What Is The Largest Negative Integer
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
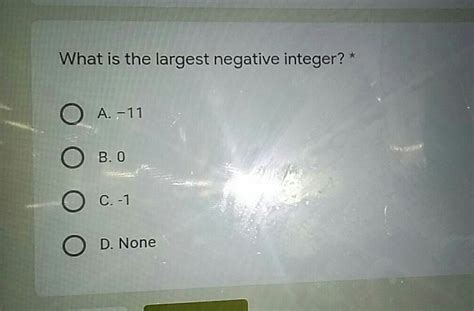
Table of Contents
What is the Largest Negative Integer? Unraveling the Mysteries of Negative Numbers
The question, "What is the largest negative integer?" might seem deceptively simple. After all, integers are whole numbers, and negative integers are those less than zero. However, the answer isn't as straightforward as it might initially appear. This article delves into the concept of negative integers, explores the mathematical reasons behind the lack of a "largest" negative integer, and examines related concepts to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Integers and Negative Numbers
Before we tackle the main question, let's establish a firm understanding of integers and their negative counterparts.
Integers: Integers are whole numbers, including zero, that can be positive, negative, or zero itself. Examples include -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. They extend infinitely in both the positive and negative directions.
Negative Integers: Negative integers are integers less than zero. They represent values opposite to their positive counterparts. For instance, -5 represents a value five units less than zero on the number line.
Why There's No Largest Negative Integer
The crux of the matter lies in the infinite nature of the number line. The number line extends infinitely in both directions – positive infinity and negative infinity. While we can visualize a "smallest" negative integer (-1, because all other negative integers are smaller than -1), there is no such thing as a "largest" negative integer.
Here's why:
-
Always a Smaller Number: For any negative integer you choose, you can always find a smaller one by simply subtracting 1. For example, if you suggest -100 as the largest negative integer, -101 is smaller. And after -101, comes -102, and so on, ad infinitum. This process has no end.
-
Mathematical Proof by Contradiction: Let's assume, for the sake of contradiction, that there is a largest negative integer, let's call it 'n'. Since 'n' is a negative integer, it must be less than zero (n < 0). Now, if we add -1 to 'n', we get 'n - 1', which is a smaller negative integer than 'n'. This contradicts our initial assumption that 'n' was the largest negative integer. Therefore, our assumption must be false, and there is no largest negative integer.
-
The Concept of Infinity: The concept of infinity is crucial here. Negative integers extend infinitely towards negative infinity. There is no endpoint; you can always go further down the number line. This is different from the positive integers where there's a clear starting point (0 or 1 depending on the context), but no endpoint.
Exploring Related Mathematical Concepts
Understanding the absence of a largest negative integer helps illuminate related concepts within mathematics:
1. Number Line and its Implications:
The number line is a visual representation of numbers, extending infinitely in both positive and negative directions. This visual representation clearly demonstrates the unending nature of negative integers. There's no boundary marking the "end" of negative numbers.
2. Ordering of Integers:
Integers are ordered. Given any two integers, one is always either greater than, less than, or equal to the other. This ordering allows us to compare integers and establish relationships between them. However, even with this clear ordering, it doesn't imply the existence of a largest negative integer.
3. Limits and Sequences:
In calculus, the concept of limits helps us analyze the behavior of functions as they approach certain values, including infinity. The sequence of negative integers (-1, -2, -3, ...) approaches negative infinity, but it never reaches a specific largest value.
4. Absolute Value:
The absolute value of an integer is its distance from zero on the number line, always expressed as a non-negative value. While the absolute value of a negative integer is always positive, this concept doesn't change the fact that there's no largest negative integer.
5. Set Theory:
In set theory, the set of negative integers is an infinite set. Infinite sets have no largest element if the set is unbounded. The set of negative integers is unbounded, meaning there is no largest number in this set.
Practical Applications and Real-world Examples
While the abstract nature of the question might seem purely theoretical, understanding the absence of a largest negative integer has practical implications in several areas:
-
Computer Programming: In computer programming, handling very large negative numbers requires careful consideration of data types and potential overflow errors. Recognizing that there is no largest negative number is vital for robust programming. Programs need to be designed to handle negative numbers of arbitrary size, potentially up to the limits of the system's memory capacity.
-
Financial Modeling: In financial modeling, particularly when dealing with debt or losses, understanding negative numbers is essential. Although there might be practical upper limits on debt levels in a specific context, the underlying mathematical principle is that the potential for accumulating larger losses is unbounded.
-
Scientific Measurement: In many scientific measurements, negative numbers represent quantities below a certain reference point (e.g., temperature below zero). While there might be practical lower limits determined by physical phenomena, the mathematical concept remains unchanged: there is no largest negative value.
-
Game Theory and Simulations: Games and simulations often incorporate negative numbers to represent penalties, scores, or resource deficits. The understanding of negative integers plays a crucial role in the development of realistic and functional game mechanics.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Several misconceptions surrounding negative numbers and their magnitudes frequently arise:
-
Confusing Magnitude with Ordering: The magnitude of a negative number refers to its absolute value, which represents its distance from zero. The largest negative number in terms of magnitude is -1, but this doesn't mean it is the largest negative integer. Magnitude deals with the size of the number without considering its sign.
-
Thinking of a "Bottom" to the Number Line: The number line extends infinitely in both directions. There's no "bottom" to the negative side of the number line. This is a crucial concept to grasp. There is no 'final' negative number.
Conclusion: Embracing the Infinity of Negative Integers
The question of the largest negative integer leads us to a profound understanding of the infinite nature of numbers. There is no such thing as a largest negative integer because you can always find a smaller one by subtracting 1. This seemingly simple question unveils the fascinating world of infinity and its implications in mathematics and its applications. The absence of a largest negative integer is a fundamental principle that underlies many mathematical concepts and is crucial for comprehending various fields, from computer science to finance. By grasping this concept, you enhance your mathematical literacy and gain a deeper appreciation for the limitless expanse of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Group Of Dogs Called
Mar 19, 2025
-
Lcm Of 6 4 And 10
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Template Strand 3 To 5
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of The Arm Of The Microscope
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Amount Of Energy In Food Is Measured In
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Largest Negative Integer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
