What Is Difference Between Ac Motor And Dc Motor
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
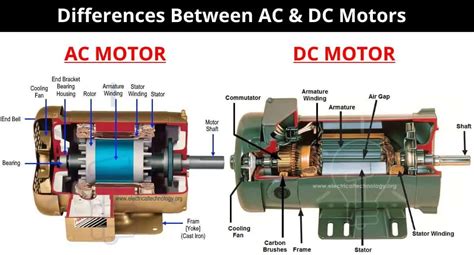
Table of Contents
AC Motor vs. DC Motor: A Comprehensive Comparison
The world of electric motors is vast, encompassing a wide range of technologies designed for diverse applications. Two dominant players in this field are AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) motors. While both convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, their underlying principles, characteristics, and applications differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate motor for a specific task. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core distinctions between AC and DC motors, examining their functionalities, advantages, disadvantages, and typical use cases.
Fundamental Differences: AC vs. DC Power Supply
The most fundamental distinction lies in the type of electrical power they utilize:
-
DC Motors: Operate on direct current, characterized by a constant flow of electrons in one direction. This constant flow produces a consistent magnetic field, simplifying the motor's design and control.
-
AC Motors: Run on alternating current, where the direction of electron flow periodically reverses. This alternating current generates a fluctuating magnetic field, requiring a more complex design to efficiently convert this fluctuating energy into rotational motion.
This seemingly simple difference cascades into numerous other distinctions in their construction, performance, and applications.
Construction and Working Principles
The internal workings of AC and DC motors significantly differ, reflecting the different nature of the power they use:
DC Motor Construction and Operation
DC motors typically employ a commutator and brushes. The commutator is a segmented cylindrical component that reverses the current direction in the motor's armature (rotating part) as it spins. Brushes, typically made of carbon, make contact with the commutator, delivering the current. The interaction between the magnetic field generated by the stator (stationary part) and the armature's electromagnets creates torque, leading to rotation.
There are different types of DC motors, including:
-
Brushed DC Motors: These are the simplest and most common type, using brushes and a commutator. They are relatively inexpensive but have limitations in speed control and longevity due to brush wear.
-
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): These motors eliminate the brushes and commutator, replacing them with electronic commutation. This results in higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and smoother operation, but they are generally more complex and expensive.
AC Motor Construction and Operation
AC motors are significantly more diverse than DC motors. The lack of a commutator necessitates different methods for creating the rotating magnetic field. Common types include:
-
Induction Motors (Asynchronous Motors): These are the most prevalent type of AC motor. They utilize a rotating magnetic field in the stator to induce current in the rotor (rotating part), creating torque. Induction motors are robust, simple, and require minimal maintenance. They are widely used in industrial applications and household appliances.
-
Synchronous Motors: In these motors, the rotor's speed is synchronized with the frequency of the AC power supply. Synchronous motors offer precise speed control and high efficiency, particularly at constant loads. They're often used in applications demanding accurate speed regulation, such as clocks and timing devices.
-
Single-Phase AC Motors: These are designed to operate on single-phase AC power, commonly found in households. They're often used in smaller appliances and tools.
-
Three-Phase AC Motors: These use three-phase AC power, providing higher power output and smoother operation than single-phase motors. They're prevalent in industrial settings for larger machinery and equipment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AC and DC Motors
Each motor type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
DC Motor Advantages:
- Precise speed control: DC motors offer excellent speed control capabilities, easily adjustable over a wide range.
- High starting torque: They can produce high torque at low speeds, suitable for applications requiring immediate starting power.
- Simple control circuitry (Brushed): Brushed DC motors are relatively simple to control, requiring less complex circuitry.
DC Motor Disadvantages:
- Maintenance (Brushed): Brushed DC motors require regular maintenance due to brush wear.
- Commutator problems: The commutator can experience sparking and wear, reducing efficiency and lifespan.
- Speed limitations: Speed can be limited due to the mechanical limitations of the commutator.
AC Motor Advantages:
- Low maintenance (Induction): Induction motors are highly reliable and require minimal maintenance, with no brushes or commutator.
- High efficiency (Induction and Synchronous): AC motors, particularly induction and synchronous types, generally boast high efficiency ratings.
- Rugged construction: They are typically robust and capable of withstanding harsh operating conditions.
- Cost-effective (Induction): Induction motors are generally less expensive than comparable DC motors.
AC Motor Disadvantages:
- Complex control circuitry (for precise speed): Achieving precise speed control in AC motors can require more complex control systems.
- Lower starting torque (compared to some DC motors): Some AC motors, especially induction motors, may have lower starting torque compared to certain DC motors.
- Less precise speed control (Induction): While speed control is achievable, it is generally less precise than in DC motors, particularly with induction motors.
Applications of AC and DC Motors
The choice between an AC or DC motor depends heavily on the specific application requirements:
DC Motor Applications:
- Electric vehicles: DC motors, particularly brushless DC motors, are increasingly prevalent in electric vehicles due to their precise speed control and high torque.
- Robotics: The ability to precisely control speed and torque makes DC motors ideal for robotic applications.
- Industrial automation: DC servo motors provide precise positioning and control in automated systems.
- Power tools: Smaller DC motors power many portable power tools.
- Computer peripherals: Many computer peripherals use small DC motors.
AC Motor Applications:
- Industrial machinery: AC induction motors are ubiquitous in industrial settings due to their robustness, efficiency, and low maintenance. They power large machinery like pumps, conveyors, and compressors.
- Household appliances: Many household appliances, including refrigerators, washing machines, and fans, utilize AC motors.
- HVAC systems: AC motors are crucial components in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Electric trains and locomotives: Large three-phase AC motors power many electric trains and locomotives.
Choosing the Right Motor: A Summary of Key Considerations
The selection between an AC and DC motor depends on several factors:
- Power requirements: The required power output directly influences the choice. High-power applications often favor AC motors, while smaller applications may use DC motors.
- Speed control needs: Applications demanding precise speed control generally benefit from DC motors, particularly BLDC motors.
- Maintenance requirements: Low-maintenance requirements point towards AC induction motors.
- Cost considerations: AC induction motors are typically more cost-effective, while DC servo motors can be more expensive.
- Operating environment: The harshness of the operating environment can also influence the choice, with robust AC motors preferred in demanding conditions.
- Efficiency needs: High-efficiency applications may favor synchronous AC motors or brushless DC motors.
Future Trends in AC and DC Motor Technology
The field of electric motors is constantly evolving. Several trends are shaping the future of AC and DC motor technology:
- Increased efficiency: Ongoing research focuses on improving the efficiency of both AC and DC motors to reduce energy consumption.
- Improved control systems: Advancements in control electronics are leading to more precise and efficient motor control.
- Miniaturization: The demand for smaller and more compact motors is driving innovation in miniaturization techniques.
- Integration with renewable energy sources: Motors are increasingly integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
- Smart motor technology: The incorporation of sensors and communication capabilities is enabling smart motors capable of self-diagnosis and predictive maintenance.
In conclusion, the choice between an AC and DC motor depends on a careful evaluation of the specific application requirements. While both play crucial roles in countless applications, their inherent differences necessitate a thoughtful selection process to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each type empowers engineers and designers to make informed decisions that drive innovation and efficiency in diverse technological fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Plants Is
Mar 18, 2025
-
Inspiratory And Expiratory Centers Are Located In The
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In 300 Yards
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Storage Form Of Glucose In Plants Is
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Chemical Name For Milk
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Difference Between Ac Motor And Dc Motor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
