What Is The Lcm Of 6 9 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
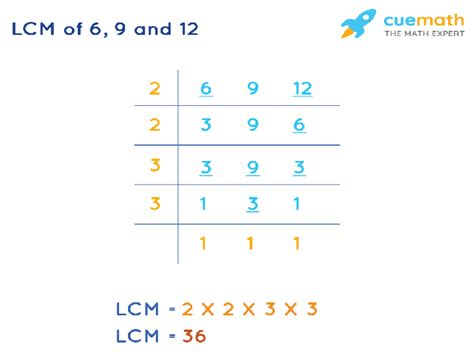
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 6, 9, and 12? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of a set of numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. This article will thoroughly explore how to determine the LCM of 6, 9, and 12, using various methods, and will delve into the broader significance of LCMs in different mathematical contexts. We'll also touch upon real-world examples to illustrate its practical use.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before diving into the specific calculation for 6, 9, and 12, let's establish a clear understanding of what an LCM is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
Think of it like finding the smallest common ground for several different rhythmic patterns. If one pattern repeats every 6 beats, another every 9 beats, and a third every 12 beats, the LCM would represent the smallest number of beats before all three patterns simultaneously align.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 6, 9, and 12
Several methods exist for determining the LCM, and we'll explore the most common and efficient approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward, though sometimes lengthy, method suitable for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 72...
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in all three lists is 36. Therefore, the LCM of 6, 9, and 12 is 36. This method works well for smaller numbers but becomes impractical for larger sets or larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more efficient method, particularly useful for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from these prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
- Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
To find the LCM using prime factorization:
- Identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations. We have 2² (from 12), and 3² (from 9).
- Multiply these highest powers together. 2² x 3² = 4 x 9 = 36
Thus, the LCM of 6, 9, and 12, using the prime factorization method, is 36. This method is generally more efficient and less prone to errors than the listing multiples method, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are closely related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two or more numbers is equal to the product of the numbers themselves. We can utilize this relationship to find the LCM.
First, let's find the GCD of 6, 9, and 12 using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization.
- Prime factorization method for GCD: The common prime factor is 3. Therefore, the GCD(6, 9, 12) = 3.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(a, b, c) = (a x b x c) / GCD(a, b, c)
In our case:
LCM(6, 9, 12) = (6 x 9 x 12) / 3 = 648 / 3 = 36
This method is also efficient and highlights the interconnectedness of LCM and GCD.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of LCM extends far beyond abstract mathematical exercises. It finds practical application in various real-world scenarios:
-
Scheduling and Time Management: Imagine you have three machines that need maintenance. Machine A needs maintenance every 6 days, Machine B every 9 days, and Machine C every 12 days. To schedule maintenance so that all machines are serviced on the same day, you need to find the LCM(6, 9, 12) = 36. All machines will be serviced together every 36 days.
-
Fraction Operations: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires finding the LCM of the denominators.
-
Gear Ratios and Rotational Mechanics: In engineering, LCM plays a crucial role in designing gear systems and calculating rotational speeds.
-
Music and Rhythms: As mentioned earlier, LCM helps determine when different rhythmic patterns will coincide, useful in music composition and performance.
-
Construction and Design: In construction, LCM might be used to determine when different stages of a project will align, optimizing scheduling and resource allocation.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Three Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than three numbers. The prime factorization method remains particularly efficient. You simply identify the highest power of each prime factor present across all the numbers and multiply them together. For example, to find the LCM of 6, 9, 12, and 15:
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 9: 3²
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
The highest powers are 2², 3², and 5. Therefore, LCM(6, 9, 12, 15) = 2² x 3² x 5 = 4 x 9 x 5 = 180
Conclusion: The Power of the LCM
The calculation of the LCM, as demonstrated with the example of 6, 9, and 12, is a fundamental mathematical operation with significant practical applications. Understanding the various methods for finding the LCM—listing multiples, prime factorization, and the GCD method—empowers you to solve problems efficiently, regardless of the number's size or the number of integers involved. The ability to determine the LCM is a valuable skill applicable in diverse fields, highlighting the relevance of even seemingly basic mathematical concepts in the real world. From scheduling to engineering to music, the LCM provides a powerful tool for problem-solving and coordination.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Calculate The Molecular Mass Of H2co3
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Study Of The Function Of Tissues Is Called
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Is Not A Property Of Living Being
Mar 22, 2025
-
In Which Two Hemispheres Is Australia Located
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Nucleotide Is Made Of Three Parts A
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 6 9 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
