What Are The Prime Factors Of 85
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
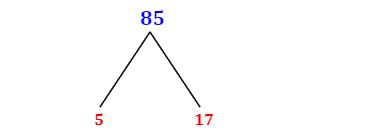
Table of Contents
What are the Prime Factors of 85? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Finding the prime factors of a number might seem like a simple mathematical exercise, but understanding the process unlocks a deeper appreciation for number theory and its applications. Let's explore the prime factorization of 85, examining the method and its significance within the broader context of mathematics.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Factorization
Before we delve into the prime factors of 85, let's establish a firm foundation by defining key terms:
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Essentially, it's a number that can be factored into smaller positive integers. Examples include 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 9 (3 x 3), and so on.
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization (or integer factorization) is the process of breaking down a composite number into its prime number components. This decomposition is unique for every composite number; that is, every composite number can be expressed as a product of primes in only one way (disregarding the order of the factors). This uniqueness is a cornerstone of number theory.
Finding the Prime Factors of 85: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's find the prime factors of 85. We can use a method called the factor tree.
-
Start with the number: Begin with the number 85.
-
Find the smallest prime factor: We need to find the smallest prime number that divides 85 evenly. We can start checking prime numbers, beginning with 2. Since 85 is an odd number, it's not divisible by 2. The next prime number is 3. 85 is not divisible by 3 (8 + 5 = 13, which is not divisible by 3). The next prime is 5. 85 is divisible by 5 (85 / 5 = 17).
-
Branching the factor tree: We now have our first prime factor: 5. We can represent this in a factor tree:
85 / \ 5 17 -
Continue the process: We are left with the number 17. 17 is also a prime number (only divisible by 1 and itself).
-
Complete Factorization: Our factor tree is complete. The prime factors of 85 are 5 and 17.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 85 is 5 x 17.
Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has far-reaching implications across various mathematical fields and applications:
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption. The security of RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime components. The larger the numbers, the more computationally intensive it becomes to find the factors, making RSA a robust encryption method.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is fundamental to number theory. It helps us understand the structure and properties of integers and aids in solving various number-theoretic problems.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization is central to concepts in abstract algebra such as unique factorization domains (UFDs) and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Understanding prime factorization is key to working with modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory that deals with remainders after division. Modular arithmetic has applications in cryptography, computer science, and other areas.
-
Simplifying Fractions: In basic arithmetic, prime factorization helps in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. By finding the prime factors of the numerator and denominator, we can cancel out common factors, resulting in a simplified fraction.
Alternative Methods for Prime Factorization
While the factor tree method is visually intuitive, especially for smaller numbers like 85, other methods exist for larger numbers:
-
Trial Division: This method systematically tests each prime number as a potential divisor. It's straightforward but can be time-consuming for very large numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This algorithm efficiently generates a list of prime numbers up to a specified limit. While not directly performing factorization, it helps identify potential prime factors to test.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: This probabilistic algorithm is more efficient than trial division for large numbers. It employs techniques based on the properties of random walks and modular arithmetic.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): GNFS is currently the most efficient algorithm for factoring very large numbers and is often employed for breaking RSA encryption when large enough numbers are used. It's a sophisticated algorithm utilizing advanced mathematical concepts.
Exploring Further: Beyond the Prime Factors of 85
While we've successfully determined the prime factors of 85 (5 and 17), understanding the broader context of prime numbers and factorization opens a world of mathematical exploration:
-
Twin Primes: These are pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13). The study of twin primes is an active area of research in number theory.
-
Goldbach's Conjecture: This unsolved conjecture proposes that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two prime numbers.
-
Riemann Hypothesis: This renowned unsolved problem in mathematics relates the distribution of prime numbers to the zeros of the Riemann zeta function. Its resolution would have profound implications for number theory and other branches of mathematics.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factors
Determining the prime factors of 85, while a seemingly basic task, serves as a gateway to the fascinating world of prime numbers and their profound influence on mathematics and its applications. From the foundational principles of number theory to the intricacies of modern cryptography, the concept of prime factorization remains central to many mathematical disciplines and continues to inspire ongoing research and development. The unique factorization theorem, which underpins this process, ensures that this seemingly simple process holds profound implications for our understanding of numbers and their relationships. The journey from understanding the prime factors of 85 to grasping the complexities of advanced algorithms and unsolved problems demonstrates the beauty and enduring power of prime numbers within the vast landscape of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Muddy Water A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Number Is A Multiple Of 6 And 8
Mar 14, 2025
-
Why Are Fossils Found Mostly In Sedimentary Rocks
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Open And Closed Circulatory Systems
Mar 14, 2025
-
10 Is A Multiple Of 5
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Prime Factors Of 85 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
