What Is The Name For Cs2
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
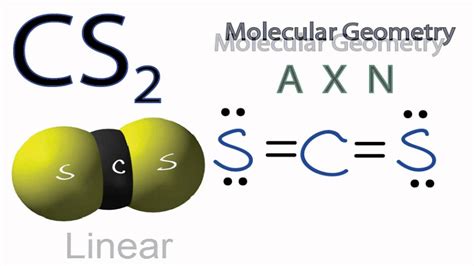
Table of Contents
What is the Name for CS2? A Deep Dive into Carbon Disulfide
Carbon disulfide (CS2) is a fascinating chemical compound with a wide array of properties and applications. While its chemical formula, CS2, is universally understood, its common name is simply carbon disulfide. However, understanding the compound requires delving deeper than just its name. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of CS2, including its nomenclature, properties, uses, safety concerns, and environmental impact.
Understanding the Nomenclature of CS2
The name "carbon disulfide" is derived from its chemical composition: one carbon atom bonded to two sulfur atoms. This systematic naming convention, based on the constituent elements, is straightforward and universally accepted within the scientific community. There aren't really any alternative common names in widespread use. While you might encounter variations in different languages (e.g., Schwefelkohlenstoff in German, sulfuro de carbono in Spanish), these are simply translations of the core name, "carbon disulfide." The chemical formula, CS2, remains the most precise and universally understood identifier.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Carbon Disulfide
Carbon disulfide is a colorless, volatile liquid at room temperature. Its distinctive odor is often described as pungent, ethereal, or even slightly sweet, though some find it unpleasant. This pungent smell is a crucial safety aspect, acting as a warning of its presence.
Here's a summary of its key properties:
- Molecular Weight: Approximately 76.14 g/mol
- Boiling Point: 46.3 °C (115.3 °F)
- Melting Point: -111.6 °C (-168.9 °F)
- Density: 1.26 g/cm³
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water but miscible with many organic solvents.
- Flammability: Highly flammable and capable of forming explosive mixtures with air.
- Reactivity: Reacts readily with many substances, including alkali metals, oxidizing agents, and some metals.
Detailed Look at Key Properties and Their Implications
The high volatility of CS2 means it evaporates quickly at room temperature. This contributes to its pungent odor and makes it crucial to handle it in well-ventilated areas to avoid inhaling potentially harmful vapors. The flammability poses significant safety risks, necessitating careful storage and handling procedures to prevent fires or explosions. The reactivity with various substances requires cautious consideration when storing or using it in conjunction with other chemicals. Its solubility profile determines its behavior in different environments and influences its application in certain industries. Understanding these properties is essential for safe handling and responsible use.
Applications of Carbon Disulfide
Despite its hazardous nature, CS2 has found a variety of industrial applications throughout history. However, its use has decreased in recent years due to growing environmental and safety concerns, with many applications being replaced by safer alternatives.
Historical and Current Applications:
-
Viscose Rayon Production: Historically, CS2 played a pivotal role in the production of viscose rayon, a type of regenerated cellulose fiber. This application involved treating cellulose with CS2 to form a soluble xanthate, which was then processed to create rayon fibers. However, this application is significantly reduced now due to environmental concerns.
-
Carbon Tetrachloride Production: CS2 served as a precursor in the synthesis of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), which has since been largely phased out due to its ozone-depleting properties.
-
Solvent: Its excellent solvent properties were used to dissolve fats, oils, resins, and rubber. Though less common now due to safety concerns, it might still see limited use in specific niche applications.
-
Pesticide Production: In the past, CS2 was employed in the production of various pesticides. However, this application has diminished significantly due to its toxicity and the availability of less harmful alternatives.
-
Analytical Chemistry: Despite its toxicity, CS2's unique properties are still utilized in some analytical chemistry techniques, especially in spectrophotometry. It's used as a solvent in certain spectroscopic analyses. However, this application is generally being replaced with safer, more environmentally benign alternatives.
Safety Precautions and Health Hazards
Working with carbon disulfide demands stringent safety protocols due to its inherent toxicity and flammability. Exposure can occur through inhalation of its vapors, skin contact, or ingestion.
Health Risks:
-
Neurotoxicity: CS2 is a known neurotoxin, capable of causing damage to the nervous system. Symptoms can include headaches, dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, more significant neurological impairments.
-
Hepatotoxicity: It can also damage the liver (hepatotoxicity), leading to liver dysfunction.
-
Cardiovascular Effects: Some studies have indicated potential cardiovascular effects, such as changes in heart rhythm.
-
Eye Irritation: Contact with eyes can cause irritation and damage.
-
Skin Irritation: Skin contact can cause irritation, dryness, and dermatitis.
Safety Measures:
-
Ventilation: Always work with CS2 in well-ventilated areas to minimize vapor inhalation.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use appropriate PPE, including gloves, safety glasses, and respirators to protect skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
-
Storage: Store CS2 in tightly sealed containers in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from ignition sources.
-
Spill Response: Have a spill response plan in place in case of accidental spills.
-
Training: Workers should receive comprehensive training on the safe handling and use of carbon disulfide.
Environmental Impact
Carbon disulfide is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release into the atmosphere contributes to global warming. It also poses a risk to aquatic life if released into water bodies. Its breakdown products can also contribute to environmental problems. Therefore, responsible use and proper disposal are crucial to mitigate its environmental impact.
Degradation and Environmental Fate:
CS2 undergoes various degradation pathways in the environment. Atmospheric degradation is influenced by factors like sunlight and reaction with hydroxyl radicals. In aquatic environments, its breakdown is affected by microbial activity and other environmental conditions. Understanding these degradation pathways is crucial for assessing its environmental persistence and potential impact.
Conclusion: Beyond the Name of CS2
While the name "carbon disulfide" is straightforward, a complete understanding of CS2 necessitates delving into its properties, applications, safety concerns, and environmental impact. Its historical significance in various industries, coupled with its inherent hazards, has prompted a shift towards safer alternatives. The ongoing research into safer solvents and substitutes reflects a commitment to minimizing the risks associated with this potent and reactive chemical. Remembering the name is just the first step; understanding its full implications is critical for safe and responsible handling and use. The future of carbon disulfide likely lies in very specialized, carefully controlled applications, with its broader use replaced by more benign options.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 To The Power Of 1
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Net Gain Of Atp From Glycolysis
Mar 23, 2025
-
Where Do The Stars Go During The Day
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples Of Seven
Mar 23, 2025
-
Why Are Most Stomata On The Bottom Of The Leaf
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Name For Cs2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
