What Are The Factors Of 77
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
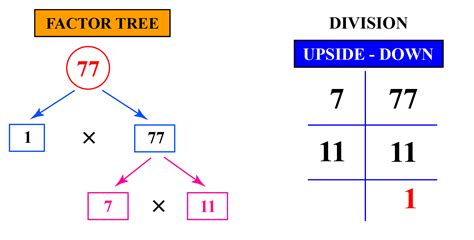
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 77? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 77?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime factorization, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, exploring this question allows us to delve into concepts that are crucial for understanding more complex mathematical principles. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the broader context of factors, prime numbers, and their significance in mathematics.
Understanding Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before we tackle the factors of 77, let's establish a clear understanding of what a factor is. A factor, also known as a divisor, is a whole number that divides another number without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by another number and get a whole number result, then the second number is a factor of the first.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly. Notice that 1 and the number itself are always factors. These are sometimes referred to as trivial factors.
Finding the Factors of 77: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's determine the factors of 77. We can systematically approach this by checking each whole number from 1 up to 77 to see if it divides 77 evenly. However, a more efficient method is to consider pairs of numbers that multiply to give 77.
- 1 and 77: 1 x 77 = 77
- 7 and 11: 7 x 11 = 77
Therefore, the factors of 77 are 1, 7, 11, and 77. These are all the whole numbers that divide 77 without leaving a remainder.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Notice that two of the factors of 77, namely 7 and 11, are prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers, as every whole number greater than 1 can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
The fact that 7 and 11 are prime numbers is crucial in understanding the factorization of 77. This leads us to the concept of prime factorization.
Prime Factorization: Deconstructing Numbers into Their Prime Components
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a whole number as a product of its prime factors. For 77, the prime factorization is simply 7 x 11. This means that 77 can be broken down into its smallest prime number components, 7 and 11, and no further prime factorization is possible.
Prime factorization is a powerful tool in various mathematical applications, including:
- Simplifying fractions: Finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers, a crucial step in simplifying fractions, often involves prime factorization.
- Solving Diophantine equations: These equations involve finding integer solutions, and prime factorization can play a critical role in determining the solutions.
- Cryptography: Prime numbers are the foundation of many modern cryptographic systems, ensuring secure data transmission.
Understanding the Uniqueness of Prime Factorization
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic guarantees that every whole number greater than 1 has a unique prime factorization. This means that no matter how you approach the factorization, you will always arrive at the same set of prime factors. This uniqueness is essential for many mathematical proofs and algorithms.
Beyond the Factors: Exploring Related Concepts
The factors of 77 provide a springboard to explore several related concepts in number theory:
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. For example, let's consider the GCD and LCM of 77 and another number, say 21.
- Prime factorization of 21: 3 x 7
- GCD(77, 21): The common prime factor is 7. Therefore, the GCD is 7.
- LCM(77, 21): The LCM includes all prime factors from both numbers, taking the highest power of each. Therefore, LCM(77, 21) = 3 x 7 x 11 = 231.
Understanding GCD and LCM is crucial in various mathematical and practical applications, from simplifying fractions to scheduling events.
Divisibility Rules: Quick Checks for Factors
Divisibility rules provide shortcuts for determining whether a number is divisible by certain factors without performing the full division. For example:
- Divisibility by 7: There isn't a simple rule for 7, but repeated division or checking factors is required.
- Divisibility by 11: This involves alternating addition and subtraction of digits. If the result is divisible by 11, then the original number is also divisible by 11.
These rules can help speed up the process of finding factors, especially for larger numbers.
Applications of Factorization in Real-World Scenarios
While the concept of factors might seem purely theoretical, it has many practical applications:
- Scheduling: Finding the LCM is crucial in scheduling events that occur at different intervals. For example, determining when two machines require maintenance at the same time.
- Resource Allocation: Understanding factors and divisors helps optimize resource distribution and allocation in various fields, such as manufacturing and project management.
- Cryptography: As previously mentioned, prime numbers and their factorization are fundamental to modern cryptography. The security of online transactions relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
- Modular Arithmetic: Used extensively in computer science, particularly in cryptography and error detection, and relies on the understanding of remainders and divisibility.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Factors
The seemingly simple question of "What are the factors of 77?" has led us on a journey through the fascinating world of number theory. We've learned about factors, prime numbers, prime factorization, the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, and the practical applications of these concepts. The exploration of 77's factors serves as a microcosm of the deeper mathematical structures that underpin many aspects of our world, from the abstract realm of theoretical mathematics to the concrete applications in technology and everyday life. The seemingly simple number 77 holds a wealth of mathematical significance, showcasing the beauty and power of number theory. Further exploration into these concepts will reveal even more intricate connections and applications within the broader field of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Degrees Are In A Half Circle
May 09, 2025
-
What Force Keeps The Planets In Orbit Around The Sun
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Products Of This Chemical Reaction
May 09, 2025
-
What Are Some Examples Of A Screw
May 09, 2025
-
What Planet Is Known As The Morning Star
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 77 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.