What Is The Chemical Formula Of Barium Phosphate
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
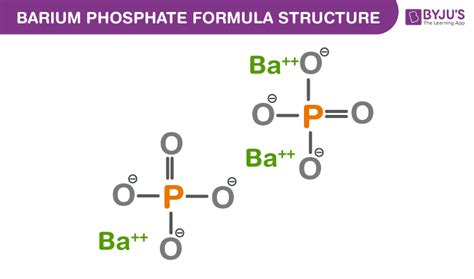
Table of Contents
What is the Chemical Formula of Barium Phosphate? A Deep Dive into its Properties and Applications
Barium phosphate, an inorganic compound, holds a significant place in various industrial applications. Understanding its chemical formula is crucial for comprehending its properties and uses. This article delves deep into the chemical formula of barium phosphate, exploring its different forms, properties, synthesis, safety precautions, and a wide range of applications across diverse industries.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: Ba₃(PO₄)₂
The chemical formula of barium phosphate is Ba₃(PO₄)₂. This formula indicates that one molecule of barium phosphate consists of three barium (Ba) atoms and two phosphate (PO₄) groups. This stoichiometric ratio is essential in determining the compound's properties and how it reacts with other substances. The subscript numbers indicate the relative number of atoms of each element within the molecule. It's vital to understand that this formula represents the empirical formula, which denotes the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound. It might not necessarily reflect the exact molecular structure, especially in complex crystalline forms.
Ionic Bonding in Barium Phosphate
Barium phosphate is an ionic compound. This means it's formed through the electrostatic attraction between positively charged barium ions (Ba²⁺) and negatively charged phosphate ions (PO₄³⁻). The barium atom loses two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, forming a cation (Ba²⁺). The phosphate group, a polyatomic ion, carries a 3- charge due to the differing electronegativities of phosphorus and oxygen. The attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms the strong ionic bonds that hold the crystal lattice together. Understanding the ionic nature of the bond is crucial in predicting its physical and chemical properties, including its solubility and reactivity.
Different Forms and Crystal Structures of Barium Phosphate
Barium phosphate exists in various crystalline forms, each exhibiting slightly different properties. These variations depend on factors like temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities during synthesis. While the chemical formula remains consistent (Ba₃(PO₄)₂), the arrangement of the ions in the crystal lattice can vary, resulting in different polymorphs. This structural diversity impacts several properties including solubility, reactivity, and optical properties.
Polymorphs and their influence on Properties
The different polymorphs of barium phosphate might display variations in their solubility in different solvents, their reactivity with acids and bases, and even their optical characteristics, like refractive index and birefringence. Identifying the specific polymorph is critical in applications where these variations significantly impact performance. The subtle differences between polymorphs highlight the complexity beyond the simple chemical formula and underscore the importance of considering the crystal structure in applications.
Synthesis of Barium Phosphate
The synthesis of barium phosphate involves reacting soluble barium salts with soluble phosphate salts. The process typically involves precipitation, where the less soluble barium phosphate forms a solid precipitate out of the solution.
Common Synthesis Methods
A common method involves reacting barium chloride (BaCl₂) with sodium phosphate (Na₃PO₄) in an aqueous solution. The reaction is represented by the following balanced chemical equation:
3BaCl₂(aq) + 2Na₃PO₄(aq) → Ba₃(PO₄)₂(s) + 6NaCl(aq)
This reaction results in the precipitation of solid barium phosphate, which can be separated from the solution through filtration and further purified through washing and drying. Controlling the reaction conditions, such as temperature and concentration, can influence the size and morphology of the resulting barium phosphate particles. Precise control is often desired for specific applications requiring particular particle size distributions or crystal morphologies.
Factors Influencing the Synthesis
Several factors influence the properties of the synthesized barium phosphate:
- Reactant concentrations: The concentration of the reactants can influence the particle size and morphology of the precipitate.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures generally lead to larger particles.
- pH: The pH of the reaction solution affects the solubility of barium phosphate and can influence the purity of the product. Careful pH control is often essential.
- Presence of impurities: Impurities in the reactants can affect the crystal structure and properties of the final product.
Properties of Barium Phosphate
Barium phosphate, in its various forms, exhibits a range of physical and chemical properties. These properties make it suitable for a variety of applications.
Physical Properties
- Appearance: It typically appears as a white, odorless powder.
- Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in water, exhibiting low solubility. This low solubility is a key factor in many applications.
- Melting point: It has a relatively high melting point, indicating strong ionic bonds within its crystal lattice.
- Density: The density varies slightly depending on the crystalline form.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity: It's relatively stable under normal conditions.
- Reaction with acids: It reacts with strong acids to form soluble barium salts and phosphoric acid.
- Thermal stability: It shows good thermal stability up to high temperatures.
Safety Precautions when Handling Barium Phosphate
Barium compounds, including barium phosphate, can be toxic if ingested or inhaled. Appropriate safety measures are essential when handling barium phosphate. These include:
- Eye protection: Always wear safety goggles or a face shield.
- Respiratory protection: Use a respirator or dust mask to avoid inhalation of the powder.
- Gloves: Wear appropriate chemical-resistant gloves to prevent skin contact.
- Proper ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize the risk of inhalation.
- Disposal: Dispose of barium phosphate according to local regulations for hazardous waste.
Applications of Barium Phosphate
Barium phosphate finds applications in several areas, leveraging its unique properties.
Industrial Applications
- Phosphor: In fluorescent lamps and cathode ray tubes (CRTs), it serves as a phosphor, converting electron energy into visible light. Its specific luminescent properties are exploited here.
- Flame retardant: Its inclusion enhances the flame retardancy in certain materials. This property is based on its thermal stability.
- Ceramic industry: It finds use in ceramic glazes and pigments, where its chemical stability and color contribute to the final product's properties.
- Catalyst support: It can act as a support material in catalysis due to its thermal stability.
Other Applications
Research is ongoing to explore further applications, such as in:
- Medicine: Though not widely used in pharmaceuticals due to its toxicity, research continues to investigate potential applications in targeted drug delivery or specific medical imaging techniques. This is a rapidly advancing field.
- Environmental remediation: It’s being studied for its potential role in sequestering phosphates from contaminated water sources. This would address environmental pollution concerns.
Conclusion: Beyond the Formula
While the chemical formula Ba₃(PO₄)₂ provides a fundamental understanding of barium phosphate, a comprehensive understanding requires considering its various forms, synthesis methods, properties, and safety considerations. Its applications span various industries, highlighting its importance in diverse technological fields. Future research and development will likely unveil further applications and improve our understanding of this versatile inorganic compound. Remember always to prioritize safety when handling barium phosphate and to consult relevant safety data sheets before undertaking any experiments or handling this substance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cual Es La Diferencia Entre Sent Y Send
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Are All Of The Factors Of 56
Mar 31, 2025
-
Five Letter Words End With Er
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is The Molecular Mass Of Koh
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is 12 16 As A Percentage
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Chemical Formula Of Barium Phosphate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
