What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 18
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
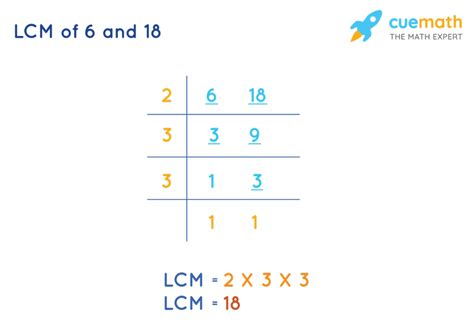
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 6 and 18? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from simplifying fractions to solving complex problems in algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question, "What is the LCM of 6 and 18?" but also explore the underlying principles, different methods for calculating LCMs, and real-world applications of this important mathematical concept.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. It's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors. This concept contrasts with the greatest common divisor (GCD), which is the largest integer that divides all the given integers without leaving a remainder.
Let's illustrate with a simple example. Consider the numbers 4 and 6. The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24... and the multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30... Notice that 12 and 24 appear in both lists. The smallest of these common multiples is 12, making 12 the LCM of 4 and 6.
Methods for Calculating the LCM
Several methods exist for finding the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method, as demonstrated in the example above, involves listing out the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple. While simple for small numbers, it becomes increasingly inefficient as the numbers grow larger.
Limitations: This method is time-consuming and impractical for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more efficient method, particularly for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the highest powers of all prime factors present in the factorizations.
Let's find the LCM of 12 and 18 using this method:
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² × 3
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 × 3²
The LCM will include the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization: 2² and 3².
Therefore, LCM(12, 18) = 2² × 3² = 4 × 9 = 36
3. Formula Using GCD
The LCM and GCD of two numbers are related through a simple formula:
LCM(a, b) × GCD(a, b) = a × b
This means you can find the LCM if you know the GCD. Let's use this to find the LCM of 12 and 18 again.
First, find the GCD(12, 18). The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12. The factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18. The greatest common factor is 6.
Now, apply the formula:
LCM(12, 18) = (12 × 18) / GCD(12, 18) = (12 × 18) / 6 = 36
Answering the Question: LCM of 6 and 18
Now, let's apply these methods to answer the question posed in the title: What is the LCM of 6 and 18?
Method 1: Listing Multiples:
Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30... Multiples of 18: 18, 36, 54...
The smallest common multiple is 18. Therefore, LCM(6, 18) = 18.
Method 2: Prime Factorization:
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 × 3
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 × 3²
The LCM is 2 × 3² = 18.
Method 3: Using GCD:
The GCD of 6 and 18 is 6.
LCM(6, 18) = (6 × 18) / GCD(6, 18) = (6 × 18) / 6 = 18
Therefore, using all three methods, we confirm that the LCM of 6 and 18 is 18.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM finds applications in various real-world scenarios:
1. Scheduling and Time Management:
Imagine two buses arrive at a bus stop at different intervals. One bus arrives every 6 minutes, and another arrives every 18 minutes. To find out when both buses arrive simultaneously, you need to find the LCM of 6 and 18. The LCM, which is 18 minutes, signifies that both buses will arrive together every 18 minutes.
2. Fraction Operations:
Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add 1/6 and 1/18, you need to find the LCM of 6 and 18 (which is 18) and then express both fractions with a denominator of 18 before adding them.
3. Gear Ratios and Rotational Speeds:
In mechanical engineering, LCM is used to determine the synchronization of rotating gears with different numbers of teeth. The LCM helps calculate when the gears will return to their initial positions simultaneously.
4. Cyclic Processes:
LCM is useful in analyzing repetitive processes or cycles that occur at different intervals. For instance, in manufacturing, it helps determine when different machines in a production line will complete their cycles at the same time.
5. Music and Rhythm:
In music, the LCM can help determine when different rhythmic patterns will coincide. For example, in composing music with overlapping rhythms, understanding LCM helps create harmonious and structured musical phrasing.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
Understanding and calculating the least common multiple is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications. Whether you're tackling fractions, solving scheduling problems, or delving into more complex mathematical concepts, mastering the LCM will significantly enhance your mathematical proficiency and problem-solving capabilities. This guide has explored multiple methods for calculating the LCM, providing a solid foundation for further exploration and application of this crucial mathematical concept. Remember to choose the method most suitable for the numbers involved, prioritizing efficiency and accuracy. The prime factorization method often provides the most efficient approach for larger numbers, while the multiples method serves as a useful introductory approach for smaller numbers. The formula using GCD offers an alternative approach, particularly useful when the GCD is readily available.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Most Abundant Substance In The Human Body
May 12, 2025
-
What Are The Monomers Of Protein Polymers
May 12, 2025
-
List Of Verbs Ending In Ing
May 12, 2025
-
What Can 37 Be Divided By
May 12, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Alcoholic And Lactic Acid Fermentation
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 18 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.