What Is The Celsius Scale Based On
Juapaving
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
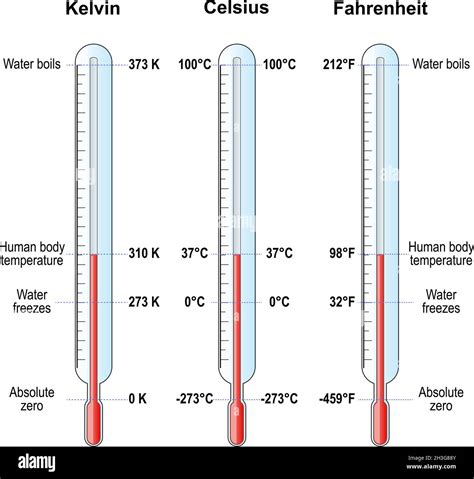
Table of Contents
What is the Celsius Scale Based On? A Deep Dive into the History and Science
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a widely used temperature scale globally. But what exactly is it based on? Understanding its foundations reveals a fascinating history of scientific development and the crucial role of water in defining our understanding of temperature. This article delves into the intricacies of the Celsius scale, exploring its origins, the scientific principles behind its construction, and its ongoing relevance in various fields.
The Birth of the Celsius Scale: Anders Celsius and His Contributions
The Celsius scale wasn't always called "Celsius." It owes its name to Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701-1744), who initially proposed a reversed version of the scale we use today. In 1742, Celsius published a paper describing a scale where 0° represented the boiling point of water and 100° represented the freezing point of water – the opposite of the current convention.
This initial inversion, though unconventional by today's standards, was a significant advancement. Prior to Celsius's work, temperature measurement was largely inconsistent and lacked a standardized system. Celsius's proposal, while inverted, provided a crucial framework based on the readily observable and reproducible phase transitions of water.
The Inversion and the Standardization of the Celsius Scale
The inversion of Celsius's original scale was quickly rectified by other scientists. Carl Linnaeus, a renowned botanist, and other contemporaries adopted a modified version of Celsius's scale, where 0° represented the freezing point and 100° represented the boiling point of water at sea level. This is the Celsius scale we recognize and utilize today.
This seemingly simple adjustment was a vital step in establishing a universally accepted temperature scale. By fixing the reference points to the easily reproducible phase transitions of water, the scale gained accuracy, consistency, and widespread adoption.
The Scientific Principles Underlying the Celsius Scale
The Celsius scale's foundation rests on the physical properties of water. The two fixed points – 0°C for freezing and 100°C for boiling – are defined under specific conditions:
-
Standard Atmospheric Pressure: The temperature readings are accurate only at standard atmospheric pressure (typically defined as 101.325 kPa or 1 atmosphere). Variations in atmospheric pressure will slightly alter the boiling and freezing points of water.
-
Pure Water: The water used must be pure; impurities can affect its freezing and boiling points.
These conditions are crucial for maintaining the accuracy and reproducibility of the Celsius scale. Any deviation from standard atmospheric pressure or the use of impure water will introduce errors in the temperature measurement.
The Triple Point of Water: A More Precise Definition
While the freezing and boiling points provide convenient reference points, modern scientific definitions have moved towards a more precise standard: the triple point of water. The triple point is the unique temperature and pressure at which water can coexist in all three phases – solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water vapor) – simultaneously.
The triple point of water is defined as exactly 0.01°C and is considered a more stable and precise reference point than the freezing point, which is susceptible to slight variations depending on the purity of the water and the presence of dissolved gases. The International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) uses the triple point of water as a primary reference for calibrating thermometers.
Celsius Scale vs. Other Temperature Scales: Fahrenheit and Kelvin
The Celsius scale is not the only temperature scale in use. Other prominent scales include Fahrenheit and Kelvin. Understanding the relationship between these scales aids in appreciating the unique characteristics of the Celsius system.
Celsius and Fahrenheit: A Comparison
The Fahrenheit scale, still used in the United States and a few other countries, uses different reference points. The freezing point of water is 32°F, and the boiling point is 212°F. The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is given by the following formulas:
- °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
- °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
The Fahrenheit scale's arbitrary reference points make it less intuitive and less widely adopted than the Celsius scale.
Celsius and Kelvin: An Absolute Scale
The Kelvin scale, also known as the absolute temperature scale, is a fundamental scale in thermodynamics and physics. It's based on absolute zero, the theoretical lowest possible temperature where all molecular motion ceases. Absolute zero is 0 K, which corresponds to -273.15°C.
The relationship between Celsius and Kelvin is simple:
- K = °C + 273.15
- °C = K - 273.15
The Kelvin scale is preferred in scientific research because it provides a more fundamental and consistent basis for understanding thermal phenomena.
Applications of the Celsius Scale: A Ubiquitous System
The Celsius scale's widespread adoption stems from its simplicity, ease of use, and clear relationship to the properties of water. It finds applications in countless areas:
Everyday Life: Weather, Cooking, and More
From daily weather reports to cooking recipes, the Celsius scale is deeply ingrained in our everyday lives. Its intuitive nature makes it readily accessible to the general public.
Scientific Research: A Crucial Tool in Diverse Fields
The Celsius scale plays a crucial role in various scientific disciplines. Chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering all rely heavily on accurate temperature measurements using the Celsius scale or its derivative, the Kelvin scale.
Medicine and Healthcare: Monitoring Body Temperature and More
In medicine, the Celsius scale is essential for monitoring body temperature, diagnosing illnesses, and ensuring patient safety. Accurate temperature readings are vital for effective medical treatment.
Industrial Processes: Maintaining Optimal Temperatures
Many industrial processes require precise temperature control. From manufacturing to food processing, maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial for product quality and safety. The Celsius scale provides a standard for these processes.
Climate Science and Meteorology: Tracking Global Temperatures
Climate science relies on accurate temperature measurements to understand climate change and its impacts. The Celsius scale is essential for tracking global temperature trends and analyzing climate patterns.
The Ongoing Relevance of the Celsius Scale
Despite the existence of other temperature scales, the Celsius scale remains a cornerstone of temperature measurement. Its direct connection to the properties of water, a ubiquitous substance, ensures its continued relevance and widespread use. Its simplicity and familiarity make it accessible for everyday use, while its precise definitions in the context of the International Temperature Scale of 1990 ensure its continued accuracy and reliability in scientific and industrial applications.
The Celsius scale's legacy extends beyond its practical applications; it represents a landmark achievement in the history of science, showcasing the power of observation, experimentation, and standardization in advancing our understanding of the physical world. Its enduring popularity and continued use testify to its enduring importance in science, technology, and everyday life. As long as water remains a fundamental substance on our planet, the Celsius scale will remain a crucial tool for understanding and interacting with the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 Main Parts Of A Nucleotide
May 09, 2025
-
Why Is Blood Considered To Be A Connective Tissue
May 09, 2025
-
Name For A Group Of Penguins
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 1 Billion X 1 Trillion
May 09, 2025
-
Vinegar Is An Acid Or Base
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Celsius Scale Based On . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.