What Is The Lcm For 8 And 10
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
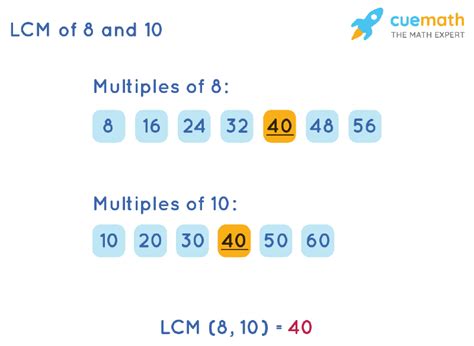
Table of Contents
What is the LCM for 8 and 10? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations. This article delves into the question: What is the LCM for 8 and 10? We'll explore multiple methods for calculating the LCM, discuss the underlying mathematical principles, and illustrate its practical significance through real-world examples.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 8 and 10, let's establish a solid understanding of the concept. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors.
For instance, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... Multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 8 and 10
Now, let's address the central question: what is the LCM of 8 and 10? We can employ several methods to determine this:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of both 8 and 10 until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88...
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100...
By comparing the lists, we see that the smallest common multiple is 40. Therefore, the LCM of 8 and 10 is 40.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³ (8 = 2 x 2 x 2)
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Multiplying these together: 8 x 5 = 40. Thus, the LCM of 8 and 10 is 40.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is always equal to the product of the two numbers. This is expressed mathematically as:
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
First, we need to find the GCD of 8 and 10. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (10) by the smaller number (8): 10 ÷ 8 = 1 with a remainder of 2.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (8) and the smaller number with the remainder (2): 8 ÷ 2 = 4 with a remainder of 0.
- The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 2.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(8, 10) * GCD(8, 10) = 8 * 10 LCM(8, 10) * 2 = 80 LCM(8, 10) = 80 / 2 = 40
Therefore, the LCM of 8 and 10 is 40 using the GCD method.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM finds practical applications in various fields:
-
Fraction addition and subtraction: To add or subtract fractions with different denominators, we need to find a common denominator, which is usually the LCM of the denominators.
-
Scheduling problems: Imagine two buses that depart from a station at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when both buses will depart simultaneously. For example, if one bus departs every 8 hours and another every 10 hours, they will depart together every 40 hours.
-
Pattern recognition: LCM helps identify when repeating patterns will align. For example, in tiling a floor with two types of tiles with different repeating patterns, the LCM dictates when the patterns will perfectly overlap.
-
Music theory: The LCM is utilized in determining the least common multiple of note durations in musical compositions.
-
Gear ratios: In mechanical engineering, the LCM helps in calculating gear ratios and the synchronization of rotating components.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The concept of LCM extends beyond two numbers. We can calculate the LCM of three or more numbers using similar methods, such as prime factorization. For example, to find the LCM of 8, 10, and 12:
- Prime factorization: 8 = 2³, 10 = 2 x 5, 12 = 2² x 3
- Highest powers: 2³ = 8, 3¹ = 3, 5¹ = 5
- LCM: 8 x 3 x 5 = 120
The LCM of 8, 10, and 12 is 120.
Furthermore, the concept of LCM is fundamental in abstract algebra and number theory, playing a crucial role in various mathematical proofs and theorems.
Conclusion: The Power of the LCM
In conclusion, the least common multiple (LCM) is a powerful mathematical tool with wide-ranging applications. We have explored multiple methods for calculating the LCM of 8 and 10, all converging on the answer of 40. Understanding the LCM is not just about solving mathematical problems; it's about grasping a fundamental concept that underpins numerous real-world applications, from scheduling problems to musical compositions. By mastering the concept of LCM, you equip yourself with a valuable tool for tackling diverse mathematical and practical challenges. The methods discussed here, including listing multiples, prime factorization, and the GCD method, provide flexible approaches depending on the numbers involved and the desired level of mathematical rigor. The ability to efficiently and accurately calculate the LCM is a skill that extends far beyond the classroom, demonstrating its enduring relevance in various aspects of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Nucleotides Contain A Sugar A Phosphate And A Nitrogenous
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Two Types Of Mechanical Energy
May 09, 2025
-
Sample Letter Of Refund Payment To Customer
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Source Of Oxygen Released During Photosynthesis
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Is 13 Inches
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm For 8 And 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.