What Distinguishes An Element From A Compound
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
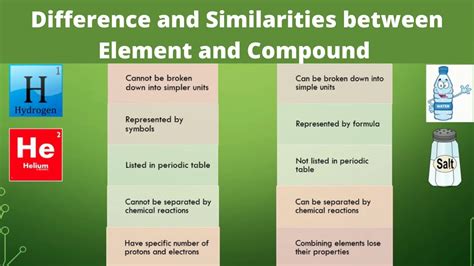
Table of Contents
What Distinguishes an Element from a Compound? A Deep Dive into Matter
The world around us is composed of matter, which exists in various forms. Understanding the fundamental building blocks of matter is crucial to grasping the complexities of chemistry and the physical world. At the heart of this understanding lies the distinction between elements and compounds. While both are forms of matter, they differ significantly in their composition, properties, and behavior. This comprehensive article will delve deep into the characteristics that set elements apart from compounds, exploring their definitions, examples, and the crucial role they play in the universe.
Defining Elements: The Fundamental Building Blocks
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. This means that no chemical reaction can decompose an element into anything other than itself. Each element is characterized by a unique number of protons in its atomic nucleus, known as its atomic number. This atomic number dictates the element's identity and its place on the periodic table. The periodic table, a beautifully organized chart of the elements, arranges them based on their atomic number and recurring chemical properties.
Key Characteristics of Elements:
- Pure Substance: Elements consist of only one type of atom. All atoms within an element possess the same number of protons.
- Indivisible by Chemical Means: They cannot be broken down into simpler substances through ordinary chemical processes like heating, cooling, or reacting with other substances. Nuclear reactions, however, can alter the element.
- Unique Properties: Each element possesses distinct physical and chemical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, density, reactivity, and conductivity. These properties are directly related to the element's atomic structure.
- Represented by Symbols: Elements are represented by unique one- or two-letter symbols, such as H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, and Fe for iron. These symbols are internationally recognized and used in chemical formulas and equations.
Examples of Elements:
The world is teeming with elements. Some are abundant, while others are incredibly rare. A few examples include:
- Hydrogen (H): The lightest and most abundant element in the universe.
- Oxygen (O): Essential for respiration and combustion.
- Carbon (C): The backbone of organic life and a key component of many materials.
- Iron (Fe): A crucial element in human biology and widely used in industry.
- Gold (Au): A highly prized precious metal known for its inertness and malleability.
- Uranium (U): A radioactive element used in nuclear power and weaponry.
Defining Compounds: Combinations of Elements
A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. This chemical combination involves the formation of chemical bonds, which are strong attractive forces that hold atoms together. The properties of a compound are distinctly different from the properties of its constituent elements. This is a fundamental aspect that differentiates compounds from simple mixtures.
Key Characteristics of Compounds:
- Fixed Ratio of Elements: Compounds always contain the same elements in the same proportion by mass. This fixed ratio is described by the compound's chemical formula. For example, water (H₂O) always contains two hydrogen atoms for every one oxygen atom.
- Chemical Combination: Elements in a compound are chemically bonded, implying a strong interaction between their atoms. This bonding is what gives compounds their unique properties.
- Distinct Properties: The properties of a compound are different from the properties of the elements it contains. For instance, sodium (Na) is a highly reactive metal, and chlorine (Cl) is a toxic gas, but their combination forms sodium chloride (NaCl), or table salt, a relatively inert and edible compound.
- Separable by Chemical Means: Compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical processes, such as electrolysis or chemical reactions.
Examples of Compounds:
Countless compounds exist, exhibiting an astonishing range of properties and applications. Some notable examples include:
- Water (H₂O): Essential for life and a universal solvent.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): A greenhouse gas vital for plant photosynthesis.
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl): Table salt, crucial for human health and numerous industrial applications.
- Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): A simple sugar that provides energy to living organisms.
- Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄): A strong acid with widespread industrial uses.
- Ammonia (NH₃): Used in fertilizers and numerous industrial processes.
The Crucial Differences: A Comparative Analysis
The following table summarizes the key distinctions between elements and compounds:
| Feature | Element | Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | One type of atom | Two or more different elements |
| Bonding | No chemical bonds between atoms | Chemical bonds hold atoms together |
| Separation | Cannot be broken down by chemical means | Can be broken down into elements chemically |
| Properties | Unique properties | Properties different from constituent elements |
| Ratio | N/A | Fixed ratio of elements by mass and atoms |
| Examples | Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Gold (Au) | Water (H₂O), Salt (NaCl), Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) |
Beyond the Basics: Mixtures and the Importance of Purity
It's crucial to differentiate elements and compounds from mixtures. Mixtures are physical combinations of substances, where the individual components retain their own properties and are not chemically bonded. For example, salt water is a mixture of salt (NaCl) and water (H₂O). The salt dissolves in the water, but it's not chemically bound to it. The components of a mixture can be separated by physical methods, like evaporation or filtration.
The purity of a substance is also critical. Pure substances, whether elements or compounds, have a fixed and definite composition. Impurities can significantly alter the properties of a substance. The study of chemistry heavily relies on the careful preparation and analysis of pure substances to ensure accurate experimental results and reliable conclusions.
Applications and Significance
The understanding of elements and compounds is fundamental to numerous fields:
- Material Science: The properties of materials are dictated by their elemental composition and the nature of the chemical bonds formed. This knowledge enables the design and creation of novel materials with specific characteristics.
- Medicine: Understanding the role of specific elements and compounds in biological processes is crucial for developing pharmaceuticals, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic treatments.
- Environmental Science: The analysis of elements and compounds in the environment is essential for monitoring pollution, understanding ecosystem dynamics, and addressing environmental challenges.
- Industrial Chemistry: The production of countless industrial chemicals and materials relies heavily on the chemical reactions between elements and compounds.
- Energy Production: The development of new energy sources, such as batteries and fuel cells, often involves sophisticated manipulation of elements and compounds.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Scientific Understanding
The distinction between elements and compounds forms the bedrock of chemical understanding. This fundamental difference dictates the properties, behavior, and applications of matter in the world around us. By appreciating the unique characteristics of elements and the chemical combinations that form compounds, we gain a deeper insight into the intricacies of the universe and the vast potential for scientific discovery and technological advancement. The continued exploration and manipulation of elements and compounds will remain critical for addressing global challenges and driving innovation across various fields for generations to come. Further research into the behaviour of specific elements and compounds continues to unveil new and exciting possibilities in chemistry and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Temp Is Celsius And Fahrenheit The Same
Apr 08, 2025
-
Sum Of Interior Angles Of Trapezoid
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Is The Lowest Common Multiple Of 7 And 8
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Base Is Only Found In Rna
Apr 08, 2025
-
Simplify The Square Root Of 121
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Distinguishes An Element From A Compound . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.