What Is Prime Factorization Of 18
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
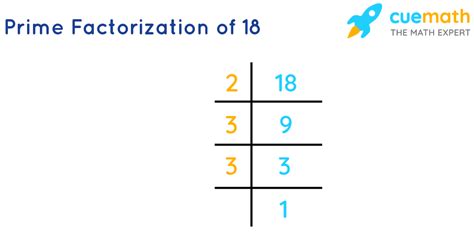
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 18? A Deep Dive into the Fundamentals of Number Theory
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. Understanding this concept unlocks a wealth of mathematical applications, from cryptography to simplifying complex calculations. Let's delve into the fascinating world of prime factorization, using the number 18 as our illustrative example.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Composite Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 18, it's crucial to understand the definitions of prime and composite numbers.
-
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Note that 1 is neither prime nor composite.
-
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Essentially, it can be factored into smaller positive integers. Examples include 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 9 (3 x 3), and 18 (which we'll be focusing on!).
Finding the Prime Factorization of 18: Methods and Steps
There are several ways to find the prime factorization of a number. Let's explore two common approaches:
1. The Factor Tree Method
This visual method is particularly helpful for beginners. We start by finding any two factors of 18 and branch them off. We continue factoring until we reach only prime numbers.
18
/ \
2 9
/ \
3 3
Following the branches down, we see that the prime factorization of 18 is 2 x 3 x 3, or 2 x 3².
2. The Division Method
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until the quotient becomes 1.
- Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 18 divided by 2 is 9.
- Continue with the next prime number: 9 is not divisible by 2, so we move to the next prime number, 3. 9 divided by 3 is 3.
- Repeat: 3 is a prime number, so we stop.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 18 is 2 x 3 x 3, or 2 x 3².
The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
A fundamental concept in number theory is the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This means that no matter which method you use to find the prime factorization of 18, you will always arrive at the same result: 2 x 3². This uniqueness is crucial in many areas of mathematics.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple concept of prime factorization has far-reaching applications across various mathematical fields and beyond. Here are a few examples:
1. Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Prime factorization is an efficient way to determine the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of both numbers.
Let's find the GCD and LCM of 18 and 24 using prime factorization:
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 x 3²
- Prime factorization of 24: 2³ x 3
GCD: We identify the common prime factors and take the lowest power of each. In this case, the common prime factor is 2 (with the lowest power of 1) and 3 (with the lowest power of 1). Therefore, GCD(18, 24) = 2 x 3 = 6.
LCM: We identify all the prime factors from both numbers and take the highest power of each. The prime factors are 2 and 3. The highest power of 2 is 2³ and the highest power of 3 is 3². Therefore, LCM(18, 24) = 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9 = 72.
2. Cryptography
Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors. The security of these systems rests on the fact that while it's relatively easy to multiply two large prime numbers, factoring their product is computationally extremely challenging.
3. Simplifying Fractions
Prime factorization simplifies fraction reduction. By factoring the numerator and denominator into their prime factors, we can easily cancel out common factors to obtain the simplest form of the fraction.
For example, to simplify the fraction 18/24:
- 18 = 2 x 3²
- 24 = 2³ x 3
18/24 = (2 x 3²) / (2³ x 3) = 3/4 (after canceling out common factors)
4. Solving Diophantine Equations
Prime factorization is also used in solving Diophantine equations, which are equations where only integer solutions are sought.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts Related to Prime Factorization
While finding the prime factorization of 18 is a relatively straightforward task, the field of number theory extends far beyond this basic concept. Here are some advanced concepts related to prime factorization:
-
The distribution of prime numbers: The Prime Number Theorem provides an approximation for the number of primes less than a given number. Understanding this distribution is crucial in various mathematical fields.
-
Mersenne primes: These are prime numbers of the form 2<sup>p</sup> - 1, where p is also a prime number. Finding Mersenne primes is an active area of research.
-
Twin primes: These are pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13). The Twin Prime Conjecture proposes that there are infinitely many twin prime pairs, but this remains unproven.
-
Goldbach's conjecture: This conjecture states that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two primes. Despite extensive testing, this conjecture remains unproven.
-
The Riemann Hypothesis: This is one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics. It deals with the distribution of prime numbers and has profound implications for our understanding of numbers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 18, seemingly a simple problem, serves as a gateway to understanding the profound concepts of number theory. From its applications in cryptography to its role in simplifying fractions and solving complex equations, prime factorization remains a fundamental tool in mathematics. The exploration of prime numbers and their properties continues to fascinate mathematicians and drive research in number theory, highlighting the enduring significance of this seemingly simple concept. Understanding prime factorization provides a solid foundation for further exploration into the rich and complex world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Do I Multiply To Get 150
Mar 06, 2025
-
Red And White Blood Cells In Fluid Matrix
Mar 06, 2025
-
Conversion Of 37 Degrees Celsius To Fahrenheit
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Has A Rhombus
Mar 06, 2025
-
Two Equal Sides Of A Triangle
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 18 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
