What Are The Factors Of 105
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
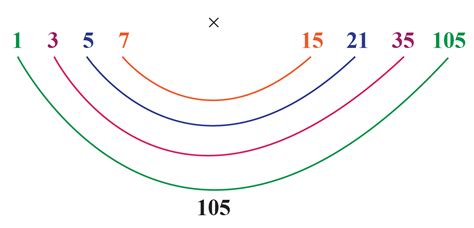
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 105? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Beyond
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 105. However, understanding the process of factorization, particularly prime factorization, unlocks a world of mathematical concepts and applications. This article will not only answer the question "What are the factors of 105?" but will also explore the underlying principles, delve into related mathematical concepts, and provide practical applications of factor analysis.
Understanding Factors
Before we delve into the specifics of 105, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. A factor of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
Finding the Factors of 105: A Step-by-Step Approach
There are several methods to find the factors of 105. Let's explore two common approaches:
1. The Systematic Approach
This method involves systematically checking each number from 1 up to the square root of 105 (approximately 10.2). For every number that divides 105 evenly, we find its corresponding pair.
- 1: 105 / 1 = 105 (Pair: 1 and 105)
- 3: 105 / 3 = 35 (Pair: 3 and 35)
- 5: 105 / 5 = 21 (Pair: 5 and 21)
- 7: 105 / 7 = 15 (Pair: 7 and 15)
Therefore, the factors of 105 are 1, 3, 5, 7, 15, 21, 35, and 105.
2. Prime Factorization
This method is more elegant and provides a deeper understanding of the number's structure. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
To find the prime factorization of 105:
- Start by dividing 105 by the smallest prime number, 2. Since 105 is odd, it's not divisible by 2.
- Try the next prime number, 3: 105 / 3 = 35.
- Now we have 3 x 35. 3 is prime, but 35 is not.
- We can further factor 35: 35 = 5 x 7. Both 5 and 7 are prime numbers.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 105 is 3 x 5 x 7.
Knowing the prime factorization allows us to easily find all the factors. We can combine the prime factors in various ways to generate all the factors:
- 3<sup>0</sup> x 5<sup>0</sup> x 7<sup>0</sup> = 1
- 3<sup>1</sup> x 5<sup>0</sup> x 7<sup>0</sup> = 3
- 3<sup>0</sup> x 5<sup>1</sup> x 7<sup>0</sup> = 5
- 3<sup>0</sup> x 5<sup>0</sup> x 7<sup>1</sup> = 7
- 3<sup>1</sup> x 5<sup>1</sup> x 7<sup>0</sup> = 15
- 3<sup>1</sup> x 5<sup>0</sup> x 7<sup>1</sup> = 21
- 3<sup>0</sup> x 5<sup>1</sup> x 7<sup>1</sup> = 35
- 3<sup>1</sup> x 5<sup>1</sup> x 7<sup>1</sup> = 105
This confirms our earlier findings: the factors of 105 are 1, 3, 5, 7, 15, 21, 35, and 105.
Beyond the Factors: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the factors of 105 opens doors to several related mathematical concepts:
1. Divisibility Rules
The process of finding factors often involves applying divisibility rules. These rules provide shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by a specific prime number without performing the actual division. For example:
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. (1 + 0 + 5 = 6, which is divisible by 3, confirming that 105 is divisible by 3).
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is either 0 or 5. (The last digit of 105 is 5, so it's divisible by 5).
- Divisibility by 7: There's a slightly more complex rule for 7, but it's still helpful. This rule isn't always the easiest to apply, so the simplest way is to divide by 7 to check.
2. Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Knowing the factors of a number is crucial for finding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers. The GCF is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers. These concepts are fundamental in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems.
For instance, if we need to find the GCF and LCM of 105 and another number, say 70, we would first find the prime factorization of both numbers. The prime factorization of 70 is 2 x 5 x 7.
Comparing the prime factorizations of 105 (3 x 5 x 7) and 70 (2 x 5 x 7), we find that the GCF is 5 x 7 = 35. The LCM would be 2 x 3 x 5 x 7 = 210.
3. Number Theory
Factorization is a core concept in number theory, a branch of mathematics that studies the properties of integers. Many advanced mathematical problems and theorems rely on the understanding of prime factorization and related concepts. For example, Fermat's Little Theorem and the Chinese Remainder Theorem are based on principles of prime factorization.
4. Cryptography
Prime factorization plays a vital role in modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms rely on the difficulty of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components. The security of these systems depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring such numbers in a reasonable timeframe.
Practical Applications of Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding factors has widespread applications in various fields:
- Algebra: Factoring is crucial for solving quadratic equations and simplifying algebraic expressions.
- Geometry: Calculating areas and volumes often involves factoring.
- Computer Science: Algorithms for data compression and optimization often utilize factorization techniques.
- Engineering: Many engineering designs rely on calculations that involve factoring for structural integrity and efficiency.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Factors
This in-depth exploration demonstrates that finding the factors of 105, while seemingly a basic mathematical task, is a gateway to a vast range of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From understanding prime factorization to applying divisibility rules and exploring concepts like GCF and LCM, the ability to factor numbers forms the basis of many advanced mathematical principles and has tangible real-world implications. By understanding the process of factorization, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the structure and properties of numbers, furthering our mathematical understanding and problem-solving capabilities. The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 105?" ultimately leads to a rich and rewarding exploration of the world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 60 Square Meters
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Formula Of A Hydronium Ion
May 09, 2025
-
Real Life Example Of A Right Angle
May 09, 2025
-
How To Multiply A 3x3 Matrix By A 3x1 Matrix
May 09, 2025
-
What X Value Makes The Set Of Ratios Equivalent
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 105 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.