What Is A Factor Of 66
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
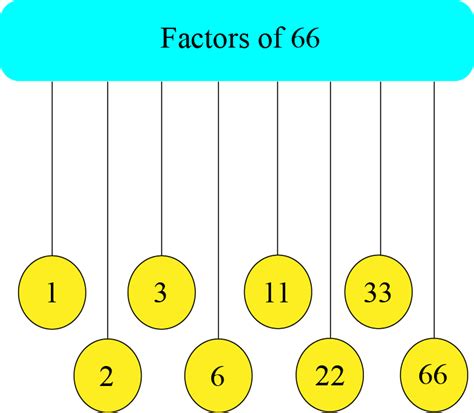
Table of Contents
What is a Factor of 66? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Understanding factors is fundamental to grasping number theory and various mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the meaning of factors, specifically focusing on the factors of 66. We'll explore different methods for finding factors, relate them to prime factorization, and touch upon their applications in various mathematical contexts. By the end, you'll have a robust understanding of what constitutes a factor of 66 and the broader implications of this concept.
Understanding Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before we pinpoint the factors of 66, let's establish a clear definition. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the given number exactly, leaving no remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by another number without getting a fraction or decimal, the second number is a factor of the first.
For instance, consider the number 12. Its factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
Key characteristics of factors:
- Always positive: Factors are always represented as positive integers.
- Pairs: Factors often come in pairs. For example, 2 and 6 are a factor pair of 12 because 2 x 6 = 12.
- 1 and the number itself: Every number has at least two factors: 1 and itself.
Finding the Factors of 66: Systematic Approaches
Now, let's systematically find the factors of 66. There are several approaches we can use:
1. The Pairwise Method:
This method involves systematically testing numbers to see if they divide 66 evenly. We start with 1 and work our way up:
- 1: 66 ÷ 1 = 66 (1 and 66 are factors)
- 2: 66 ÷ 2 = 33 (2 and 33 are factors)
- 3: 66 ÷ 3 = 22 (3 and 22 are factors)
- 6: 66 ÷ 6 = 11 (6 and 11 are factors)
- 11: 66 ÷ 11 = 6 (we've already found this pair)
We stop here because the next number to test (12) is greater than the square root of 66 (approximately 8.12). Once we reach a number larger than the square root, we've already identified all factor pairs.
Therefore, the factors of 66 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 22, 33, and 66.
2. Prime Factorization: A More Elegant Approach
Prime factorization is a powerful technique for finding all factors of a number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization involves expressing a number as the product of its prime factors.
Let's find the prime factorization of 66:
66 = 2 x 33 = 2 x 3 x 11
So, the prime factorization of 66 is 2 x 3 x 11. This tells us that 2, 3, and 11 are the prime factors of 66.
To find all factors, we consider all possible combinations of these prime factors:
- 2<sup>0</sup> x 3<sup>0</sup> x 11<sup>0</sup> = 1
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3<sup>0</sup> x 11<sup>0</sup> = 2
- 2<sup>0</sup> x 3<sup>1</sup> x 11<sup>0</sup> = 3
- 2<sup>0</sup> x 3<sup>0</sup> x 11<sup>1</sup> = 11
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3<sup>1</sup> x 11<sup>0</sup> = 6
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3<sup>0</sup> x 11<sup>1</sup> = 22
- 2<sup>0</sup> x 3<sup>1</sup> x 11<sup>1</sup> = 33
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3<sup>1</sup> x 11<sup>1</sup> = 66
This method confirms that the factors of 66 are indeed 1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 22, 33, and 66. Prime factorization offers a structured and efficient way to find all factors, especially for larger numbers.
The Significance of Factors in Mathematics and Beyond
Understanding factors isn't just an academic exercise; it has practical applications in various mathematical fields and beyond:
1. Number Theory:
Factors are crucial in number theory, laying the foundation for concepts like:
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The largest number that divides two or more numbers without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD is often done using the prime factorization method.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. The LCM and GCD are interconnected and have applications in simplifying fractions and solving problems involving ratios and proportions.
- Divisibility Rules: Factors help establish divisibility rules, which provide quick ways to determine whether a number is divisible by another number without performing long division. For example, a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. This is directly related to the factors of the number.
2. Algebra:
Factors play a vital role in algebraic manipulations, including:
- Factoring Polynomials: Expressing a polynomial as a product of simpler expressions. This is essential for solving equations and simplifying algebraic expressions.
- Simplifying Fractions: Factors are used to simplify fractions by canceling common factors in the numerator and denominator.
3. Real-World Applications:
Beyond pure mathematics, factors have practical applications in various fields, such as:
- Data Organization: Factors can help in organizing data into groups or arrays, especially when dealing with data structures in computer science.
- Geometry: Factors are involved in calculating areas and volumes of geometric shapes, often in the context of finding divisors of lengths, widths, and heights.
- Scheduling and Logistics: Factors are useful in planning activities that require repetition or cycles, like scheduling work shifts or coordinating transportation routes.
Exploring the Factors of 66: A Deeper Look
Let's delve deeper into the specific factors of 66 and their properties:
- 1 and 66: These are the trivial factors, present in every number.
- 2 and 33: Illustrate that 66 is an even number, divisible by 2.
- 3 and 22: Show that 66 is divisible by 3, and hence the sum of its digits (6+6=12) is divisible by 3.
- 6 and 11: This factor pair highlights the composite nature of 66. It's built from smaller composite factors as well as prime factors.
By examining these factor pairs, we can gain a deeper understanding of the number 66's composition and its relationships with other numbers. This understanding is crucial in various mathematical contexts and demonstrates the practical application of factor analysis.
Conclusion: The Importance of Factorization
Understanding what constitutes a factor of 66, and the broader concept of factors in general, is fundamental to many areas of mathematics. The methods for finding factors, especially prime factorization, offer powerful tools for solving various mathematical problems and exploring number properties. This knowledge extends beyond theoretical mathematics into practical applications across diverse fields, highlighting the significance of factorization in both academic and real-world scenarios. The seemingly simple question, "What is a factor of 66?" opens a door to a rich and rewarding exploration of the world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Are Compounds
May 09, 2025
-
Which Statement About Dna Replication Is Correct
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Vertical Column In The Periodic Table Called
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Communicable Disease And Non Communicable Disease
May 09, 2025
-
The Energy Required To Start A Chemical Reaction Is Called
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Factor Of 66 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.