What Is The Factors Of 10
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
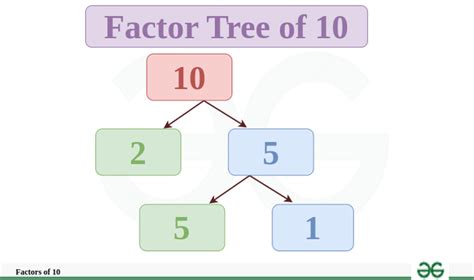
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 10? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 10?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of numbers. While the immediate answer is straightforward, delving deeper reveals interconnected concepts crucial to understanding more complex mathematical structures. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the underlying principles, providing a comprehensive understanding of factors, divisors, and their significance in mathematics.
Understanding Factors and Divisors
Before we dive into the factors of 10, let's establish a clear understanding of the terms involved. Factors, also known as divisors, are whole numbers that divide another number without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if a number a divides another number b exactly, then a is a factor of b. The process of finding factors is called factorization.
For example, if we consider the number 12, its factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder. The act of finding these numbers is called finding the factors of 12, or the factorization of 12.
Finding the Factors of 10: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's address the central question: what are the factors of 10? To find the factors of any number, we systematically check each whole number starting from 1, determining if it divides the target number without a remainder.
- 1: 10 divided by 1 equals 10 (no remainder). Therefore, 1 is a factor of 10.
- 2: 10 divided by 2 equals 5 (no remainder). Therefore, 2 is a factor of 10.
- 3: 10 divided by 3 equals 3 with a remainder of 1. Therefore, 3 is not a factor of 10.
- 4: 10 divided by 4 equals 2 with a remainder of 2. Therefore, 4 is not a factor of 10.
- 5: 10 divided by 5 equals 2 (no remainder). Therefore, 5 is a factor of 10.
- 6: 10 divided by 6 equals 1 with a remainder of 4. Therefore, 6 is not a factor of 10.
- 7, 8, 9: These numbers are also not factors of 10 as they leave remainders when dividing 10.
- 10: 10 divided by 10 equals 1 (no remainder). Therefore, 10 is a factor of 10.
This systematic approach reveals that the factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, and 10.
Prime Factorization and the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The concept of factors is intrinsically linked to prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Numbers that are not prime are called composite numbers.
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic states that every composite number can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers, regardless of the order of the factors.
Let's apply prime factorization to 10:
10 = 2 x 5
This shows that the prime factorization of 10 is 2 x 5. Both 2 and 5 are prime numbers, and their product is 10. This decomposition into prime factors is unique to 10.
The Significance of Factors in Mathematics and Beyond
Understanding factors extends far beyond simple arithmetic. They play a fundamental role in various mathematical areas, including:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD often involves examining the factors of the numbers involved.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. Again, understanding the factors of the numbers is essential for calculating the LCM.
-
Algebra: Factorization is a crucial technique in algebra for simplifying expressions and solving equations. Factoring polynomials, for instance, relies heavily on understanding the factors of numerical coefficients.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization forms the basis of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components is what makes these systems secure.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Modular arithmetic, the system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus), heavily utilizes the concept of factors and divisibility.
-
Real-World Applications: Factors are used in various real-world scenarios, such as dividing resources equally, arranging objects in arrays, or determining optimal packaging sizes.
Expanding on Factor Pairs
When we examine the factors of 10, we can also consider them in terms of factor pairs. A factor pair is a set of two numbers whose product equals the given number. For 10, the factor pairs are:
- 1 and 10
- 2 and 5
These pairs highlight the multiplicative relationships between the factors.
Visualizing Factors: Factor Trees
A useful tool for visualizing the factors of a number, particularly for prime factorization, is a factor tree. A factor tree starts with the original number and branches out, repeatedly breaking down the number into smaller factors until all branches end in prime numbers.
For 10, a factor tree would look like this:
10
/ \
2 5
This clearly shows the prime factorization of 10 as 2 x 5.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
The exploration of factors leads to more complex concepts in number theory. Some related ideas include:
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (divisors excluding the number itself). 6 is the first perfect number (1 + 2 + 3 = 6).
-
Abundant Numbers: An abundant number is a positive integer that is less than the sum of its proper divisors.
-
Deficient Numbers: A deficient number is a positive integer that is greater than the sum of its proper divisors.
-
Highly Composite Numbers: A highly composite number is a positive integer with more divisors than any smaller positive integer.
These concepts demonstrate the rich tapestry of relationships and properties associated with factors and divisors.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Factors
The factors of 10, while seemingly simple at first glance (1, 2, 5, and 10), serve as a gateway to a vast and intricate world of number theory. Understanding factors is not just about basic arithmetic; it's about grasping fundamental concepts that underpin many areas of mathematics and have practical applications in various fields. By exploring the properties of factors, we gain insights into the structure and behavior of numbers, which is crucial for advanced mathematical pursuits and problem-solving in numerous domains. The seemingly straightforward question, “What are the factors of 10?” ultimately unlocks a wealth of knowledge, demonstrating the elegance and power of mathematical exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sound Will Travel Slowest Through Which Medium
May 10, 2025
-
Bending Of The Light Is Called
May 10, 2025
-
Difference Between An Immigrant And A Migrant
May 10, 2025
-
Is The Centroid Always Inside The Triangle
May 10, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Is One Kilometer
May 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factors Of 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.