What Is The Lcm Of 9 And 18
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
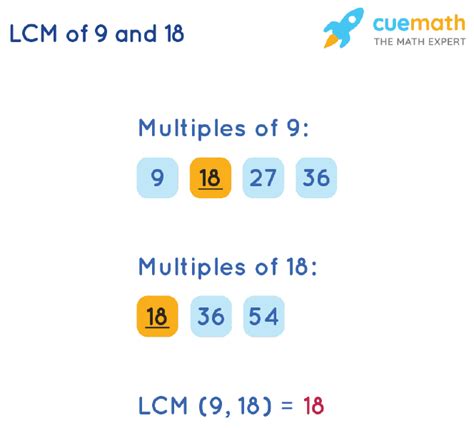
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 9 and 18? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and various methods for calculating it can be surprisingly enriching. This article will delve deep into determining the LCM of 9 and 18, exploring multiple approaches and expanding on the broader significance of LCMs in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before jumping into the calculation, let's solidify our understanding of LCMs. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors.
Think of it like finding the smallest common ground between different sets of multiples. For example, the multiples of 9 are 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, and so on. The multiples of 18 are 18, 36, 54, 72, and so on. The LCM is the smallest number that appears in both lists – in this case, 18.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method, particularly for smaller numbers like 9 and 18, is to list the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple.
Steps:
- List multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54...
- List multiples of 18: 18, 36, 54, 72...
- Identify the smallest common multiple: The smallest number that appears in both lists is 18.
Therefore, the LCM of 9 and 18 is 18.
This method is effective for small numbers but becomes cumbersome and inefficient as the numbers get larger. Imagine trying this with numbers like 144 and 288; the list would become very long!
Method 2: Prime Factorization
A more efficient and robust method, especially for larger numbers, involves prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
Steps:
- Find the prime factorization of 9: 9 = 3 x 3 = 3²
- Find the prime factorization of 18: 18 = 2 x 3 x 3 = 2 x 3²
- Identify the highest power of each prime factor: The prime factors present are 2 and 3. The highest power of 2 is 2¹ and the highest power of 3 is 3².
- Multiply the highest powers together: 2¹ x 3² = 2 x 9 = 18
Therefore, the LCM of 9 and 18 is 18.
This method is significantly more efficient for larger numbers because it avoids the need for extensive listing.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers are intimately related. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. There's a handy formula that connects the LCM and GCD:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
Steps:
- Find the GCD of 9 and 18: The factors of 9 are 1, 3, and 9. The factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The largest common factor is 9. Therefore, GCD(9, 18) = 9.
- Apply the formula: LCM(9, 18) = (9 x 18) / 9 = 18
Therefore, the LCM of 9 and 18 is 18.
This method is also efficient, especially when dealing with larger numbers where finding the GCD might be easier than directly finding the LCM through listing or prime factorization. Algorithms like the Euclidean algorithm can efficiently calculate the GCD, making this a powerful approach for complex calculations.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
While finding the LCM of 9 and 18 might seem like a purely academic exercise, the concept of LCM has numerous practical applications:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses arrive at a bus stop at different intervals. One bus arrives every 9 minutes, and the other every 18 minutes. The LCM (18 minutes) determines when both buses will arrive at the stop simultaneously.
-
Fractions: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires finding the LCM of the denominators.
-
Cyclic Events: Consider events that repeat cyclically, like the phases of the moon or the rotation of planets. LCM helps determine when these events will coincide.
-
Project Management: In project management, determining the timing of various tasks that depend on each other often involves LCM calculations to optimize the overall project timeline.
-
Engineering and Design: Many engineering and design applications, from building construction to circuit design, utilize LCM principles for synchronization and optimization purposes.
Beyond Two Numbers: Extending the LCM Concept
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, you would simply include all prime factors from all numbers, taking the highest power of each. For the GCD-based method, you'd need to find the GCD of all numbers iteratively.
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM
Finding the least common multiple of 9 and 18, as demonstrated through multiple methods, provides a foundational understanding of this crucial mathematical concept. Whether you're a student grappling with arithmetic or a professional working with complex systems, understanding LCMs allows you to tackle problems efficiently and effectively. The ability to choose the most appropriate method – listing multiples, prime factorization, or the GCD approach – depends on the specific numbers and the context of the problem. This flexible understanding makes the concept of LCM a versatile tool applicable across numerous mathematical and real-world scenarios. The more you practice, the more intuitive and efficient the process of finding LCMs will become. Remember, the core idea remains consistent: finding the smallest common multiple, the smallest number that satisfies divisibility by all given numbers. This fundamental concept, although seemingly simple, opens doors to solving more complex problems in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Is Coal Not Considered A Mineral
Mar 13, 2025
-
Square Root Of 200 In Radical Form
Mar 13, 2025
-
Both Pairs Of Opposite Sides Parallel
Mar 13, 2025
-
Which Triangles Are Congruent According To The Sas Criterion
Mar 13, 2025
-
Lcm Of 3 7 And 2
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 9 And 18 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
