What Are The Factors Of 76
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
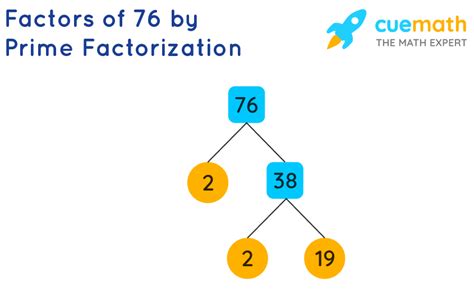
Table of Contents
What Are the Factors of 76? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Divisibility
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the process reveals fundamental concepts in number theory, crucial for various mathematical applications. This article delves into the factors of 76, exploring the methods to identify them, the underlying principles of prime factorization, and the broader implications of divisibility rules. We’ll also examine how these concepts connect to more advanced mathematical ideas.
Understanding Factors
Before we tackle the factors of 76, let's establish a clear definition. A factor (also known as a divisor) of a number is an integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by a factor and get a whole number result, then that number is a factor.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Finding the Factors of 76: A Step-by-Step Approach
Several methods exist to determine the factors of a number like 76. Here are two common approaches:
1. Pair-wise Factorization
This method involves systematically checking each integer to see if it divides 76 evenly. We start with 1, which is always a factor of any positive integer, and work our way up:
- 1: 76 / 1 = 76 (1 and 76 are factors)
- 2: 76 / 2 = 38 (2 and 38 are factors)
- 4: 76 / 4 = 19 (4 and 19 are factors)
- 19: 76 / 19 = 4 (We've already found 4)
Notice that after reaching 19, we've effectively found all pairs. Any subsequent number larger than 19 will not be a factor. Therefore, the factors of 76 are 1, 2, 4, 19, 38, and 76.
2. Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more powerful method, especially for larger numbers. It involves breaking down a number into its prime factors – numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
The prime factorization of 76 is found as follows:
- Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 76 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 76 / 2 = 38.
- Continue with 2: 38 is also even, so it's divisible by 2. 38 / 2 = 19.
- Check for other prime factors: 19 is a prime number itself.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 76 is 2 x 2 x 19, or 2² x 19.
This method provides a concise representation of the number's composition. From the prime factorization, we can easily derive all the factors.
Connecting Factors to Divisibility Rules
Understanding divisibility rules can significantly speed up the process of finding factors. Divisibility rules provide quick checks to see if a number is divisible by specific integers without performing the full division. Some relevant rules for 76 are:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8). Since 76 ends in 6, it's divisible by 2.
- Divisibility by 4: A number is divisible by 4 if its last two digits form a number divisible by 4. Since 76 is divisible by 4, it's also divisible by 4.
- Divisibility by 19: There isn't a simple divisibility rule for 19, but knowing that 19 is a factor is helpful.
Using divisibility rules eliminates the need to try every number. These rules work in conjunction with the prime factorization method for efficient factor finding.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number is not merely a step in finding factors; it holds significant mathematical importance:
- Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers. This uniqueness is fundamental to many number-theoretic proofs and algorithms.
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization is essential for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. These concepts are crucial in simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and other mathematical problems.
- Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a vital role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors forms the basis of the security of these systems.
- Modular Arithmetic: Understanding prime factorization helps in simplifying calculations involving modular arithmetic (arithmetic with remainders). This is crucial in various areas, including computer science and coding theory.
Beyond the Factors of 76: Expanding the Concepts
The principles illustrated by finding the factors of 76 are widely applicable. Let's expand on the broader context:
Factors and Number Theory
Number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers, relies heavily on concepts of factors, divisibility, and prime numbers. Advanced topics like modular arithmetic, Diophantine equations, and analytic number theory are deeply rooted in these fundamental ideas.
Factors in Algebra
Factors are crucial in algebra for simplifying expressions, factoring polynomials, and solving equations. Factoring techniques like the difference of squares, perfect square trinomials, and grouping rely on the ability to identify factors and their relationships.
Factors in Computer Science
Factors and prime factorization algorithms are important in computer science for tasks like cryptography, data compression, and hash table design. Efficient algorithms for finding prime factors are actively researched due to their computational significance.
Factors in Real-World Applications
Although seemingly abstract, the concepts of factors and divisibility find practical applications in various fields:
- Scheduling and Resource Allocation: Determining optimal schedules or resource allocations often involves finding common factors or multiples.
- Engineering and Design: Many engineering designs involve dimensions and measurements that need to be divisible by specific units or factors.
- Music Theory: Musical intervals and harmonies are related to mathematical ratios and fractions, which involve concepts of factors and divisors.
Conclusion: The Richness of Factorization
The seemingly straightforward task of finding the factors of 76 opens a door to a wealth of mathematical concepts. From simple divisibility rules to the fundamental theorem of arithmetic and its applications in advanced mathematics and computer science, understanding factors provides a solid foundation for exploring the fascinating world of numbers. The seemingly simple process of factorization underpins much of modern mathematics and its applications, highlighting its enduring importance. Remember, the journey of exploring numbers is endless, and each number holds a unique story waiting to be discovered. The seemingly simple process of finding factors is a gateway to a much wider and deeper understanding of mathematical principles that are essential for various applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Degrees Are In A Half Circle
May 09, 2025
-
What Force Keeps The Planets In Orbit Around The Sun
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Products Of This Chemical Reaction
May 09, 2025
-
What Are Some Examples Of A Screw
May 09, 2025
-
What Planet Is Known As The Morning Star
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 76 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.