What Is The Lcm Of 5 And 11
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 5 min read
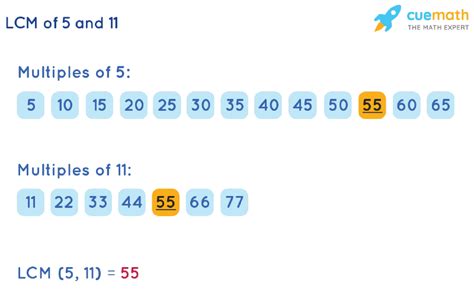
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 5 and 11? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from simplifying fractions to solving complex problems in algebra and beyond. This article will delve into the process of determining the LCM of 5 and 11, explaining the underlying principles and exploring different methods to achieve the solution. We'll also discuss the broader significance of LCMs and their applications in various fields.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 5 and 11, let's clarify what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The least common multiple is 6.
Key characteristics of the LCM:
- Positive: The LCM is always a positive integer.
- Smallest: It's the smallest number that satisfies the divisibility condition.
- Divisibility: It is divisible by all the numbers in the set.
Methods for Finding the LCM
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM of two or more numbers. We'll explore the most common and effective ones:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
Let's apply this to 5 and 11:
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60...
- Multiples of 11: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77...
The smallest number appearing in both lists is 55. Therefore, the LCM of 5 and 11 is 55.
This method works well for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome and inefficient for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient and scalable for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
Let's break down 5 and 11 using prime factorization:
- 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
- 11: 11 (11 is a prime number)
Both 5 and 11 are prime numbers. To find the LCM, we simply multiply the prime factors together:
LCM(5, 11) = 5 × 11 = 55
This method is significantly faster and more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers or a greater number of integers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two numbers are related through the following formula:
LCM(a, b) × GCD(a, b) = a × b
This means that if we know the GCD of two numbers, we can easily calculate the LCM. The GCD of 5 and 11 is 1 (because they share no common factors other than 1).
Therefore:
LCM(5, 11) = (5 × 11) / GCD(5, 11) = 55 / 1 = 55
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding the GCD using the Euclidean algorithm is more efficient than directly finding the LCM through prime factorization or listing multiples.
The Significance of LCM in Mathematics and Beyond
The concept of the least common multiple transcends simple arithmetic; it plays a crucial role in numerous mathematical areas and practical applications:
1. Fraction Addition and Subtraction
LCM is essential when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add or subtract fractions, we need a common denominator, and the LCM of the denominators is the most efficient common denominator to use.
For example, to add 1/5 + 1/11, we would find the LCM of 5 and 11 (which is 55) and then rewrite the fractions with the common denominator before adding them.
2. Solving Equations
LCMs can be used to simplify equations involving fractions or multiples. By finding the LCM of the denominators, we can eliminate the fractions and solve the equations more easily.
3. Cyclic Events
LCM finds application in problems involving repeating cycles or events. For instance, if two events occur with periods of 5 and 11 units of time, the LCM (55) represents the time after which both events will occur simultaneously again. This is useful in various scheduling and synchronization problems.
4. Modular Arithmetic
In modular arithmetic, the LCM plays a crucial role in solving congruence equations. This area of mathematics has applications in cryptography and other fields that require secure communication.
5. Music Theory
Surprisingly, LCMs have a place in music theory. They help determine the least common multiple of note durations which helps in calculating the length of a musical phrase or the period after which a rhythmic pattern repeats.
Conclusion: The LCM of 5 and 11 is 55
In conclusion, we have demonstrated through various methods that the least common multiple of 5 and 11 is 55. We've explored the different techniques for calculating the LCM, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. The importance of LCM extends beyond simple calculations; it's a foundational concept with wide-ranging applications across diverse fields of mathematics and beyond. Understanding LCM provides a stronger mathematical foundation and helps in solving a vast array of problems, from simple fractions to complex cyclic event predictions. The ability to efficiently calculate and apply the LCM is a valuable skill for students and professionals alike.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Radioactive Elements In The Periodic Table
May 09, 2025
-
How To Balance C8h18 O2 Co2 H2o
May 09, 2025
-
How Are The Desert And Tundra Similar
May 09, 2025
-
What Is Meant By Saying Charge Is Quantized
May 09, 2025
-
Undifferentiated Diploid Spermatogenic Cells Are Called
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 5 And 11 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.