What Is 35 In Roman Numerals
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 4 min read
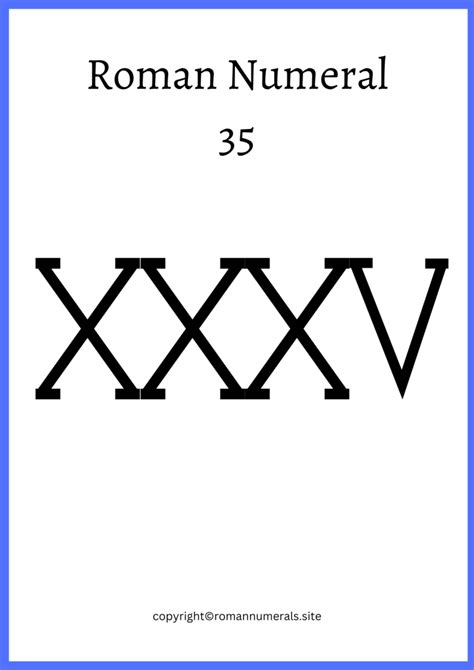
Table of Contents
What is 35 in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeration
The question, "What is 35 in Roman numerals?" seems simple at first glance. A quick search might give you the answer: XXXV. But let's go beyond the simple answer and explore the fascinating world of Roman numerals, delving into their history, structure, and the logic behind representing numbers like 35. This comprehensive guide will not only answer your initial question but equip you with a deeper understanding of this ancient numerical system.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation originating in ancient Rome, are still used today, albeit less frequently than the Hindu-Arabic numeral system we commonly use. They rely on a combination of seven letters from the Latin alphabet to represent various values:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
The system’s ingenuity lies in its additive and subtractive principles. Numbers are formed by combining these symbols, adding their values when placed in descending order and subtracting when a smaller value precedes a larger one.
Additive Principle: Adding Values
The additive principle is straightforward. To express a number, you simply add the values of the individual symbols. For example:
- XII = 10 + 1 + 1 = 12
- XXVI = 10 + 10 + 5 + 1 = 26
- LXXXVIII = 50 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 5 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 88
Subtractive Principle: Subtracting Values
The subtractive principle introduces a level of complexity and elegance. Specific combinations of symbols indicate subtraction rather than addition. The key subtractive pairs are:
- IV = 4 (5 - 1)
- IX = 9 (10 - 1)
- XL = 40 (50 - 10)
- XC = 90 (100 - 10)
- CD = 400 (500 - 100)
- CM = 900 (1000 - 100)
This subtractive principle avoids the cumbersome repetition of symbols necessary in purely additive systems. For instance, instead of writing IIII for 4, the more concise IV is used.
Deconstructing 35 in Roman Numerals: XXXV
Now, let's break down the representation of 35 in Roman numerals: XXXV.
This numeral uses both the additive and the implied additive principles:
- XXX represents 30 (10 + 10 + 10). This is a straightforward additive representation.
- V represents 5.
Therefore, XXXV = 30 + 5 = 35.
The Roman numeral system's efficiency shines in this example. Using only four symbols, it clearly and concisely represents the number 35.
Beyond 35: Exploring Larger and Smaller Numbers in Roman Numerals
While 35 is a relatively small number, the Roman numeral system can represent significantly larger values. By combining the basic symbols and applying both additive and subtractive principles, you can express numbers well into the thousands and beyond. Consider these examples:
- 1999 (MCMXCIX): 1000 (M) + 900 (CM) + 90 (XC) + 9 (IX)
- 2023 (MMXXIII): 1000 (M) + 1000 (M) + 10 (XX) + 10 (X) + 1 (I) + 1(I) + 1 (I)
- 3498 (MMMCDXCVIII): 3000 (MMM) + 400 (CD) + 90 (XC) + 90 (XC) + 8 (VIII)
Limitations of the Roman Numeral System
While elegant in its simplicity for smaller numbers, the Roman numeral system possesses several limitations compared to the Hindu-Arabic system:
- Lack of a zero: Roman numerals do not have a symbol for zero. This absence significantly impacts mathematical operations like multiplication and division.
- Cumbersome for large numbers: Representing very large numbers becomes lengthy and unwieldy. Imagine writing out 1,000,000 in Roman numerals!
- Ambiguity in certain cases: Although generally unambiguous, in rare instances, the order of numerals could lead to slight confusion if the rules are not strictly followed.
- No place value system: The system does not incorporate a place value system, unlike the Hindu-Arabic system, making complex calculations more difficult.
The Historical Significance and Modern Relevance of Roman Numerals
Despite its limitations, the Roman numeral system holds significant historical importance, serving as a cornerstone of Roman civilization's record-keeping, engineering, and cultural practices. Inscriptions on buildings, coins, and various artifacts showcase the system's longevity and influence.
Even today, Roman numerals persist in certain contexts:
- Clock faces: Many clocks still display Roman numerals for the hours.
- Outlines and numbering: Outlines and lists often use Roman numerals for major points or sections.
- Copyright dates: Sometimes copyright dates appear in Roman numerals.
- Book chapters: Roman numerals might still be seen as chapter markers in some books.
- Monarchs' regnal numbers: Ruling monarchs are frequently numbered using Roman numerals (e.g., King George VI).
Conclusion: Appreciating the Elegance of XXXV and the Roman Numeral System
The answer to "What is 35 in Roman numerals?" is definitively XXXV. However, this seemingly simple question has opened a door to a much richer understanding of this ancient and surprisingly enduring numerical system. While the Roman numeral system may lack the efficiency and versatility of our modern system, it offers a glimpse into the mathematical thinking of a bygone era and maintains its charm and relevance in various applications today. Its enduring presence serves as a testament to its inherent elegance and historical significance. Understanding its structure and limitations allows us to appreciate both its historical context and its continued presence in our modern world. The enduring legacy of XXXV and its brethren continues to captivate and intrigue, reminding us of the rich history behind the numbers we use daily.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Draw A Quadrilateral That Is Not A Rhombus
May 09, 2025
-
The Cellular Organelle Responsible For Protein Synthesis Is
May 09, 2025
-
Calculate Area Of A Scalene Triangle
May 09, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 484
May 09, 2025
-
Identify The Meso Isomer Of The Following Compound
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 35 In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.