What Are The Prime Factors Of 300
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
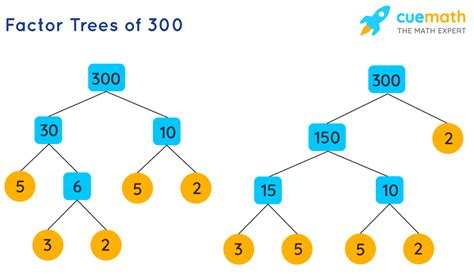
Table of Contents
What Are the Prime Factors of 300? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Finding the prime factors of a number might seem like a simple mathematical exercise, but understanding the process reveals fundamental concepts in number theory and has practical applications in various fields, from cryptography to computer science. This article delves deep into determining the prime factors of 300, explaining the methodology in detail and exploring related mathematical concepts. We’ll also explore why prime factorization is important and its broader significance.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before we tackle the prime factors of 300, let's refresh our understanding of key terms:
Prime Number: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on.
Composite Number: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Essentially, it's a number that can be factored into smaller whole numbers. Examples include 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 9 (3 x 3), and so on.
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization (or integer factorization) is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, will result in the original number. Every composite number can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This uniqueness is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Finding the Prime Factors of 300: A Step-by-Step Approach
There are several methods to find the prime factors of 300. Let's explore a common and straightforward approach:
Method 1: Successive Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible until you are left with 1.
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 300 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 300 / 2 = 150. We now have 2 as one of our prime factors.
-
Continue dividing by 2: 150 is also even, so we can divide again: 150 / 2 = 75. We now have another factor of 2.
-
Move to the next prime number, 3: 75 is divisible by 3: 75 / 3 = 25. We've found another prime factor, 3.
-
Continue with the next prime number, 5: 25 is not divisible by 3, but it is divisible by 5: 25 / 5 = 5. We have another prime factor, 5.
-
The final result: We are left with 5, which is itself a prime number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 300 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 5.
Method 2: Factor Tree
The factor tree is a visual method that helps in systematically finding the prime factors.
-
Start with 300: We begin by finding any two factors of 300. Let's use 2 and 150.
-
Branch out: We write 2 and 150 as branches from 300.
-
Continue factoring: 2 is a prime number, so we stop there. 150 is composite, so we find its factors (e.g., 2 and 75).
-
Repeat the process: Continue branching out and factoring until all the branches end in prime numbers. You’ll find the prime factors at the end of each branch.
(Visual representation of a factor tree would be included here if this were a visual medium. The tree would show 300 branching into 2 and 150; 150 branching into 2 and 75; 75 branching into 3 and 25; and 25 branching into 5 and 5. The prime factors would be clearly visible at the bottom of the tree.)
Both methods yield the same result: the prime factorization of 300 is 2² x 3 x 5².
Significance of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization isn't just an academic exercise. It has crucial applications in various fields:
1. Cryptography:
The security of many encryption algorithms relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The RSA algorithm, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, relies on this principle. The larger the numbers involved, the more computationally intensive it is to break the encryption.
2. Computer Science:
Prime factorization algorithms are used in various computer science applications, including:
- Hashing: Prime numbers are frequently used in hashing algorithms to minimize collisions.
- Random Number Generation: Prime numbers play a role in generating pseudorandom numbers.
- Data Structures: Some data structures utilize prime numbers for efficiency.
3. Number Theory:
Prime factorization is fundamental to many theorems and concepts in number theory, including:
- The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (disregarding the order of the factors).
- Modular Arithmetic: Prime numbers are crucial in understanding modular arithmetic, used extensively in cryptography and computer science.
4. Other Applications:
Prime factorization also finds applications in areas like:
- Coding Theory: Error detection and correction codes often utilize prime numbers.
- Abstract Algebra: Prime numbers are essential in various abstract algebra concepts, such as prime ideals and prime fields.
Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding prime factorization opens doors to exploring several related mathematical concepts:
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides all the numbers without leaving a remainder. Prime factorization simplifies finding the GCD. By comparing the prime factorizations of the numbers, we can easily identify the common factors and determine the GCD.
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the numbers. Again, prime factorization offers an efficient way to calculate the LCM.
Euler's Totient Function: This function counts the positive integers up to a given integer n that are relatively prime to n (i.e., they share no common factors other than 1). Prime factorization is critical in computing Euler's totient function.
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factors
The seemingly simple task of finding the prime factors of 300 – 2² x 3 x 5² – unveils a world of mathematical richness and practical applications. From securing online transactions to optimizing computer algorithms, the concept of prime factorization plays a crucial role in shaping our modern technological landscape. Mastering this fundamental concept opens doors to a deeper understanding of number theory and its far-reaching implications. While the process of finding prime factors for smaller numbers like 300 is relatively straightforward, the challenge of factoring extremely large numbers forms the basis of many modern cryptographic systems, highlighting the enduring significance of prime numbers in mathematics and computer science. Understanding prime factorization is not just about solving a mathematical puzzle; it's about appreciating the fundamental building blocks of numbers and their profound impact on various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Plants That Make Their Own Food Are Called
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 11 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 3 100 As A Decimal
Mar 17, 2025
-
Volume Of A Single Drop Of Water
Mar 17, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between A Lady And A Woman
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Prime Factors Of 300 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
