What Is The Factor Of 31
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
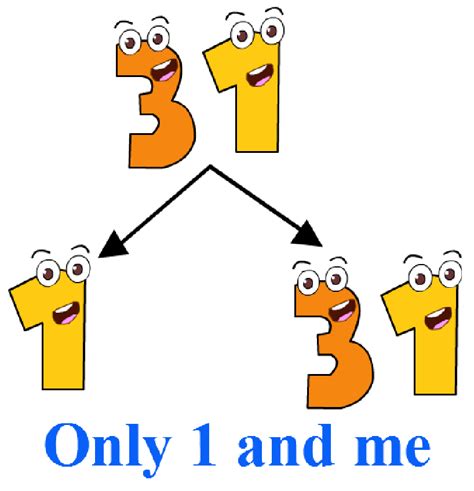
Table of Contents
What is the Factor of 31? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The question "What is the factor of 31?" might seem deceptively simple. However, understanding the answer requires a journey into the fascinating world of number theory, specifically focusing on prime numbers and factorization. This exploration will go beyond a simple answer, delving into the concepts, properties, and implications of 31's unique status as a prime number.
Understanding Factors and Prime Numbers
Before we address the factors of 31, let's establish a clear understanding of the fundamental terms involved.
What are Factors?
In mathematics, a factor (also known as a divisor) of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
What are Prime Numbers?
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This means it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other integers, as every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Determining the Factors of 31
Now, let's return to our original question: What are the factors of 31?
Given the definition of a prime number, the answer becomes clear. 31 is a prime number. Therefore, its only factors are 1 and 31.
This seemingly simple answer opens the door to exploring the deeper properties and significance of prime numbers.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers hold a central position in number theory and have far-reaching implications in various fields, including:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are the foundation of many modern encryption techniques, such as RSA encryption. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components is the key to the security of these systems. The larger the prime numbers used, the more secure the encryption.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers play a crucial role in algorithms and data structures, such as hash tables and distributed systems. Understanding prime factorization is vital for optimizing these systems for efficiency and speed.
-
Mathematics: Prime numbers are fundamental to many mathematical theorems and conjectures, including the Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics. The distribution and properties of prime numbers continue to be an active area of research.
-
Physics: Surprisingly, prime numbers have also found applications in physics, particularly in areas involving chaotic systems and quantum mechanics. The patterns and distribution of prime numbers reveal underlying structures and relationships within seemingly random phenomena.
Exploring the Properties of 31
While 31 might seem like a relatively small prime number, exploring its properties reveals interesting aspects:
-
Its place in the sequence of primes: 31 is the 11th prime number in the sequence. The sequence of prime numbers is famously irregular, and predicting the next prime number is a challenging problem in mathematics.
-
Its digital root: The digital root of a number is the iterative sum of its digits until a single-digit number is obtained. For 31, the digital root is 3 + 1 = 4. Digital roots can be used as a simple divisibility test for certain numbers.
-
Its representation in other bases: The representation of 31 varies depending on the number base used. For example, in binary (base-2), it's 11111; in hexadecimal (base-16), it's 1F. Exploring a number's representation in different bases can reveal hidden patterns and relationships.
-
31 as a Mersenne prime candidate: Mersenne primes are prime numbers that are one less than a power of two (2<sup>n</sup> - 1). While 31 is not a Mersenne prime itself, exploring Mersenne primes can shed light on the distribution and properties of specific types of prime numbers.
Beyond 31: Factorization Techniques
Understanding the factors of 31 sets the stage for exploring more complex factorization techniques for larger numbers. While trial division works well for smaller numbers, more sophisticated methods are needed for larger integers. These include:
-
Trial Division: This is the simplest method, where you systematically try dividing the number by each integer from 2 up to the square root of the number. If it's divisible, you've found a factor.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This algorithm efficiently finds all prime numbers up to a specified limit. It's a powerful tool for identifying potential factors.
-
Pollard's rho algorithm: This probabilistic algorithm is effective in finding small prime factors of large composite numbers. It's particularly useful when dealing with very large numbers that are difficult to factor using trial division.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): This is the most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers. It's used for breaking modern cryptographic systems based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.
These algorithms illustrate the complexity and computational challenges involved in factoring large composite numbers. The security of modern cryptography relies heavily on this difficulty.
Applications of Factorization
The ability to efficiently factor numbers has wide-ranging applications, including:
-
Cryptography: As previously mentioned, the difficulty of factoring large numbers forms the basis of many modern encryption methods. Breaking these systems relies on finding efficient factorization algorithms.
-
Coding Theory: Factorization techniques are used in coding theory to design error-correcting codes. These codes help ensure reliable data transmission and storage.
-
Computer Algebra Systems: Modern computer algebra systems use sophisticated factorization algorithms to perform complex calculations and simplify mathematical expressions.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of 31's Primeness
The seemingly simple question, "What is the factor of 31?" leads to a rich exploration of prime numbers, factorization techniques, and their significance in various fields. While 31 itself has only two factors, 1 and 31, its primeness contributes to a deeper understanding of the fundamental building blocks of mathematics and their applications in our modern world. The study of prime numbers continues to be a dynamic and crucial area of research, with ongoing implications for cryptography, computer science, and mathematics as a whole. The seemingly simple nature of 31's factors belies the profound complexity and importance of prime numbers in the vast landscape of mathematics and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 3
Mar 09, 2025
-
Moment Of Inertia Of A Semicircle
Mar 09, 2025
-
Where Does Dna Replication Occur In Eukaryotic Cells
Mar 09, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Chlorine
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The First Five Multiples Of 9
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factor Of 31 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
