What Is The Distance Between Point A And Point B
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 5 min read
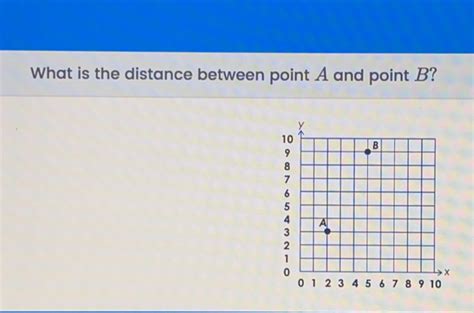
Table of Contents
What is the Distance Between Point A and Point B? A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the distance between two points is a fundamental concept in various fields, from everyday navigation to advanced scientific calculations. This seemingly simple task has several approaches, depending on the context and the information available. This comprehensive guide will explore various methods for calculating the distance between Point A and Point B, addressing different scenarios and levels of complexity.
Understanding the Basics: Cartesian Coordinates
The most common method involves using Cartesian coordinates. These coordinates define a point's location on a two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) plane using perpendicular axes. In 2D, we use x and y coordinates; in 3D, we add a z coordinate.
Calculating Distance in 2D Space
Imagine Point A located at (x₁, y₁) and Point B at (x₂, y₂). We can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the straight-line distance between them. The theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In our case, the distance between A and B is the hypotenuse, and the differences in x-coordinates (x₂ - x₁) and y-coordinates (y₂ - y₁) form the other two sides. Therefore, the distance (d) is calculated as:
d = √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
This formula provides the Euclidean distance, which represents the shortest distance between two points in a flat plane.
Example:
Let's say Point A is at (2, 3) and Point B is at (7, 15). The distance would be:
d = √[(7 - 2)² + (15 - 3)²] = √[5² + 12²] = √[25 + 144] = √169 = 13
Therefore, the distance between Point A and Point B is 13 units.
Calculating Distance in 3D Space
Extending the concept to 3D space, where Point A is at (x₁, y₁, z₁) and Point B is at (x₂, y₂, z₂), we simply add the square of the z-coordinate difference to the formula:
d = √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)² + (z₂ - z₁)²]
Example:
If Point A is at (1, 2, 3) and Point B is at (4, 6, 10), the distance is:
d = √[(4 - 1)² + (6 - 2)² + (10 - 3)²] = √[3² + 4² + 7²] = √[9 + 16 + 49] = √74
The distance between Point A and Point B in this 3D space is √74 units.
Beyond Cartesian Coordinates: Other Coordinate Systems
While Cartesian coordinates are prevalent, other coordinate systems exist, each requiring a different approach to distance calculation.
Polar Coordinates
In a polar coordinate system, a point's location is defined by its distance from the origin (r) and its angle (θ) from a reference direction. Converting polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates allows us to use the Euclidean distance formula.
The conversion formulas are:
- x = r * cos(θ)
- y = r * sin(θ)
Once converted, the Euclidean distance formula can be applied.
Spherical Coordinates
Spherical coordinates extend the concept to three dimensions, using radius (r), azimuth (θ), and elevation (φ) to define a point's position. Similar to polar coordinates, conversion to Cartesian coordinates is necessary before applying the distance formula.
Geodetic Coordinates (Latitude and Longitude)
When dealing with locations on the Earth's surface, latitude and longitude are used. Calculating the distance between two points using these coordinates requires considering the Earth's curvature. The Haversine formula is commonly used for this purpose. This formula accounts for the Earth's sphericity, providing a more accurate distance compared to using a simple Euclidean approach. It utilizes the Earth's radius and the latitudes and longitudes of the two points to calculate the great-circle distance – the shortest distance between two points on a sphere.
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
Non-Euclidean Spaces
The Euclidean distance formula assumes a flat space. However, in non-Euclidean geometries (like those found in curved spaces), the distance calculation becomes more complex and depends on the specific geometry involved.
Distance Metrics Beyond Euclidean Distance
The Euclidean distance is just one type of distance metric. Other metrics, such as Manhattan distance (sum of absolute differences in coordinates) or Chebyshev distance (maximum absolute difference in coordinates), are used in various applications, depending on the specific needs of the problem.
Practical Applications
The calculation of distance between points has numerous real-world applications:
- GPS Navigation: Determining the shortest route between two locations using latitude and longitude.
- Robotics: Calculating distances for robot path planning and obstacle avoidance.
- Computer Graphics: Rendering images and simulating movement in 3D environments.
- Image Processing: Measuring distances between pixels for feature detection and object recognition.
- Machine Learning: Calculating distances between data points for clustering and classification algorithms.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Analyzing spatial data and calculating distances between geographical features.
- Physics and Engineering: Calculating distances in simulations and modeling physical systems.
Conclusion
Determining the distance between Point A and Point B is a crucial task across many disciplines. The best approach depends heavily on the coordinate system used and the nature of the space being considered. While the simple Euclidean distance formula suffices for many situations, understanding other coordinate systems and distance metrics is vital for tackling more complex problems, such as those involving curved spaces or geographical locations. Mastering these concepts empowers problem-solving across various fields, from everyday tasks to advanced scientific endeavors. Remember to choose the appropriate formula based on the available information and the context of your problem. Understanding the underlying principles allows for accurate and efficient distance calculations, providing valuable insights and solutions in diverse applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Calculate The Bandwidth Of A Signal
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Are In 1 Coulomb
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find The Average Cost Of A Function
May 09, 2025
-
How Does A Switch Work In A Circuit
May 09, 2025
-
8 Millimeters Equals How Many Centimeters
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Distance Between Point A And Point B . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.