What Are The Factors For 92
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
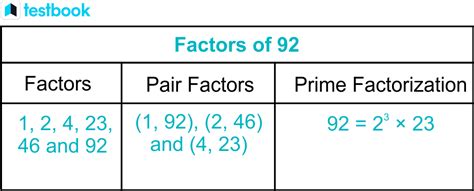
Table of Contents
What Are the Factors for 92? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 92?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While finding the factors of a small number like 92 might seem straightforward, understanding the underlying principles reveals broader concepts applicable to much larger numbers and complex mathematical problems. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the concepts of factors, prime factorization, and their significance in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Factors
A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In other words, if a is a factor of b, then b/a is a whole number. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Finding the factors of a number is a fundamental concept in arithmetic, with applications in algebra, geometry, and cryptography. It helps us understand the structure of numbers and their relationships.
Finding the Factors of 92: A Step-by-Step Approach
To find the factors of 92, we can use a systematic approach:
-
Start with 1 and the number itself: Every number is divisible by 1 and itself. Therefore, 1 and 92 are factors of 92.
-
Check for divisibility by small prime numbers: Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.). We systematically check for divisibility by these prime numbers.
-
Divisibility by 2: 92 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 92 / 2 = 46, so 2 and 46 are factors.
-
Divisibility by 3: The sum of the digits of 92 (9 + 2 = 11) is not divisible by 3, so 92 is not divisible by 3.
-
Divisibility by 5: 92 does not end in 0 or 5, so it's not divisible by 5.
-
Divisibility by 7: 92 divided by 7 leaves a remainder, so 7 is not a factor.
-
Divisibility by 11: 92 divided by 11 leaves a remainder, so 11 is not a factor.
-
-
Continue checking prime numbers: We continue this process, but we can stop when we reach the square root of 92 (approximately 9.59). If we haven't found any other factors by this point, we've found all the factors.
-
Identify factor pairs: Notice that factors often come in pairs. For example, since 2 is a factor, so is 46 (because 2 x 46 = 92). Similarly, if we find another factor x, then 92/x will also be a factor.
Therefore, the factors of 92 are 1, 2, 4, 23, 46, and 92.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Building Blocks
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. This is a unique representation for every number (except 1, which has no prime factors). It provides a fundamental understanding of the number's structure.
To find the prime factorization of 92, we can use a factor tree:
92
/ \
2 46
/ \
2 23
This shows that 92 = 2 x 2 x 23 = 2² x 23. The prime factors of 92 are 2 and 23. This is the unique prime factorization of 92.
The Significance of Factors and Prime Factorization
The concepts of factors and prime factorization are not just abstract mathematical ideas; they have practical applications in many areas:
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption, which relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Understanding factors is essential in modular arithmetic, which is used in various fields, including computer science and cryptography. Modular arithmetic deals with remainders after division.
-
Algebra: Factoring is a fundamental technique in algebra, used to solve equations and simplify expressions.
-
Number Theory: Factors and prime factorization are central concepts in number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of numbers.
-
Computer Science: Efficient algorithms for finding factors and performing prime factorization are crucial in computer science, especially in cryptography and data compression.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding factors leads to more advanced concepts in number theory:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. For instance, the GCD of 12 and 18 is 6. Finding the GCD is important in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems. The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCD.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. For example, the LCM of 12 and 18 is 36. The LCM is used in solving problems involving fractions and finding the least common denominator.
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding the number itself). For example, 6 is a perfect number (1 + 2 + 3 = 6). Finding perfect numbers is a challenging problem in number theory.
-
Abundant Numbers: An abundant number is a positive integer that is less than the sum of its proper divisors.
-
Deficient Numbers: A deficient number is a positive integer that is greater than the sum of its proper divisors.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The concepts of factors and prime factorization are not confined to the classroom; they have many real-world applications:
-
Scheduling: Finding the LCM is useful in scheduling events that occur at different intervals. For example, if Event A occurs every 12 days and Event B occurs every 18 days, the LCM (36) tells us when both events will coincide.
-
Resource Allocation: Understanding factors can help in allocating resources efficiently. For instance, if you have 92 items to distribute equally among groups, knowing the factors of 92 helps determine the possible group sizes.
-
Music Theory: The relationship between musical intervals can be understood using the concepts of factors and ratios.
-
Geometry: Factors play a role in determining the dimensions of shapes and solving geometric problems.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Factors
The seemingly simple task of finding the factors of 92 reveals a wealth of mathematical concepts with far-reaching applications. From the fundamental principles of divisibility to the complex world of cryptography, the ability to understand and manipulate factors is a crucial skill across many disciplines. This article provides a comprehensive overview, but the exploration of number theory is a lifelong journey filled with fascinating discoveries. The simple number 92, therefore, serves as a springboard to a deeper appreciation of the beauty and power of mathematics. By mastering these concepts, one gains a more profound understanding of the numerical world around us. Further exploration into advanced number theory will undoubtedly reveal even more intricate and fascinating relationships within the realm of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Prove A Square Is A Square
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is 34 An Even Or Odd Number
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of A Decomposer
Mar 17, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 24 And 36
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Goes Up And Down But Doesnt Move
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 92 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
