What Is The Factors For 32
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
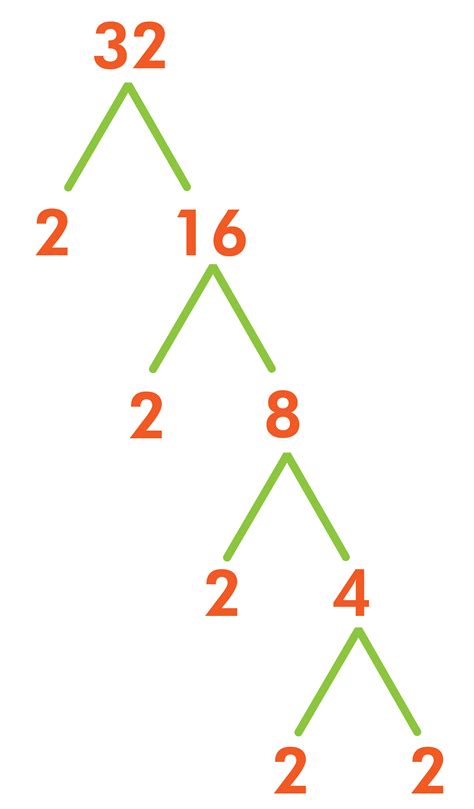
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 32? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 32. However, understanding the concept of factors, prime factorization, and their applications extends far beyond basic arithmetic. This article delves into the factors of 32, explores the broader concepts of number theory related to factorization, and offers practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Factors
A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In other words, if you divide the number by the factor, the result is another whole number.
For example, let's consider the number 12. The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. This is because:
- 12 ÷ 1 = 12
- 12 ÷ 2 = 6
- 12 ÷ 3 = 4
- 12 ÷ 4 = 3
- 12 ÷ 6 = 2
- 12 ÷ 12 = 1
Notice that the factors always come in pairs. This is because factorization inherently involves finding two numbers that multiply to give the original number.
Finding the Factors of 32
Now, let's apply this understanding to find the factors of 32. We'll systematically check each whole number to see if it divides 32 without leaving a remainder:
- 1: 32 ÷ 1 = 32
- 2: 32 ÷ 2 = 16
- 4: 32 ÷ 4 = 8
- 8: 32 ÷ 8 = 4
- 16: 32 ÷ 16 = 2
- 32: 32 ÷ 32 = 1
Therefore, the factors of 32 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32.
Prime Factorization: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization helps us understand the fundamental building blocks of a number.
To find the prime factorization of 32, we can use a factor tree:
32
/ \
2 16
/ \
2 8
/ \
2 4
/ \
2 2
Following the branches down, we see that 32 can be expressed as 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2, or 2<sup>5</sup>. This is the prime factorization of 32. This tells us that 32 is built entirely from the prime number 2, multiplied by itself five times.
Applications of Factors and Prime Factorization
Understanding factors and prime factorization isn't just an academic exercise; it has practical applications in various areas of mathematics and beyond:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, simplifying 16/32 involves finding the GCF of 16 and 32 (which is 16), resulting in the simplified fraction 1/2.
-
Solving Equations: Factorization is crucial in solving algebraic equations, particularly quadratic equations. Factoring the quadratic expression allows us to find the roots or solutions of the equation.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers and factorization play a vital role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptosystems like RSA. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors forms the basis of the security of these systems.
-
Computer Science: Concepts of divisibility and prime factorization are fundamental in algorithm design and optimization in computer science. Efficient algorithms for factorization are continuously being researched and improved.
Beyond the Basics: More on Number Theory
The study of factors and factorization leads us into the fascinating world of number theory, a branch of mathematics with profound implications. Here are some related concepts:
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): The largest number that divides two or more numbers without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCF is often useful in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems. The GCF of 16 and 32 is 16.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. The LCM is useful in solving problems involving fractions, ratios, and cycles. The LCM of 16 and 32 is 32.
-
Divisibility Rules: These rules provide shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by certain numbers without performing the actual division. For example, a number is divisible by 2 if it's an even number, divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3, and so on. These rules can greatly speed up the process of finding factors.
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding itself). 6 is the first perfect number (1 + 2 + 3 = 6). Finding perfect numbers is an active area of research in number theory.
-
Abundant Numbers: An abundant number is a number where the sum of its proper divisors is greater than the number itself. For example, 12 is an abundant number (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 = 16 > 12).
-
Deficient Numbers: A deficient number is a number where the sum of its proper divisors is less than the number itself. Most numbers are deficient numbers.
Practical Exercises
To reinforce your understanding, try the following exercises:
- Find all the factors of 48.
- Find the prime factorization of 72.
- What is the GCF of 24 and 36?
- What is the LCM of 12 and 18?
- Is 28 a perfect, abundant, or deficient number?
By working through these exercises, you can strengthen your grasp of factors, prime factorization, and related concepts.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Factors
The factors of 32, while seemingly simple at first glance, open a door to a rich and complex world of number theory. Understanding factors and prime factorization is essential not only for basic arithmetic but also for higher-level mathematical concepts and various applications in other fields. The exploration of factors extends far beyond simple division; it's a journey into the fundamental building blocks of numbers and their intricate relationships. As you delve deeper into the world of numbers, you'll discover the elegance and power of these fundamental concepts. Continue exploring, and you'll find that the seemingly simple act of finding the factors of a number can lead to a wealth of mathematical discovery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 2 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is 23 A Composite Or Prime Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
Consecutive Angles In A Parallelogram Are
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is Root 72 A Rational Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 15
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factors For 32 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
