What Are The Factors For 68
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
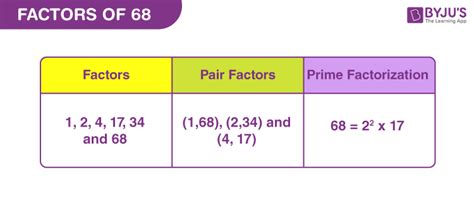
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma of "Factors for 68": A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 68?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, encompassing concepts like prime factorization, divisibility rules, and the very nature of integers. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, exploring the broader context reveals a wealth of mathematical intricacies and applications. This article will delve deep into the factors of 68, exploring the underlying principles and extending the discussion to broader mathematical concepts.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we tackle the specific case of 68, let's establish a solid foundation. A factor (or divisor) of a number is an integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. In simpler terms, if we can divide a number by a factor and get a whole number as the result, then that number is a factor.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. This is because 12 can be divided evenly by each of these numbers. The process of finding factors is intrinsically linked to the concept of divisibility. A number is divisible by another number if the division results in a whole number (integer) quotient with no remainder.
Finding the Factors of 68: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's focus on finding the factors of 68. We can approach this systematically:
-
Start with 1 and the number itself: Every number is divisible by 1 and itself. Thus, 1 and 68 are factors of 68.
-
Check for small prime numbers: Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Let's check if 68 is divisible by these:
- 68 ÷ 2 = 34 (Yes, 2 is a factor)
- 68 ÷ 3 = 22.66... (No)
- 68 ÷ 5 = 13.6 (No)
- 68 ÷ 7 = 9.71... (No)
- and so on...
-
Consider the factors we've found: Since 2 is a factor, and 68 ÷ 2 = 34, we know that 34 is also a factor.
-
Systematic search: We can continue checking numbers until we reach the square root of 68 (approximately 8.25). Any factors beyond this point will have a corresponding factor we've already found.
-
Complete Factor List: Following this systematic approach, the complete list of factors for 68 is: 1, 2, 4, 17, 34, and 68.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Building Blocks
Prime factorization is a powerful technique in number theory. It involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime factor is a factor that is also a prime number. This method provides a unique representation of any composite number (a number that is not prime).
Let's find the prime factorization of 68:
- We know 68 is divisible by 2: 68 = 2 x 34
- 34 is also divisible by 2: 34 = 2 x 17
- 17 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 68 is 2² x 17. This means that 68 can be built solely from the prime numbers 2 and 17. This representation is unique to 68 and is fundamental to various number-theoretic applications.
Applications and Extensions
Understanding factors has far-reaching applications beyond simple arithmetic:
-
Algebra: Factoring is a crucial skill in algebra, allowing us to simplify expressions, solve equations, and analyze polynomial functions. The ability to find the factors of a number directly relates to the ability to factor algebraic expressions.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization is the cornerstone of many modern cryptographic systems. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components forms the basis of the security of these systems.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms related to prime factorization and divisibility are fundamental in computer science, used in tasks like data compression, hashing, and random number generation.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Understanding factors is essential for working with modular arithmetic, which involves performing arithmetic operations within a finite set of numbers (e.g., clock arithmetic).
Beyond 68: Exploring Other Numbers and Concepts
The principles applied to finding the factors of 68 can be extended to any positive integer. Here are some related concepts to explore:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. Algorithms like the Euclidean algorithm are used to efficiently compute GCDs.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. The GCD and LCM are closely related concepts.
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (excluding the number itself). For example, 6 is a perfect number (1 + 2 + 3 = 6).
-
Abundant and Deficient Numbers: Abundant numbers have the sum of their proper divisors greater than the number itself, while deficient numbers have the sum less than the number itself.
Conclusion: The Significance of Factorization
The seemingly simple task of finding the factors of 68 opens a gateway to a rich mathematical landscape. From the fundamentals of divisibility to the advanced applications in cryptography and computer science, the concept of factorization is a cornerstone of number theory and numerous other fields. By understanding the principles discussed in this article, you've not only learned about the factors of 68 but also gained a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of mathematical concepts. This knowledge provides a foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and understanding the underlying structures of the number system. The exploration of numbers, their factors, and their properties is an ongoing journey, constantly revealing new insights and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 60 Square Meters
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Formula Of A Hydronium Ion
May 09, 2025
-
Real Life Example Of A Right Angle
May 09, 2025
-
How To Multiply A 3x3 Matrix By A 3x1 Matrix
May 09, 2025
-
What X Value Makes The Set Of Ratios Equivalent
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 68 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.