What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 14
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
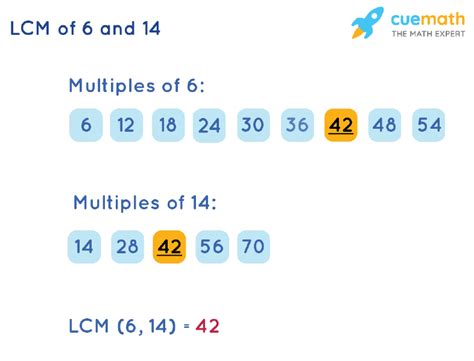
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 6 and 14? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts reveals a fascinating glimpse into number theory. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of calculating the LCM of 6 and 14, exploring various methods and their practical applications. We'll also discuss the significance of LCM in various mathematical contexts and real-world scenarios.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the prime factors of the given numbers. Understanding LCM is crucial in various mathematical operations, including simplifying fractions, solving equations, and working with rhythms and cycles.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 6 and 14
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore the most common approaches to determine the LCM of 6 and 14.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method, while straightforward, can be time-consuming for larger numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48...
- Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56...
The smallest multiple common to both lists is 42. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 14 is 42.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- Highest power of 2: 2¹ = 2
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 7: 7¹ = 7
Multiplying these together: 2 x 3 x 7 = 42. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 14 is 42.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor). The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers.
First, we need to find the GCD of 6 and 14. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide 14 by 6: 14 = 2 x 6 + 2
- Divide 6 by the remainder 2: 6 = 3 x 2 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 2.
Now, we can use the formula: LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
LCM(6, 14) = (6 x 14) / 2 = 84 / 2 = 42
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where prime factorization might be more challenging.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends beyond simple mathematical exercises. It finds practical applications in various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two machines that need regular maintenance. Machine A requires maintenance every 6 days, and Machine B every 14 days. To schedule maintenance such that both machines are serviced on the same day, you need to find the LCM of 6 and 14. The LCM (42) represents the number of days until both machines require maintenance simultaneously.
2. Fractions and Rational Numbers
Finding the LCM is essential when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add 1/6 and 1/14, you need to find the LCM of 6 and 14 (which is 42), and then rewrite the fractions with a common denominator of 42 before performing the addition.
3. Music and Rhythms
In music theory, LCM is used to determine the least common period of two or more musical rhythms. If one rhythm repeats every 6 beats and another every 14 beats, the LCM (42) indicates the number of beats until both rhythms coincide.
4. Cyclic Processes
Many natural and artificial processes exhibit cyclical behavior. LCM helps determine when these cycles coincide. For instance, in astronomy, LCM could be used to calculate when certain planetary alignments occur.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method remains particularly efficient. For instance, to find the LCM of 6, 14, and 21:
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
- Prime factorization of 21: 3 x 7
The highest powers of each prime factor are: 2¹, 3¹, and 7¹. Therefore, the LCM(6, 14, 21) = 2 x 3 x 7 = 42.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding LCM
The seemingly simple task of finding the least common multiple reveals a deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical principles. From its role in simplifying complex calculations to its practical applications in various fields, the LCM demonstrates the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their relevance to the real world. Mastering the techniques for calculating LCM, especially the prime factorization method, is crucial for efficient problem-solving in mathematics and beyond. The example of finding the LCM of 6 and 14, while seemingly basic, serves as a solid foundation for tackling more complex LCM problems and appreciating its significance in various applications. This understanding allows for better problem-solving skills, improved time management techniques, and a deeper appreciation of the beauty and practicality of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ice Melting Is A Chemical Change
Mar 10, 2025
-
Is Neon Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 10, 2025
-
Why Do We Call Fossil Fuels Non Renewable
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Inches In Meter Stick
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is The Correct Sequence Of Events In Viral Reproduction
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
