What Is Prime Factorization Of 132
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
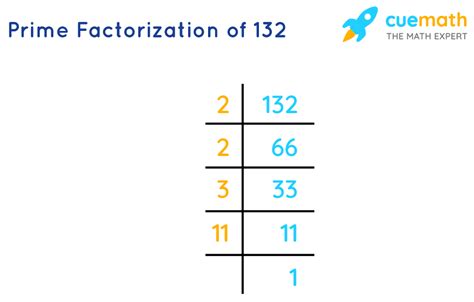
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 132? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching applications in cryptography, computer science, and other fields. It simply means expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This article will explore the prime factorization of 132, explaining the process step-by-step and then delving into the broader significance of prime factorization in mathematics.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Composite Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 132, let's clarify some key terms.
-
Prime Number: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other numbers.
-
Composite Number: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. In other words, it's a number that can be factored into smaller positive integers. For example, 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), and 12 (2 x 2 x 3) are composite numbers.
-
Prime Factorization: This is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This representation is unique for every composite number (excluding the order of the factors).
Finding the Prime Factorization of 132
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 132. We'll use a method known as the factor tree.
-
Find the smallest prime factor: The smallest prime number is 2. Since 132 is an even number, it's divisible by 2. Divide 132 by 2: 132 ÷ 2 = 66.
-
Continue factoring: Now we have 132 = 2 x 66. 66 is also an even number, so it's divisible by 2. Divide 66 by 2: 66 ÷ 2 = 33.
-
Identify the next prime factor: We now have 132 = 2 x 2 x 33. 33 is not divisible by 2. Let's try the next prime number, 3. 33 is divisible by 3: 33 ÷ 3 = 11.
-
The final prime factor: We now have 132 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 11. 11 is a prime number. We've reached the end of our factorization.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 132 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 11, or 2² x 3 x 11. This means that 132 can only be expressed as the product of these prime numbers.
Visual Representation (Factor Tree):
132
/ \
2 66
/ \
2 33
/ \
3 11
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has significant applications across various fields:
1. Cryptography
Prime factorization is the cornerstone of many modern encryption systems, particularly RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman). RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components. The security of the system depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring these large numbers in a reasonable timeframe. Breaking RSA encryption would require finding the prime factors of a massive composite number, a task that even the most powerful computers struggle with for sufficiently large numbers.
2. Computer Science
Prime factorization algorithms are used in various computer science applications, including:
-
Hashing: Prime numbers are often used in hash table algorithms to minimize collisions and improve efficiency.
-
Random Number Generation: Prime numbers play a role in generating pseudo-random numbers, ensuring a more even distribution and improved randomness.
-
Error Detection and Correction: Prime numbers are utilized in some error detection and correction codes, helping to ensure data integrity during transmission.
3. Number Theory
Prime factorization is central to many areas of number theory, including:
-
Modular Arithmetic: Prime numbers are essential in modular arithmetic, which is used in cryptography and other areas.
-
Diophantine Equations: Prime factorization can be used to solve certain types of Diophantine equations, which involve finding integer solutions to polynomial equations.
4. Other Applications
Beyond cryptography and computer science, prime factorization finds applications in various other areas such as:
-
Data Compression: Understanding the factors of a number can assist in data compression techniques.
-
Scientific Computing: Certain algorithms in scientific computing leverage properties of prime numbers.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The prime factorization of 132 illustrates a crucial theorem in number theory: the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, ignoring the order of the factors. This uniqueness is vital; it guarantees that there's only one correct prime factorization for any given number. This principle is fundamental to much of higher-level mathematics.
Methods for Prime Factorization
While the factor tree is a visually intuitive method for smaller numbers like 132, more sophisticated algorithms are needed for larger numbers. Some prominent algorithms include:
-
Trial Division: This is a straightforward method that involves testing divisibility by successive prime numbers. It's efficient for smaller numbers but becomes computationally expensive for larger ones.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It's useful for generating a list of primes to be used in other factorization methods.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: This is a probabilistic algorithm that's particularly effective for finding small prime factors.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): This is currently the most efficient algorithm known for factoring very large numbers. It's used for factoring numbers with hundreds of digits, often encountered in cryptography.
Conclusion
The prime factorization of 132, while seemingly simple, offers a glimpse into a profound area of mathematics. Understanding this concept provides the foundation for comprehending more complex mathematical ideas and its applications across diverse fields, most notably in the realm of cryptography where its security relies on the difficulty of prime factorization of extremely large numbers. The seemingly straightforward process of breaking down a number into its prime factors reveals a rich landscape of mathematical intricacies and computational challenges. The continued research and development of more efficient prime factorization algorithms remains a crucial area of study in computer science and mathematics, particularly in the context of enhancing the security of cryptographic systems. As technology continues to advance, the quest for faster and more efficient factorization algorithms remains an exciting and ongoing challenge.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 15 And 20
May 09, 2025
-
5 Letter Words Beginning With Ps
May 09, 2025
-
How Do You Write 3 5 As A Percentage
May 09, 2025
-
What Happens When Light Goes Through A Prism
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Importance Of The Start And Stop Codons
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 132 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.