What Are The Factors Of 67
Juapaving
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
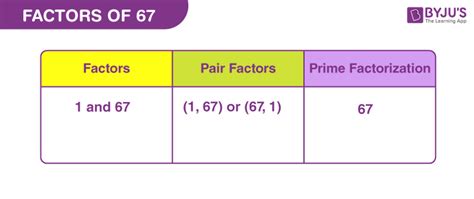
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 67? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 67?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime numbers, and factorization. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, exploring the concept allows us to delve into the fundamental building blocks of mathematics and understand the significance of prime numbers in various applications.
Understanding Factors
Before we tackle the factors of 67 specifically, let's define what a factor is. A factor of a number is any whole number that divides evenly into that number without leaving a remainder. In other words, if we divide the number by its factor, the result is a whole number. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
Identifying the Factors of 67
Now, let's focus on the number 67. To find its factors, we need to systematically check which whole numbers divide 67 without leaving a remainder. We can start by checking the smallest whole numbers:
- 1: 67 divided by 1 is 67, so 1 is a factor.
- 2: 67 is not divisible by 2 (it's not an even number).
- 3: 67 is not divisible by 3 (the sum of its digits, 6 + 7 = 13, is not divisible by 3).
- 4: 67 is not divisible by 4.
- 5: 67 is not divisible by 5 (it doesn't end in 0 or 5).
- 6: 67 is not divisible by 6.
- 7: 67 divided by 7 is approximately 9.57, not a whole number.
- 8: 67 is not divisible by 8.
- 9: 67 is not divisible by 9.
- 10: 67 is not divisible by 10.
We can continue this process, but we'll quickly notice a pattern. As we move towards larger numbers, the chances of finding a factor diminish. In fact, we will find that the only whole numbers that divide 67 evenly are 1 and 67 itself.
67: A Prime Number
This brings us to a crucial concept in number theory: prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself. Since 67 only has the factors 1 and 67, it is a prime number.
Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks in number theory. They are the "atoms" of numbers, and every other whole number (except 1) can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
For example:
- 12 = 2 x 2 x 3 (2 and 3 are prime factors)
- 18 = 2 x 3 x 3 (2 and 3 are prime factors)
- 24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 (2 and 3 are prime factors)
This decomposition into prime factors is extremely useful in various mathematical and computational applications, including:
- Cryptography: Prime numbers form the basis of many modern encryption algorithms, ensuring secure online communication.
- Coding Theory: Prime numbers are used in error-correcting codes, which help ensure data integrity during transmission.
- Hashing: In computer science, prime numbers play a role in hash functions, which are used to efficiently store and retrieve data.
Finding Prime Numbers: A Brief History
The search for prime numbers has captivated mathematicians for centuries. Ancient Greek mathematicians, like Euclid, studied prime numbers extensively. Euclid famously proved that there are infinitely many prime numbers – a remarkable result that highlights the endless nature of these fundamental building blocks.
Over time, mathematicians have developed various methods and algorithms to identify and generate prime numbers. Some notable examples include:
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: A simple but efficient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
- Miller-Rabin Primality Test: A probabilistic test used to determine whether a number is likely prime. While not guaranteed to be accurate 100% of the time, it's highly reliable and computationally efficient.
- AKS Primality Test: A deterministic polynomial-time algorithm that definitively determines whether a number is prime. While theoretically significant, it's generally less efficient than probabilistic tests for practical applications.
Beyond 67: Exploring Other Prime Numbers
Understanding the factors of 67 leads us to appreciate the broader context of prime numbers. There are infinitely many prime numbers, each with its own unique characteristics. Some notable examples include:
- 2: The only even prime number.
- 3, 5, 7, 11, 13...: The first few prime numbers, illustrating the irregular distribution of primes among integers.
- Mersenne Primes: Prime numbers that are one less than a power of 2 (e.g., 3, 7, 31, 127...). The largest known prime numbers are often Mersenne primes.
- Twin Primes: Pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13, 17 and 19...). The existence of infinitely many twin primes remains an open question in number theory.
Practical Applications of Prime Factorization
While the concept might seem abstract, prime factorization has numerous practical applications:
-
Public-key cryptography: RSA encryption, widely used to secure online transactions, relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of this method hinges on the computational complexity of finding the prime factors of extremely large numbers.
-
Hashing algorithms: Prime numbers are often used in hashing algorithms to minimize collisions, ensuring data integrity and efficient retrieval in databases and other data structures.
-
Coding theory: Error detection and correction codes often employ prime numbers to enhance their efficiency and effectiveness. These codes ensure reliable data transmission in various communication systems.
-
Random number generation: Prime numbers are crucial in creating pseudorandom number generators, which have applications in simulations, cryptography, and statistical analysis.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of 67's Factors
The seemingly simple question about the factors of 67 unveils a profound journey into the world of prime numbers and their significance in mathematics and beyond. The fact that 67 is a prime number highlights its fundamental role as a building block within the number system. Its unique factorization (1 and 67) demonstrates the core principles of number theory and underscores the crucial role prime numbers play in various areas of computer science, cryptography, and other fields. The exploration of prime numbers, initiated by a seemingly simple question about the factors of 67, illustrates the fascinating depth and beauty of mathematics and its enduring impact on our technological world. The journey from a seemingly simple question to understanding the implications of prime numbers exemplifies how a fundamental mathematical concept can have far-reaching and practical consequences in our modern world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Hydrogen Is In Group 1
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Mins In 9 Hours
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 0 8
May 09, 2025
-
Which Is An Interconnection Of Food Chains In An Ecosystem
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Opposite Word Of Cruel
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 67 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.