What Is The Lcm Of 2 4 5
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
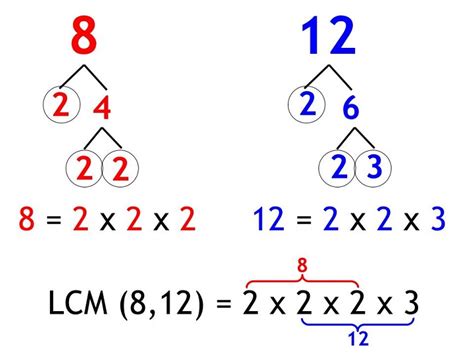
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 2, 4, and 5? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications in various fields, from scheduling tasks to simplifying fractions and solving complex equations. This article will thoroughly explore the concept of LCM, explain how to calculate it for the numbers 2, 4, and 5, and delve into the broader implications and applications of LCM in different contexts.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. This is different from the greatest common divisor (GCD), which is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder.
Why is LCM important?
The LCM has significant practical applications in various scenarios, including:
- Scheduling: Determining when events that occur at different intervals will happen simultaneously (e.g., buses arriving at a stop).
- Fractions: Finding the least common denominator (LCD) when adding or subtracting fractions. The LCD is simply the LCM of the denominators.
- Number Theory: Solving problems related to divisibility, modular arithmetic, and other number-theoretic concepts.
- Music: Determining the shortest length of time before two notes with different frequencies repeat their initial combination.
- Construction and Engineering: Aligning and synchronizing various components and processes with different cycles.
Calculating the LCM of 2, 4, and 5: Methods and Explanation
There are several ways to calculate the LCM of 2, 4, and 5. Let's explore two common approaches:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to all three:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40...
By inspecting the lists, we can see that the smallest number that appears in all three lists is 20. Therefore, the LCM of 2, 4, and 5 is 20.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a systematic approach. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number:
- Prime factorization of 2: 2
- Prime factorization of 4: 2 x 2 = 2²
- Prime factorization of 5: 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5
Now, multiply these highest powers together: 4 x 5 = 20
Therefore, the LCM of 2, 4, and 5 is 20.
A Deeper Look at Prime Factorization and LCM
Prime factorization is the cornerstone of efficiently calculating LCMs, especially for larger sets of numbers. It's based on the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors).
Steps involved in using prime factorization to find the LCM:
- Find the prime factorization of each number: Break down each number into its prime factors.
- Identify the highest power of each prime factor: Determine the largest exponent for each prime number appearing in the factorizations.
- Multiply the highest powers together: The product of these highest powers gives the LCM.
Example: Let's find the LCM of 12, 18, and 30 using prime factorization:
-
Prime factorizations:
- 12 = 2² x 3
- 18 = 2 x 3²
- 30 = 2 x 3 x 5
-
Highest powers:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3² = 9
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
-
Multiply the highest powers: 4 x 9 x 5 = 180
Therefore, the LCM of 12, 18, and 30 is 180.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The seemingly simple concept of LCM has far-reaching implications across numerous fields:
-
Calendars and Scheduling: Imagine three events: A occurs every 2 days, B every 4 days, and C every 5 days. When will all three events occur on the same day? The answer is the LCM(2, 4, 5) = 20 days.
-
Music Theory: Finding the LCM is crucial in music theory when determining the least common period of two or more notes with different frequencies. This helps in identifying when the notes will repeat their initial combination.
-
Gear Ratios: In mechanical engineering, the LCM is used in determining gear ratios to synchronize rotations in machines.
-
Project Management: Determining the intervals at which different stages of a project need to be synchronized. This ensures efficient resource allocation and timely completion.
LCM and GCD: A Complementary Relationship
The least common multiple (LCM) and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are closely related concepts. For any two positive integers a and b, the following relationship holds:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
This identity provides a convenient way to calculate the LCM if the GCD is known, or vice-versa. For example, let's calculate the LCM of 12 and 18:
-
Find the GCD: The GCD of 12 and 18 is 6.
-
Apply the formula: LCM(12, 18) x GCD(12, 18) = 12 x 18 LCM(12, 18) x 6 = 216 LCM(12, 18) = 216 / 6 = 36
Therefore, the LCM of 12 and 18 is 36.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
Understanding and mastering the concept of least common multiples is essential for anyone seeking proficiency in mathematics. Whether you're tackling fractions, solving scheduling problems, or delving into more advanced mathematical concepts, the ability to efficiently calculate the LCM is a valuable skill. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of LCM, explored different calculation methods, and highlighted the broad applicability of this seemingly simple mathematical concept in various real-world contexts. By grasping the principles outlined here, you'll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of mathematical challenges and confidently apply this fundamental concept to diverse situations. Remember, practice is key to mastering any mathematical skill; so keep practicing and exploring the world of numbers!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Words That End With A S
May 09, 2025
-
25 Is 50 Of What Number
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 9 Percent In Decimal Form
May 09, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Containing S And I
May 09, 2025
-
Difference Between Experimental Probability And Theoretical Probability
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 2 4 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.