What Is The Lcm Of 5 And 6
Juapaving
Mar 05, 2025 · 5 min read
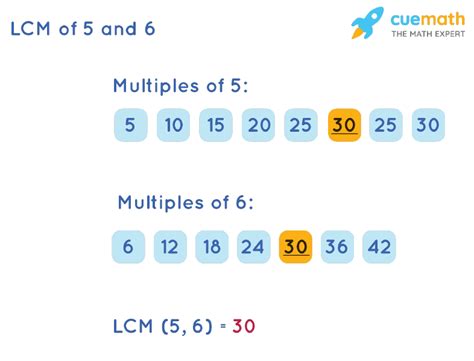
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 5 and 6? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the concept thoroughly unlocks its significance in various mathematical applications. This article will delve into the question: What is the LCM of 5 and 6? We'll not only answer this specific question but also explore the broader concept of LCMs, explaining different methods to calculate them and showcasing their practical uses.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors. For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer divisible by both 2 and 3.
Understanding LCMs is crucial in various areas, including:
- Fraction arithmetic: Finding the LCM of denominators is essential for adding and subtracting fractions.
- Solving problems involving cycles: LCMs help determine when cyclical events coincide (e.g., when two planets align).
- Scheduling and planning: LCMs are useful in scheduling tasks or events that repeat at different intervals.
Calculating the LCM of 5 and 6
Now, let's address the core question: What is the LCM of 5 and 6? We can use several methods to determine this:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The simplest method is to list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35…
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36…
Notice that the smallest number appearing in both lists is 30. Therefore, the LCM of 5 and 6 is 30.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations and multiply them together. In this case:
- The prime factors are 2, 3, and 5.
- The highest power of 2 is 2<sup>1</sup> = 2
- The highest power of 3 is 3<sup>1</sup> = 3
- The highest power of 5 is 5<sup>1</sup> = 5
LCM(5, 6) = 2 x 3 x 5 = 30
Method 3: Using the Formula (for two numbers)
For two numbers, a and b, there's a formula that connects the LCM and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD):
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the GCD of 5 and 6. The GCD is the greatest number that divides both 5 and 6 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(5, 6) = 1 (as 5 and 6 share no common factors other than 1).
Applying the formula:
LCM(5, 6) = (5 x 6) / GCD(5, 6) = 30 / 1 = 30
Beyond the Basics: LCMs with More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. Let's consider finding the LCM of 5, 6, and 10.
Using Prime Factorization for Multiple Numbers
-
Prime factorization:
- 5 = 5
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 10 = 2 x 5
-
Identify highest powers:
- The prime factors are 2, 3, and 5.
- The highest power of 2 is 2<sup>1</sup> = 2
- The highest power of 3 is 3<sup>1</sup> = 3
- The highest power of 5 is 5<sup>1</sup> = 5
-
Calculate the LCM: LCM(5, 6, 10) = 2 x 3 x 5 = 30
Real-World Applications of LCM
The seemingly simple concept of LCM finds surprisingly diverse applications in various fields:
-
Music Theory: Understanding LCM is crucial in determining the intervals between musical notes and creating harmonious compositions. The frequencies of notes often share relationships determined by their LCMs.
-
Calendars and Time: Determining when specific dates align requires calculating LCMs. For instance, finding out when a particular weekday falls on the same date in different years involves calculating the LCM of the number of days in a year (365 or 366) and the number of days in a week (7).
-
Industrial Processes: In manufacturing processes involving cyclical operations, calculating LCMs helps determine the synchronization of various machine cycles for optimal efficiency.
-
Construction and Engineering: Calculating the LCM helps in projects that involve repeating patterns or cycles, enabling more efficient planning and resource allocation. Consider tasks where materials need to be replenished at specific intervals – LCM calculations streamline the process.
-
Software Development: LCM concepts are employed in various algorithms and scheduling tasks within software systems. Effective scheduling of concurrent processes often relies on LCM calculations for optimal performance.
Advanced Concepts: LCM and GCD Relationship
The relationship between LCM and GCD is fundamental in number theory. For any two positive integers a and b:
- LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
This formula highlights the inherent connection between these two concepts, offering another method for calculating the LCM if the GCD is known.
Conclusion
The question "What is the LCM of 5 and 6?" leads us down a path of exploring the significant role least common multiples play in mathematics and its real-world applications. From straightforward calculations using listing multiples or prime factorization to the more advanced applications involving multiple numbers and their relationship with GCDs, understanding LCM is a valuable tool for various fields. This exploration has hopefully illuminated the importance and versatility of this fundamental mathematical concept. Mastering LCM calculations enhances problem-solving skills and provides a foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Gcf Of 42 And 28
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Division Of The Nucleus Is Called
Mar 06, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 8 And 16
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Are The Factors For 11
Mar 06, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 8
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 5 And 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
