What Is The Percentage Of Water In Urine
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
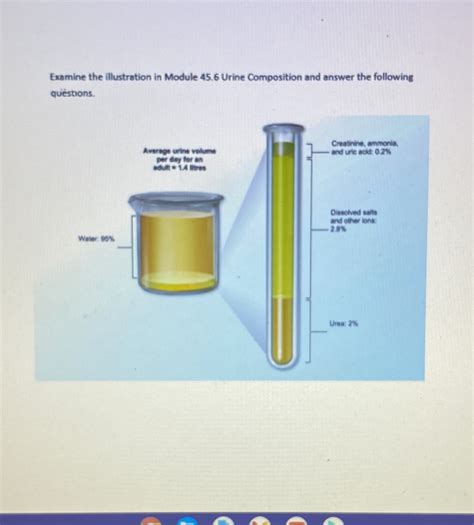
Table of Contents
What is the Percentage of Water in Urine? A Deep Dive into Urine Composition
Understanding the composition of urine is crucial for various reasons, ranging from maintaining overall health to diagnosing specific medical conditions. While many associate urine solely with waste products, it's a complex fluid containing a surprising array of substances dissolved in water. A key aspect of this composition is the percentage of water present, which plays a pivotal role in overall hydration and renal function. This article delves deep into the intricacies of urine composition, focusing specifically on the water content and the factors influencing its fluctuation.
The Predominant Component: Water in Urine
Urine is primarily composed of water, typically accounting for 95% to 96% of its total volume. This high water percentage highlights the kidneys' critical role in maintaining fluid balance within the body. The kidneys act as sophisticated filtration systems, constantly regulating the amount of water retained or excreted based on factors like fluid intake, physical activity, and overall metabolic processes. The remaining 4-5% consists of a complex mixture of dissolved substances, as detailed further below.
Why is Water so Important in Urine?
The high water content serves several vital functions:
-
Waste Removal: Water acts as the primary solvent, dissolving and transporting metabolic waste products, such as urea, creatinine, and uric acid, out of the body. Without sufficient water, these waste products would accumulate, leading to potential health complications.
-
Maintaining Osmotic Balance: Water helps maintain the proper balance of electrolytes and other solutes within the body. This osmotic balance is crucial for the proper functioning of cells and tissues.
-
Regulating Blood Pressure: The kidneys adjust water excretion to help regulate blood volume and, consequently, blood pressure. Increased water intake leads to increased urine output, reducing blood volume and blood pressure.
-
Temperature Regulation: The excretion of urine helps regulate body temperature through evaporative cooling. While less significant than sweating, this contributes to overall thermoregulation.
Factors Influencing Urine Water Percentage
While the average percentage of water in urine hovers around 95-96%, several factors can cause significant fluctuations:
1. Fluid Intake: The Most Significant Factor
This is perhaps the most obvious influencer. Increased fluid intake directly correlates with increased urine production and, consequently, a higher water percentage in urine. Conversely, dehydration leads to reduced urine output and a potentially lower water percentage as the body conserves fluids. This concentration of solutes can be observed in the color of the urine - concentrated urine is darker yellow, while diluted urine is lighter.
2. Physical Activity and Sweating
Intense physical activity leads to increased sweating, a crucial mechanism for thermoregulation. Sweating results in fluid loss, prompting the kidneys to conserve water, thus producing less urine with a potentially lower water percentage. The urine becomes more concentrated, reflecting the body's effort to retain fluids.
3. Diet
Dietary intake significantly impacts urine composition. A diet rich in water-containing fruits and vegetables will naturally increase urine output and maintain a higher water percentage. Conversely, a diet low in fluids and high in sodium can lead to concentrated urine with a lower water percentage. The type of fluids consumed also matters; caffeinated and alcoholic beverages can have diuretic effects, increasing urine production.
4. Medications
Certain medications can act as diuretics, increasing urine production and potentially influencing the water percentage. These diuretics are often used to treat conditions like high blood pressure and edema. Understanding the effects of prescribed medications on urine output is crucial for proper hydration management.
5. Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions can affect urine composition and water percentage. Kidney diseases, for example, can impair the kidneys' ability to regulate water balance, leading to either excessive or insufficient urine production. Diabetes insipidus, a condition affecting the body's ability to regulate vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), results in the production of large volumes of dilute urine. Conversely, certain kidney diseases can lead to decreased urine production and potentially higher solute concentration.
6. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, play a role. In hot and humid environments, increased sweating necessitates greater water conservation, potentially decreasing the water percentage in urine. Conversely, in cooler climates, the need for thermoregulation is reduced, potentially resulting in higher urine output and water percentage.
Measuring Urine Water Percentage: Practical Considerations
Accurately determining the precise water percentage in urine requires laboratory analysis, typically involving specific gravity measurement and other chemical tests. While home urine tests provide an indication of overall hydration and potential health issues, they don't offer precise water percentage figures. These tests often focus on the presence of other components, such as glucose, protein, and blood, as indicators of underlying health problems.
Understanding Specific Gravity
Specific gravity is a measure of the density of urine compared to water. A higher specific gravity indicates more concentrated urine with a lower water percentage, while a lower specific gravity suggests dilute urine with a higher water percentage. This is a valuable parameter in assessing hydration status and identifying potential renal issues.
The Remaining 4-5%: A Closer Look at Other Urine Constituents
While water dominates urine composition, the remaining 4-5% consists of a diverse array of substances, each providing valuable insights into overall health:
-
Urea: The primary nitrogenous waste product of protein metabolism, urea constitutes a significant portion of the dissolved solids in urine.
-
Creatinine: A waste product of muscle metabolism, creatinine levels can help assess kidney function.
-
Uric Acid: The end product of purine metabolism, uric acid levels can be indicative of gout or kidney stones.
-
Electrolytes: Sodium, potassium, chloride, and other electrolytes are present in varying concentrations, reflecting overall fluid and electrolyte balance.
-
Hormones: Trace amounts of hormones are excreted in urine, reflecting hormonal activity within the body. Urine analysis can be used to detect hormonal imbalances.
-
Pigments: Urochrome, a yellow pigment, is the primary contributor to urine color. The concentration of urochrome, and therefore the color of urine, reflects the concentration of urine and hydration status.
Clinical Significance of Urine Water Percentage
Variations in urine water percentage, often reflected in specific gravity changes, are vital indicators used in medical diagnostics. Monitoring urine concentration is crucial in assessing hydration status, kidney function, and detecting potential health issues. Deviations from the norm can signal underlying medical conditions requiring further investigation.
For instance, consistently high specific gravity (concentrated urine) could indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or diabetes. Conversely, consistently low specific gravity (dilute urine) could point towards diabetes insipidus, excessive fluid intake, or certain kidney disorders.
Conclusion: The Importance of Hydration and Urine Analysis
The percentage of water in urine, while seemingly straightforward, is a vital parameter reflecting overall health and fluid balance. Understanding the factors influencing this percentage, along with the composition of the remaining dissolved substances, is critical for maintaining optimal health and diagnosing potential medical conditions. While the average hovers around 95-96%, variations can indicate underlying issues requiring medical attention. Maintaining proper hydration through adequate fluid intake is crucial for ensuring healthy kidney function and optimal urine composition. Regular urine tests, as part of routine health checkups, can help identify potential problems early on. Consulting a healthcare professional for any concerns about urine color, volume, or frequency is always advisable.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are All The Factors Of 99
Mar 09, 2025
-
Difference Between Monohybrid And Dihybrid Cross
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Capacity To Do Work Is Known As
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is Prime Factorization Of 70
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is A Factor Of 93
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Percentage Of Water In Urine . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
