What Is The Formula Of Iron Ii Sulfate
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
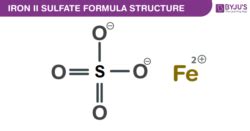
Table of Contents
What is the Formula of Iron(II) Sulfate? A Deep Dive into its Chemistry, Properties, and Uses
Iron(II) sulfate, also known as ferrous sulfate, is a chemical compound with a fascinating history and a wide range of applications. Understanding its chemical formula is crucial to grasping its properties and uses. This comprehensive article will delve deep into the formula, exploring its composition, structure, and how this translates to its various applications in diverse fields.
The Chemical Formula: FeSO₄
The chemical formula for iron(II) sulfate is FeSO₄. This concise formula tells us a great deal about the compound:
-
Fe: Represents the element iron (ferrum). The Roman numeral II in the name, or sometimes a 2+ superscript (Fe²⁺), signifies that iron exists in its +2 oxidation state. This means each iron atom has lost two electrons. This is crucial because iron can exist in other oxidation states (+3 being the most common), resulting in different chemical compounds with distinct properties. Iron(III) sulfate, for example, has a different formula and properties.
-
S: Represents the element sulfur.
-
O₄: Represents four oxygen atoms. These four oxygen atoms are bonded to the sulfur atom to form a sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻), a polyatomic anion with a -2 charge.
Understanding the Sulfate Ion (SO₄²⁻)
The sulfate ion is a crucial component of iron(II) sulfate. It's a tetrahedral structure where the sulfur atom is at the center, covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms. Each oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge, while the sulfur atom carries a partial positive charge, resulting in the overall -2 charge of the ion. This negatively charged ion is highly stable and readily forms ionic bonds with positively charged ions like Fe²⁺.
Ionic Bonding in Iron(II) Sulfate
The bond between the Fe²⁺ ion and the SO₄²⁻ ion is an ionic bond. This means that the iron ion donates its two electrons to the sulfate ion, forming an electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions. This electrostatic attraction holds the compound together in a crystalline structure. The strength of this bond contributes to the properties of iron(II) sulfate, such as its melting point and solubility.
Different Forms and Hydrates of Iron(II) Sulfate
Iron(II) sulfate doesn't always exist simply as FeSO₄. It often incorporates water molecules into its crystal structure, forming hydrates. The most common hydrate is iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate, with the formula FeSO₄·7H₂O. This means each formula unit of iron(II) sulfate is associated with seven water molecules. Other hydrates also exist, such as the tetrahydrate (FeSO₄·4H₂O) and monohydrate (FeSO₄·H₂O). The presence of water molecules significantly impacts the compound's properties, especially its solubility and appearance. The heptahydrate, for instance, is a pale green crystalline solid, whereas the anhydrous form (FeSO₄) is typically a white or pale yellow powder.
Physical Properties of Iron(II) Sulfate and its Hydrates
The physical properties of iron(II) sulfate and its hydrates vary depending on the amount of water incorporated. Some key properties include:
-
Appearance: Iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate is a pale green crystalline solid, while the anhydrous form is white or pale yellow. Exposure to air can cause oxidation, leading to a brownish discoloration.
-
Solubility: Iron(II) sulfate is soluble in water, although the solubility varies depending on the hydrate. The heptahydrate is particularly soluble in water.
-
Melting Point: The melting point depends on the hydrate; the heptahydrate starts to decompose before melting at around 60-64°C.
-
Density: The density also varies depending on the hydrate.
-
Odor: Iron(II) sulfate is generally odorless.
Chemical Properties of Iron(II) Sulfate
Iron(II) sulfate exhibits various chemical properties due to its ionic nature and the presence of iron in the +2 oxidation state:
-
Oxidation: Iron(II) sulfate readily oxidizes in the presence of oxygen and moisture, converting to iron(III) sulfate (Fe₂(SO₄)₃). This oxidation is responsible for the brownish discoloration often observed in samples exposed to air.
-
Reaction with Bases: Iron(II) sulfate reacts with bases to form iron(II) hydroxide (Fe(OH)₂), a precipitate.
-
Reaction with Oxidizing Agents: Strong oxidizing agents can oxidize iron(II) to iron(III).
-
Complex Formation: Iron(II) sulfate can form complexes with various ligands, affecting its properties and reactivity.
Uses of Iron(II) Sulfate
The versatile nature of iron(II) sulfate makes it useful in a wide range of applications:
-
Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia: Iron(II) sulfate is a common treatment for iron deficiency anemia, as it provides a readily absorbable source of iron.
-
Agricultural Applications: It's used as a micronutrient in fertilizers to supply iron to plants.
-
Water Treatment: It's used in water treatment to remove phosphates, preventing eutrophication in lakes and rivers.
-
Dyeing and Printing: Historically, iron(II) sulfate was used as a mordant in dyeing and printing fabrics.
-
Wood Preservation: It has been used as a wood preservative due to its ability to inhibit fungal growth.
-
Reducing Agent: Its reducing properties find application in some chemical processes.
-
Photography: Certain photographic processes utilize iron(II) sulfate.
Safety Precautions
While iron(II) sulfate is generally considered safe when used as directed, precautions should be taken:
-
Avoid ingestion: Large doses can be toxic.
-
Handle with care: Avoid skin and eye contact.
-
Store properly: Store in a cool, dry place away from moisture and oxidizing agents.
Conclusion
The simple formula FeSO₄ belies the complexity and versatility of iron(II) sulfate. Its chemical structure, with its ionic bonding and the presence of the sulfate ion, dictates its various physical and chemical properties. The ability to form hydrates adds further complexity. Understanding the formula is crucial for appreciating its diverse applications, from treating anemia to water treatment and agricultural use. However, it's vital to handle it with care, observing appropriate safety precautions. The continued study and application of iron(II) sulfate undoubtedly hold potential for further discoveries and advancements in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Humans Belong To The Phylum And Class
Mar 22, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between A Monitor And Tv
Mar 22, 2025
-
Derivative Of X With Respect To Y
Mar 22, 2025
-
Why Is The Melting Of Ice Not A Chemical Reaction
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is 3 4 Bigger Than 4 5
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula Of Iron Ii Sulfate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
