 2, so we move to the next smallest prime, 3: 75 / 3 = 25
- 25 is not divisible by 3, but it is divisible by 5: 25 / 5 = 5
- 5 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factors are 2, 2, 3, 5, and 5, leading to the same prime factorization: 2² x 3 x 5²
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly abstract concept of prime factorization has surprisingly practical applications across various fields:
-
Cryptography: As mentioned earlier, the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors is the foundation of many modern encryption algorithms, ensuring secure communication and data protection.
-
Computer Science: Prime factorization plays a role in algorithms related to data structures, hashing, and random number generation.
-
Mathematics: Prime factorization simplifies calculations, aids in solving number theory problems, and underlies concepts like modular arithmetic.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers are used in error-correcting codes, ensuring the reliable transmission and storage of data.
Conclusion: The Power of Prime Factorization
Understanding prime factorization, as demonstrated through the example of 300 (2² x 3 x 5²), provides a deeper appreciation for the structure and properties of numbers. This fundamental concept is not just a mathematical curiosity; it's a crucial element in various scientific and technological advancements, from securing online transactions to ensuring reliable data transmission. While finding the prime factorization of small numbers like 300 is straightforward, the challenge of factoring extremely large numbers forms the backbone of secure communication systems, highlighting the profound impact of seemingly simple mathematical concepts. The next time you encounter a number, consider its prime factorization – you might be surprised by its hidden power and significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Electronic Banking Is Also Known As
May 09, 2025
-
What Is A Group Of Tissues Working Together Called
May 09, 2025
-
Part Of The Flower That Makes Pollen
May 09, 2025
-
Newtons Second Law Of Motion Examples In Everyday Life
May 09, 2025
-
Most Reactive Metal On The Periodic Table
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factor Of 300 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.