What Is The Factor Of 53
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
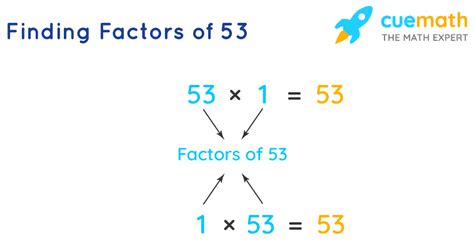
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 53? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The question, "What are the factors of 53?" might seem deceptively simple. However, understanding the answer unlocks a deeper appreciation of number theory, prime numbers, and the process of factorization. Let's explore this seemingly straightforward query in detail.
Understanding Factors
Before we delve into the specifics of 53, let's establish a firm understanding of what constitutes a factor. A factor of a number is any whole number that divides evenly into that number without leaving a remainder. In other words, if you divide the number by its factor, the result is another whole number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides evenly into 12:
- 12 ÷ 1 = 12
- 12 ÷ 2 = 6
- 12 ÷ 3 = 4
- 12 ÷ 4 = 3
- 12 ÷ 6 = 2
- 12 ÷ 12 = 1
Identifying the Factors of 53
Now, let's apply this understanding to the number 53. To find the factors of 53, we need to determine all the whole numbers that divide evenly into 53.
Let's start with the most obvious factors:
- 1: Every whole number has 1 as a factor. 53 ÷ 1 = 53
- 53: Every whole number is divisible by itself. 53 ÷ 53 = 1
Now, let's consider other potential factors. We can systematically check numbers:
- Is 2 a factor of 53? No, 53 is not an even number.
- Is 3 a factor of 53? No, the sum of the digits (5 + 3 = 8) is not divisible by 3.
- Is 4 a factor of 53? No, 53 is not divisible by 4.
- Is 5 a factor of 53? No, 53 doesn't end in 0 or 5.
- Is 6 a factor of 53? No, 53 is not divisible by both 2 and 3.
We can continue this process, but we'll quickly realize that no other whole numbers divide evenly into 53. Therefore, the only factors of 53 are 1 and 53.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
The fact that 53 only has two factors – 1 and itself – makes it a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In other words, it's only divisible by 1 and itself.
Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks in number theory. They are indivisible and form the basis for many mathematical concepts and applications, including cryptography. The discovery and study of prime numbers have been a continuous pursuit in mathematics for centuries.
The prime factorization of a number is the expression of that number as a product of its prime factors. Since 53 is a prime number, its prime factorization is simply 53.
Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the factors of 53 provides a gateway to exploring related concepts within number theory:
1. Divisibility Rules
Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by another number without performing the actual division. While we checked for divisibility by several small numbers, understanding divisibility rules can streamline the process, especially for larger numbers.
2. Sieve of Eratosthenes
The Sieve of Eratosthenes is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit. It's a visual method that systematically eliminates composite numbers (non-prime numbers) leaving only the primes. While not directly used to find the factors of 53 in this case, it highlights the importance of prime numbers and provides a way to identify them efficiently.
3. Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This theorem underlines the importance of prime numbers as the building blocks of all integers. Since 53 is prime, its unique prime factorization is simply 53.
4. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The concepts of GCD and LCM are closely related to factorization. The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the numbers. When finding the GCD or LCM, prime factorization can simplify the calculations. Since 53 is prime, finding its GCD or LCM with other numbers becomes relatively straightforward.
Practical Applications of Prime Numbers
The seemingly simple question of the factors of 53 touches upon concepts with significant practical applications:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are crucial in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The security of these systems relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers and their properties are essential in various algorithms and data structures in computer science.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a vital role in error-correcting codes, ensuring data integrity during transmission.
Conclusion
While the factors of 53 might seem trivial at first glance – simply 1 and 53 – understanding the implications of this reveals a much richer landscape within number theory. The fact that 53 is a prime number connects it to fundamental concepts with significant implications across mathematics, computer science, and cryptography. This seemingly simple question serves as a perfect entry point for exploring the fascinating world of prime numbers and their importance in various fields. The unique properties of prime numbers, like 53, underpin many of the technologies we use daily, showcasing the depth and significance of what might seem like a basic mathematical concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Neutral Particle In The Nucleus Of An Atom
May 09, 2025
-
Label The Structures Of The Vertebrae
May 09, 2025
-
4 6 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
May 09, 2025
-
If X Is A Multiple Of 18 And 60
May 09, 2025
-
Does Light Require A Medium To Travel
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factor Of 53 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.