What Gas Is The Most Abundant In The Atmosphere
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
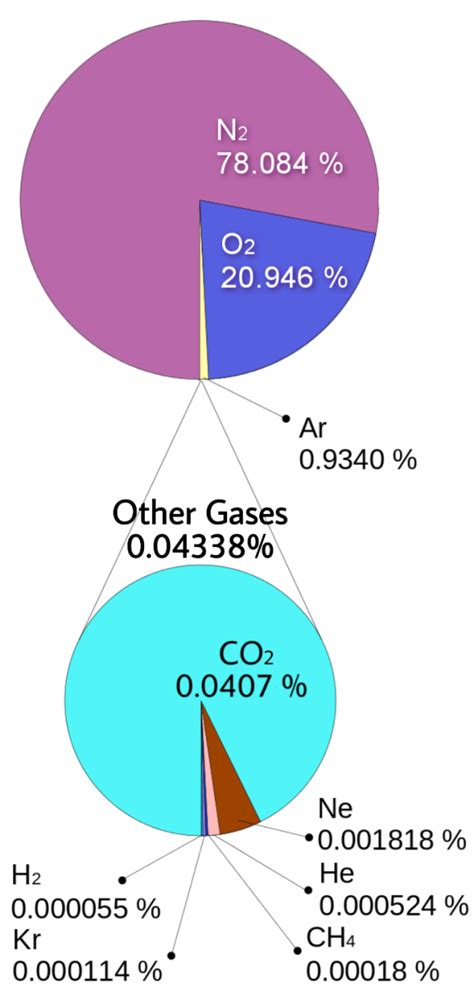
Table of Contents
What Gas Is the Most Abundent in the Atmosphere?
The Earth's atmosphere is a complex mixture of gases, each playing a vital role in shaping our planet's climate, supporting life, and influencing various atmospheric processes. Understanding the composition of this gaseous envelope is crucial for comprehending weather patterns, climate change, and the overall health of our planet. While many gases are present, one overwhelmingly dominates: nitrogen.
The Predominance of Nitrogen
Nitrogen (N<sub>2</sub>) constitutes approximately 78% of the Earth's atmosphere by volume. This makes it by far the most abundant gas. Its inert nature, meaning it doesn't readily react with other substances, is a key factor in its prevalence. While crucial for life, nitrogen in its gaseous form (diatomic nitrogen, N<sub>2</sub>) is largely unusable by most organisms directly. This inertness is both a blessing and a curse: it prevents the atmosphere from being highly reactive and unstable, yet it necessitates a complex biological process (nitrogen fixation) to make nitrogen available to plants and animals.
The Role of Nitrogen in the Atmosphere
Despite its relative inactivity, nitrogen plays several important roles:
- Atmospheric Stability: The abundance of nitrogen contributes significantly to the stability of the atmosphere. Its inertness prevents rapid chemical reactions that could disrupt atmospheric balance.
- Dilution of Reactive Gases: Nitrogen acts as a diluent, reducing the concentration of more reactive gases like oxygen. This helps to moderate the intensity of combustion and other chemical processes.
- Component of the Nitrogen Cycle: While inert in its gaseous form, nitrogen is a fundamental building block of life. Through biological processes (nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, and ammonification), nitrogen cycles through various forms, making it available to plants and ultimately, the entire food chain.
- Influence on Climate: While not a direct greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide or methane, nitrogen oxides (NOx) formed through combustion processes and other human activities contribute to the formation of smog and ozone, impacting air quality and indirectly contributing to climate change.
Oxygen: The Second Most Abundant Gas
Coming in a distant second is oxygen (O<sub>2</sub>), accounting for roughly 21% of the Earth's atmosphere. Unlike nitrogen, oxygen is highly reactive and essential for respiration in most living organisms. It plays a crucial role in combustion and other oxidation processes.
The Importance of Oxygen
- Respiration: Oxygen is vital for aerobic respiration, the process by which most organisms extract energy from food.
- Combustion: Oxygen supports combustion, a process that releases energy from fuels.
- Ozone Formation: Oxygen plays a critical role in the formation of the ozone layer (O<sub>3</sub>) in the stratosphere, which protects life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- Oxidation: Oxygen participates in various oxidation reactions, influencing the weathering of rocks and the decomposition of organic matter.
Argon: The Third Most Abundant Gas
Argon (Ar) makes up about 0.93% of the atmosphere. It's a noble gas, meaning it's inert and doesn't readily react with other substances. Unlike nitrogen, argon plays a less prominent role in biological processes. However, it finds applications in various industrial processes, such as welding and creating inert atmospheres.
Argon's Atmospheric Role
- Inert Atmosphere: Argon's inertness makes it valuable in applications requiring an inert environment to prevent reactions.
- Atmospheric Tracer: Argon isotopes are used in atmospheric science as tracers to study atmospheric circulation patterns.
Trace Gases and Their Significance
While nitrogen, oxygen, and argon dominate the atmospheric composition, several other gases are present in much smaller quantities, yet play significant roles in various atmospheric processes. These are often referred to as trace gases. These include:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO<sub>2</sub>): Although present in relatively small amounts (around 0.04%), carbon dioxide is a crucial greenhouse gas influencing the Earth's climate. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly increased its atmospheric concentration, leading to global warming.
- Water Vapor (H<sub>2</sub>O): The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere is highly variable depending on location and temperature. It's a powerful greenhouse gas and plays a crucial role in the water cycle and weather patterns.
- Neon (Ne), Helium (He), Methane (CH<sub>4</sub>), Krypton (Kr), Hydrogen (H<sub>2</sub>), Nitrous Oxide (N<sub>2</sub>O), Xenon (Xe), Ozone (O<sub>3</sub>): These gases, among others, are present in trace amounts but have significant impacts on the atmosphere, contributing to various chemical reactions, influencing climate, and affecting air quality. Methane, for example, is a potent greenhouse gas, while ozone in the troposphere (lower atmosphere) is a harmful pollutant.
Human Impact on Atmospheric Composition
Human activities have significantly altered the composition of the Earth's atmosphere, primarily through the emission of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. This has led to:
- Global Warming: The increased concentration of greenhouse gases traps more heat in the atmosphere, leading to a warming planet.
- Climate Change: Global warming is causing widespread changes in weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems.
- Air Pollution: Emissions from various sources contribute to air pollution, impacting human health and the environment.
Conclusion: The Ever-Changing Atmosphere
While nitrogen remains the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, the relative proportions of other gases, particularly greenhouse gases, are constantly changing due to human activities. Understanding these changes and their impacts is crucial for addressing the challenges posed by climate change and air pollution. Continued monitoring of atmospheric composition, combined with efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality, is essential for protecting the health of our planet and future generations.
Further Exploration: Delving Deeper into Atmospheric Science
This exploration of atmospheric composition only scratches the surface. For a more comprehensive understanding, further research into these topics is encouraged:
- The Nitrogen Cycle: A detailed study of the processes involved in the cycling of nitrogen through the atmosphere, biosphere, and geosphere.
- Greenhouse Effect: A deeper dive into the mechanisms of the greenhouse effect and its impact on global climate.
- Atmospheric Chemistry: An examination of the various chemical reactions occurring in the atmosphere and their effects.
- Climate Modeling: An understanding of how scientists use models to predict future climate changes.
- Air Quality Monitoring: An exploration of the methods used to monitor air quality and the effects of pollutants on human health and the environment.
By continuing to learn about the Earth's atmosphere and its complex interactions, we can better understand the challenges we face and work towards a more sustainable future. The most abundant gas, nitrogen, might be inert, but the consequences of altering the composition of our atmosphere are far from inert. This underscores the importance of continued research and responsible actions to preserve the delicate balance of our planet's gaseous envelope.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Does Reactivity Of Metals Increase
Apr 08, 2025
-
Ecology Is One Component Of Environmental Science That Studies Organismal
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Does An Equal Sign With Three Lines Mean
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Is The Arrhenius Definition Of An Acid
Apr 08, 2025
-
Features Of A Rational Graph Calculator
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Gas Is The Most Abundant In The Atmosphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.