What Is The Outermost Layer Of The Sun Called
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
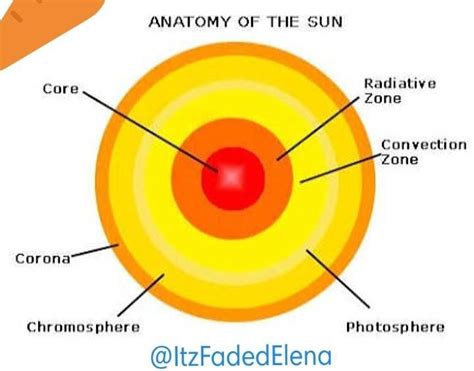
Table of Contents
What is the Outermost Layer of the Sun Called? Unveiling the Secrets of the Corona
The Sun, our life-giving star, is a complex and dynamic celestial body. Its structure is layered, each layer possessing unique characteristics and playing a crucial role in the Sun's overall behavior. While many are familiar with the Sun's visible surface, the photosphere, the outermost layer is far less understood and vastly more intriguing. This outermost layer is called the corona. This article will delve deep into the corona, exploring its properties, its relationship with other solar layers, its influence on space weather, and the ongoing scientific efforts to unravel its mysteries.
Understanding the Sun's Layered Structure
Before focusing on the corona, let's briefly review the Sun's overall structure. The Sun isn't a solid body; instead, it's a giant ball of plasma, primarily hydrogen and helium, held together by its immense gravity. The layers, from innermost to outermost, are:
- Core: The innermost region where nuclear fusion takes place, converting hydrogen into helium and releasing vast amounts of energy.
- Radiative Zone: Energy generated in the core travels outward through this zone via radiation. The process is slow, taking hundreds of thousands of years.
- Convective Zone: Energy transport shifts to convection in this zone. Hot plasma rises, cools, and sinks in a cycle, carrying energy towards the surface.
- Photosphere: The visible surface of the Sun, appearing as a bright, granular layer. Sunspots, cooler, darker areas, are found here.
- Chromosphere: A relatively thin layer above the photosphere, characterized by a reddish hue visible during solar eclipses.
- Transition Region: A narrow zone between the chromosphere and corona, where temperature dramatically increases.
- Corona: The outermost layer, extending millions of kilometers into space.
The Corona: A Realm of Extreme Temperatures and Mysteries
The corona, meaning "crown" in Latin, is a breathtaking spectacle. Its ethereal glow, visible only during total solar eclipses, is a testament to its extreme temperature and unique properties. Here's what makes the corona so fascinating:
Extreme Temperatures: A Solar Paradox
One of the most striking features of the corona is its incredibly high temperature. While the photosphere's temperature is around 5,500 degrees Celsius (9,932 degrees Fahrenheit), the corona's temperature soars to millions of degrees Celsius. This presents a significant scientific puzzle: how can the outermost layer be so much hotter than the layers beneath it? The precise mechanism responsible for coronal heating remains a topic of intense research and debate, with several leading hypotheses:
- Nanoflares: Numerous small, explosive events constantly occurring in the corona, releasing energy in bursts.
- Magnetic Reconnection: The breaking and rejoining of magnetic field lines, converting magnetic energy into heat.
- Alfvén Waves: Magnetohydrodynamic waves that propagate through the corona, transferring energy from the Sun's interior.
Structure and Dynamics: A Complex Tapestry
The corona isn't a uniform layer; its structure is incredibly complex and dynamic. It's characterized by:
- Coronal Loops: Giant arcs of plasma tracing magnetic field lines, often glowing brightly.
- Coronal Holes: Regions with open magnetic field lines, allowing the solar wind to escape more readily.
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): Massive eruptions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun, capable of impacting Earth.
The Solar Wind: A Constant Outflow
The corona isn't static; it continuously releases a stream of charged particles known as the solar wind. This wind flows outward through the solar system, impacting planets and influencing space weather. The speed and density of the solar wind are influenced by coronal features like coronal holes and CMEs.
Observing the Corona: Technological Advancements
Studying the corona directly is challenging because its faint light is overwhelmed by the Sun's brilliance. However, advancements in technology have enabled scientists to overcome this obstacle:
- Coronagraphs: Instruments that block out the Sun's bright disk, allowing observation of the corona.
- Space-based Observatories: Telescopes in space, such as SOHO (Solar and Heliospheric Observatory) and STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory), provide continuous observation of the corona, unaffected by Earth's atmosphere.
- Radio Telescopes: These detect radio emissions from the corona, providing insights into its magnetic fields and energetic processes.
The Corona's Influence on Space Weather and Earth
The corona plays a critical role in shaping space weather, which significantly affects our planet:
- Geomagnetic Storms: CMEs can trigger geomagnetic storms, disrupting radio communications, satellite operations, and power grids.
- Auroras: Charged particles from the solar wind interact with Earth's atmosphere, producing stunning auroral displays in the polar regions.
- Radiation Hazards: Increased solar activity can pose radiation hazards to astronauts and satellites.
Ongoing Research and Future Explorations
Despite significant progress, many mysteries surrounding the corona remain. Scientists are actively engaged in research to better understand:
- Coronal Heating: The precise mechanisms driving the corona's extreme temperatures.
- CME Initiation and Propagation: Understanding the triggers and evolution of CMEs to improve space weather forecasting.
- Solar Wind Acceleration: The processes accelerating the solar wind to its high speeds.
Future missions and advancements in technology promise further insights. The Parker Solar Probe, currently orbiting the Sun, is making unprecedented close-up observations of the corona, providing invaluable data to refine our understanding.
Conclusion: A Celestial Crown of Mysteries and Marvels
The corona, the outermost layer of the Sun, is a fascinating and complex region characterized by extreme temperatures, dynamic structures, and a continuous outflow of the solar wind. Its influence extends far beyond the Sun itself, shaping space weather and impacting our planet. Ongoing research and future exploration promise to unveil even more of its secrets, deepening our understanding of our star and its profound impact on our solar system. The corona continues to be a source of wonder and a testament to the immense power and complexity of our Sun. Further study is crucial not just for scientific understanding but also for the practical application of improved space weather forecasting, protecting our technological infrastructure and ensuring the safety of astronauts venturing further into space. The mysteries of the corona still hold many answers, beckoning us to continue exploring this incredible celestial realm.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Strongest Force On Earth
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Is Larger A Pound Or Kilogram
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Are Characteristics Of Natural Selection Select Three Options
Mar 16, 2025
-
Why Is Melting Ice A Physical Change
Mar 16, 2025
-
Whats The Roman Numeral For 500
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Outermost Layer Of The Sun Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
