What Is The Atomic Mass Of Magnesium
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
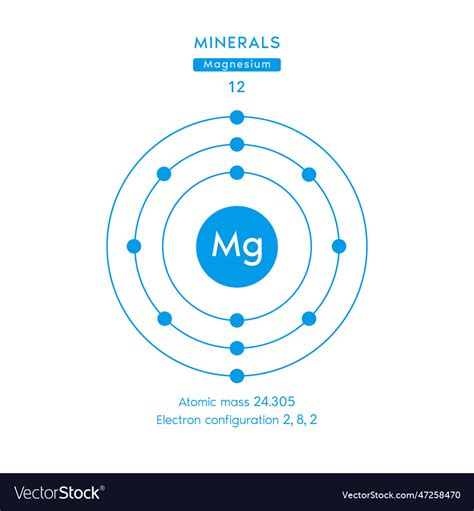
Table of Contents
What is the Atomic Mass of Magnesium? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Average Atomic Weight
Magnesium, a vital element for life and a cornerstone of many industrial processes, has an atomic mass that's more nuanced than a simple number. Understanding magnesium's atomic mass requires delving into the concept of isotopes and how average atomic weight is calculated. This article will provide a comprehensive overview, explaining the intricacies of magnesium's isotopic composition and its impact on the reported atomic mass.
Understanding Atomic Mass and Isotopes
Before we delve into the specifics of magnesium, let's establish a clear understanding of fundamental concepts. Atomic mass, also known as atomic weight, refers to the mass of an atom. It's typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu), where 1 amu is defined as one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Crucially, this isn't a single, fixed value for most elements, including magnesium.
This variability stems from the existence of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons (defining the element) but different numbers of neutrons. Since neutrons contribute to the mass of an atom, isotopes of the same element have different atomic masses.
For example, consider carbon. The most common isotope is carbon-12 (¹²C), with 6 protons and 6 neutrons. However, carbon also exists as carbon-13 (¹³C), with 6 protons and 7 neutrons, and carbon-14 (¹⁴C), with 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Each of these isotopes has a different atomic mass.
Magnesium's Isotopic Composition: The Key to its Atomic Mass
Magnesium (Mg), with atomic number 12 (meaning 12 protons), has three naturally occurring isotopes:
- Magnesium-24 (²⁴Mg): This is the most abundant isotope, comprising approximately 78.99% of naturally occurring magnesium. It has 12 protons and 12 neutrons.
- Magnesium-25 (²⁵Mg): This isotope constitutes about 10% of naturally occurring magnesium. It possesses 12 protons and 13 neutrons.
- Magnesium-26 (²⁶Mg): The least abundant of the three, ²⁶Mg makes up roughly 11.01% of naturally occurring magnesium. It contains 12 protons and 14 neutrons.
These three isotopes, with their varying abundances, determine the average atomic weight of magnesium found in nature.
Calculating Magnesium's Average Atomic Weight
The average atomic weight of an element is a weighted average of the atomic masses of its isotopes, taking into account their relative abundances. For magnesium, this calculation is as follows:
(Abundance of ²⁴Mg × Atomic mass of ²⁴Mg) + (Abundance of ²⁵Mg × Atomic mass of ²⁵Mg) + (Abundance of ²⁶Mg × Atomic mass of ²⁶Mg)
Using the approximate values:
(0.7899 × 23.985 amu) + (0.1000 × 24.986 amu) + (0.1101 × 25.983 amu) ≈ 24.305 amu
Therefore, the average atomic mass of magnesium is approximately 24.305 amu. This value is what you'll find listed on the periodic table. It's important to note that slight variations may occur due to differences in isotopic ratios found in different geological locations. However, 24.305 amu represents a highly accurate average based on extensive measurements.
The Significance of Magnesium's Atomic Mass
The average atomic mass of magnesium is not merely an abstract number; it has practical implications across various fields:
- Chemistry: In chemical calculations, using the average atomic mass allows chemists to accurately determine the amount of magnesium in a compound or reaction. Knowing the average mass simplifies stoichiometric calculations.
- Material Science: The atomic mass influences the properties of magnesium-based materials. Understanding the isotopic composition can help tailor materials with specific characteristics for different applications, like lightweight alloys in aerospace or biomedical implants.
- Nuclear Physics: Isotopes of magnesium are used in various nuclear research applications, allowing scientists to study nuclear reactions and decay processes. The differing masses of the isotopes are crucial in these experiments.
- Geochemistry: The isotopic ratios of magnesium in rocks and minerals can provide valuable insights into geological processes, including the formation and age of rocks. Variations in magnesium isotopic abundance can trace geological events over millions of years.
- Biology: Magnesium plays a crucial role in many biological processes. Understanding its atomic mass and isotopic composition is important in studying its metabolism and function in living organisms.
Beyond the Average: Isotopic Variations and Applications
While the average atomic mass of magnesium is useful for many calculations, it's important to recognize that the actual isotopic composition can vary slightly depending on the source of the magnesium. These variations, though small, can have significant implications in specialized applications:
- Isotope Geochemistry: Studying the subtle variations in magnesium isotopic ratios allows geologists to trace the origin and movement of materials in the Earth's systems. This has applications in understanding mantle processes, oceanic circulation, and the formation of ore deposits.
- Cosmochemistry: Isotopic ratios of magnesium in meteorites can provide insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. Differences in magnesium isotopic compositions compared to Earth's can reveal clues about the early history of the solar system.
- Environmental Science: Magnesium isotopes can be used as tracers in environmental studies to track pollution sources, understand nutrient cycling, and assess the impact of environmental changes.
Conclusion: Understanding Magnesium's Atomic Mass in Context
The atomic mass of magnesium, while seemingly a simple number (approximately 24.305 amu), is a complex reflection of its isotopic composition and abundance. Understanding this nuanced aspect of magnesium is crucial in a variety of scientific and industrial fields. From stoichiometric calculations in chemistry to tracing geological processes in geochemistry, the average atomic mass and the individual isotopic masses are essential tools for researchers and practitioners alike. The ability to precisely measure and interpret magnesium's isotopic ratios opens up a world of opportunities for further discoveries and applications across diverse scientific disciplines. The seemingly simple question, "What is the atomic mass of magnesium?" ultimately leads to a deep exploration of the fundamental nature of matter and its profound implications in our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm For 5 And 7
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between A Democracy And A Monarchy
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 18 And 45
Apr 06, 2025
-
The Smallest Particle Of An Element Is An
Apr 06, 2025
-
Is Good Conductor Of Heat A Physical Or Chemical Property
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Atomic Mass Of Magnesium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
