What Does Composition Mean In Science
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
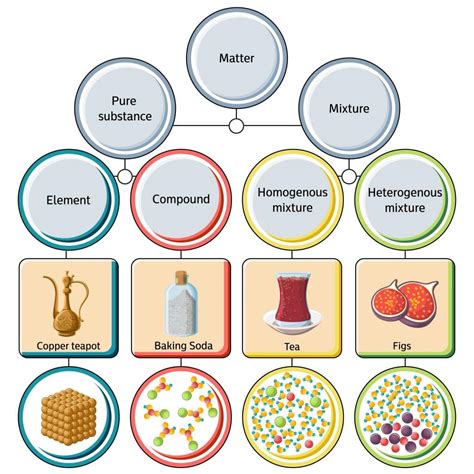
Table of Contents
What Does Composition Mean in Science? A Deep Dive
Composition, in the scientific realm, signifies far more than simply a list of ingredients. It represents a fundamental concept crucial for understanding the properties and behaviors of matter, whether it's the chemical makeup of a compound, the elemental distribution in a rock sample, or the species diversity within an ecosystem. This article delves deep into the multifaceted meaning of "composition" across various scientific disciplines, examining its applications, analytical techniques, and significance in research and practical applications.
Composition in Chemistry: Unveiling the Building Blocks of Matter
In chemistry, composition refers to the types and relative amounts of elements or compounds that constitute a substance. This is pivotal for identifying unknown substances, predicting their properties, and understanding chemical reactions. We can analyze composition on different scales:
Elemental Composition:
This delves into the types and proportions of elements present in a substance. For example, water (H₂O) has an elemental composition of two hydrogen atoms for every one oxygen atom. Determining elemental composition often involves techniques like:
-
Spectroscopy: Techniques such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyze the light emitted or absorbed by elements to determine their presence and abundance. These methods are crucial in analyzing everything from trace metals in water samples to the composition of alloys.
-
Combustion Analysis: For organic compounds, combustion analysis burns a sample in pure oxygen to determine the mass percentages of carbon, hydrogen, and other elements present. This provides critical information for determining the empirical and molecular formulas.
Molecular Composition:
This focuses on the types and relative amounts of molecules present in a sample. This is particularly relevant in organic chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. Determining molecular composition involves methods such as:
-
Chromatography: This separation technique (e.g., gas chromatography (GC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)) separates different molecules based on their properties, allowing for identification and quantification. This is vital in analyzing complex mixtures like perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and environmental pollutants.
-
Mass Spectrometry (MS): MS measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, enabling the determination of the molecular weight and structure of individual molecules. Coupled with chromatography (e.g., GC-MS, LC-MS), it's a powerful tool for identifying unknown compounds in complex mixtures.
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: NMR provides detailed information about the structure and connectivity of molecules within a sample. This is especially useful for identifying isomers and determining the 3D structure of molecules, particularly biomolecules.
Composition in Geology and Materials Science: A Look at Earth and its Materials
In geology and materials science, composition refers to the relative proportions of minerals, elements, or phases within a sample. This is essential for understanding the formation, properties, and applications of rocks, minerals, alloys, and other materials. Analyzing compositional variations helps reveal crucial information about:
Petrology and Mineralogy:
Geologists analyze the mineral composition of rocks to understand their formation, origin, and history. Techniques such as:
-
Thin Section Microscopy: Observing thin slices of rock under a microscope reveals the mineralogical composition, texture, and other features. This allows geologists to classify rocks and interpret their geological history.
-
X-ray Diffraction (XRD): XRD identifies minerals based on their crystal structure. This non-destructive technique is valuable for analyzing a wide range of materials, from clay minerals to metallic alloys.
Materials Science:
Understanding the composition of materials is crucial for designing materials with specific properties. For instance:
-
Alloy Composition: The composition of alloys determines their strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and other properties. Scientists carefully control the composition of alloys to achieve desired characteristics in various applications, from aerospace engineering to biomedical devices.
-
Polymer Composition: The composition of polymers determines their flexibility, strength, and other properties. Scientists can modify the composition of polymers to tailor their properties for specific applications, such as packaging, textiles, and medical implants.
Composition in Biology and Ecology: The Diversity of Life
In biological and ecological contexts, composition refers to the relative abundance of different species or components within a community or ecosystem. This is vital for understanding biodiversity, ecosystem function, and environmental health. Analyzing compositional changes can reveal important insights into:
Species Composition:
This refers to the types and relative abundances of species within a community or ecosystem. This is often studied using methods such as:
-
Species Surveys: Researchers directly count or estimate the abundance of species within a defined area. This involves various techniques depending on the species being studied, from visual observations to DNA-based methods.
-
Community Analysis: Analysis of species composition data, often using statistical methods like diversity indices (e.g., Shannon diversity index, Simpson diversity index), reveals the biodiversity of a community and its stability.
Community Structure and Function:
Species composition is closely linked to ecosystem function. Changes in species composition can indicate shifts in environmental conditions or human impacts. For instance:
-
Indicator Species: Certain species serve as indicators of environmental health. Changes in their abundance or distribution can signal pollution, habitat degradation, or other environmental stressors.
-
Trophic Levels and Food Webs: Species composition is crucial for understanding the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. Analyzing the species present and their interactions reveals the trophic structure and stability of the food web.
Composition in Environmental Science: Analyzing Air, Water, and Soil
Environmental science frequently involves analyzing the composition of different environmental compartments to assess their quality and potential impacts on human health and ecosystems. This encompasses:
Air Composition:
Monitoring the composition of air involves measuring the levels of various gases, including pollutants like ozone, particulate matter, and various volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This is crucial for assessing air quality and understanding the impact of air pollution on human health and the environment. Techniques often used include gas chromatography and mass spectrometry.
Water Composition:
Water composition analysis determines the levels of dissolved minerals, nutrients, pollutants, and other substances in water bodies. This is crucial for assessing water quality for drinking, irrigation, and aquatic life. Techniques like ICP-MS, ion chromatography, and various wet chemical analyses are commonly employed.
Soil Composition:
Soil composition analysis focuses on the proportions of different soil components including minerals, organic matter, water, and air. This is vital for understanding soil fertility, productivity, and suitability for various uses. Techniques like XRF, XRD, and various laboratory analyses are widely used.
Conclusion: The Broad Scope of Compositional Analysis
The term "composition" in science encompasses a wide array of disciplines and analytical techniques, always aiming to determine the relative abundance of components within a system. Whether analyzing the elements in a chemical compound, the minerals in a rock, the species in an ecosystem, or the pollutants in a water sample, understanding composition is paramount for numerous scientific endeavors. The diverse range of analytical methods available—from spectroscopy and chromatography to microscopy and DNA sequencing—highlights the sophistication and power of compositional analysis in furthering our understanding of the natural world and its materials. The continual development of new and improved techniques ensures that compositional analysis will remain a cornerstone of scientific discovery and technological innovation for years to come. Its significance spans from basic research to applied applications, making it a vital tool for problem-solving and advancing our knowledge across various scientific domains.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 19 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
May 09, 2025
-
Is Force Increase On An Inclined Plane
May 09, 2025
-
Interesting Words That Start With V
May 09, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast A Light Microscope And An Electron Microscope
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 6 25 Meters In Feet And Inches
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does Composition Mean In Science . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.