What Is The Chemical Formula For Phosphorus Pentachloride
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
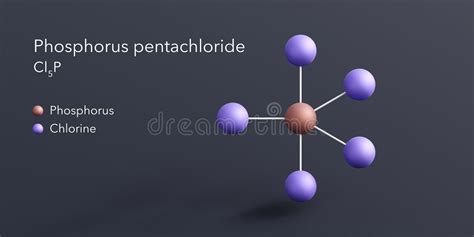
Table of Contents
What is the Chemical Formula for Phosphorus Pentachloride? A Deep Dive into its Properties and Reactions
Phosphorus pentachloride, a crucial compound in various chemical industries, holds a significant place in chemistry. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and reactions is essential for anyone working with or studying this substance. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of phosphorus pentachloride, providing a detailed exploration of its characteristics and applications.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: PCl<sub>5</sub>
The chemical formula for phosphorus pentachloride is PCl<sub>5</sub>. This formula clearly indicates the composition of the molecule: one atom of phosphorus (P) bonded to five atoms of chlorine (Cl). This simple formula belies the complex nature of this fascinating compound and its diverse applications.
Beyond the Formula: Structure and Bonding
The formula PCl<sub>5</sub> doesn't fully illustrate the molecule's three-dimensional structure. While the formula suggests a planar structure, phosphorus pentachloride exhibits a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. This means the phosphorus atom sits at the center, with three chlorine atoms forming an equatorial plane and two chlorine atoms occupying the axial positions. This structure is a consequence of the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory, which dictates that electron pairs arrange themselves to minimize repulsion. The axial bonds are slightly longer than the equatorial bonds due to greater repulsions from the equatorial chlorine atoms.
The Importance of the Formula in Chemical Reactions
The chemical formula, PCl<sub>5</sub>, is critical for predicting and understanding the reactions in which phosphorus pentachloride participates. It provides crucial information about the stoichiometry of reactions, enabling accurate calculations of reactant quantities and product yields. Knowing the formula allows chemists to balance chemical equations involving phosphorus pentachloride, ensuring that the law of conservation of mass is adhered to in all chemical transformations. This precise knowledge is vital in various applications, from laboratory synthesis to large-scale industrial processes.
Physical Properties of Phosphorus Pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride presents a unique set of physical properties that distinguish it from other phosphorus halides and contribute to its specific applications. Understanding these properties is paramount for safe handling and effective utilization.
Appearance and State: A Sublimation Story
At room temperature, phosphorus pentachloride exists as a pale yellow-white crystalline solid. Unlike many compounds that transition directly from solid to liquid upon heating, phosphorus pentachloride undergoes sublimation. This means it transitions directly from a solid to a gas without passing through a liquid phase. This property influences its handling and purification methods, often requiring specialized techniques to control the sublimation process.
Melting and Boiling Points: High Temperatures
Phosphorus pentachloride possesses relatively high melting (160-161°C) and boiling points (160-161°C). This reflects the strong covalent bonds between phosphorus and chlorine atoms within the molecule. The strong intermolecular forces require significant energy to overcome, thus explaining the elevated melting and boiling points.
Reactivity and Stability: A Reactive Compound
Phosphorus pentachloride is a highly reactive compound. Its reactivity stems from the presence of polar P-Cl bonds and the electrophilic nature of the phosphorus atom. This high reactivity dictates that it must be handled with care, and appropriate safety measures must be implemented to prevent accidents. Furthermore, it's crucial to store phosphorus pentachloride under dry conditions to avoid hydrolysis, a reaction discussed in detail later.
Chemical Reactions of Phosphorus Pentachloride
The chemical reactivity of phosphorus pentachloride is diverse and significant. Its ability to participate in a variety of reactions makes it a valuable reagent in organic and inorganic chemistry.
Hydrolysis: Reaction with Water
Phosphorus pentachloride readily reacts with water (H<sub>2</sub>O) in a highly exothermic reaction (releases heat) resulting in the formation of phosphoric acid (H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub>) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas. The reaction is represented as follows:
PCl<sub>5</sub> + 4H<sub>2</sub>O → H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub> + 5HCl
This reaction highlights the importance of storing and handling phosphorus pentachloride under strictly anhydrous conditions (free of water) to prevent uncontrolled hydrolysis. The liberated HCl gas is corrosive and potentially hazardous.
Reaction with Alcohols: Formation of Alkyl Chlorides
Phosphorus pentachloride reacts with alcohols (ROH) to yield alkyl chlorides (RCl) and phosphoric acid. This reaction is a useful method for converting alcohols to their corresponding alkyl chlorides, a common transformation in organic synthesis:
PCl<sub>5</sub> + ROH → RCl + POCl<sub>3</sub> + HCl
The reaction mechanism involves initial substitution followed by elimination of phosphoryl chloride (POCl<sub>3</sub>).
Reaction with Carboxylic Acids: Formation of Acid Chlorides
Phosphorus pentachloride is a powerful reagent for converting carboxylic acids (RCOOH) into acid chlorides (RCOCl), which are crucial intermediates in organic synthesis. The reaction proceeds as follows:
RCOOH + PCl<sub>5</sub> → RCOCl + POCl<sub>3</sub> + HCl
The acid chloride produced can then undergo various subsequent transformations, making this reaction a cornerstone in organic synthesis.
Reaction with Amines: Formation of Amides
While less common than other reactions, phosphorus pentachloride can react with primary amines (RNH<sub>2</sub>) to form amides (RCONH<sub>2</sub>), although it's not the preferred method for amide synthesis. The reaction involves several steps and is often less efficient than other established amide synthesis routes.
Applications of Phosphorus Pentachloride
The unique properties and reactivity of phosphorus pentachloride make it a valuable reagent in diverse industrial and laboratory applications. Its role extends across various chemical fields, highlighting its significance in modern chemistry.
Industrial Applications: Chlorination and Synthesis
In the industrial setting, phosphorus pentachloride is predominantly used as a chlorinating agent for organic compounds. Its ability to convert alcohols to alkyl chlorides and carboxylic acids to acid chlorides makes it a crucial reagent in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and dyes. It's also utilized in the synthesis of other phosphorus compounds and as a catalyst in certain industrial processes.
Laboratory Applications: Synthesis and Reagent
In the laboratory, phosphorus pentachloride finds extensive use as a reagent in organic synthesis. Its capability to convert various functional groups, such as alcohols, carboxylic acids, and amines, into their corresponding chlorinated derivatives makes it an indispensable tool in the chemist's arsenal. It's employed in the synthesis of numerous organic compounds and as a dehydration agent for certain reactions.
Safety Precautions: Handling a Reactive Compound
Because of its high reactivity and potential hazards, phosphorus pentachloride demands careful handling and appropriate safety precautions. It's crucial to wear personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat, when handling this compound. Furthermore, working in a well-ventilated area or using a fume hood is essential to minimize exposure to potentially harmful fumes and byproducts. Always refer to safety data sheets (SDS) for comprehensive information on handling and disposal procedures.
Environmental Considerations and Disposal
The use of phosphorus pentachloride necessitates careful consideration of its potential environmental impact. Its hydrolysis products, phosphoric acid and hydrogen chloride, can be detrimental to the environment if not properly managed. Responsible disposal methods are crucial to minimize environmental contamination. Proper disposal procedures should be strictly adhered to, ideally in accordance with local and national regulations concerning hazardous waste.
Conclusion: A Versatile and Crucial Compound
Phosphorus pentachloride, with its chemical formula PCl<sub>5</sub>, is a versatile and important compound in chemistry. Its unique physical and chemical properties, along with its diverse applications in both industrial and laboratory settings, make it a cornerstone reagent in many chemical processes. Understanding its chemical formula, structure, reactions, and safety precautions is vital for its safe and effective use. Always remember to prioritize safety and responsible environmental practices when working with this powerful compound. Continuing research and development will undoubtedly uncover further applications and deepen our understanding of this fascinating chemical species.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The First 5 Multiples Of 2
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Numeral For 42
Apr 01, 2025
-
Butter Melting Is A Physical Change
Apr 01, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 20 And 8
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Mixture Can Be Made Up Of Two Or More
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Chemical Formula For Phosphorus Pentachloride . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
