Type Of Energy Transformed By A Toaster Into Thermal Energy
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
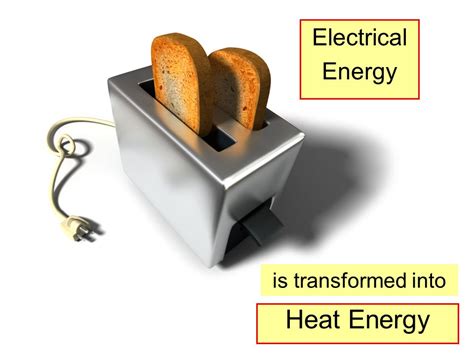
Table of Contents
The Wonderful World of Toasters: Transforming Electrical Energy into Thermal Energy
Toasters. Those ubiquitous kitchen appliances that transform dull slices of bread into golden-brown, crispy perfection. But have you ever stopped to consider the fascinating physics behind this simple act? It's all about the transformation of energy, specifically the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy, a process that involves several intriguing steps and concepts. This article delves into the intricacies of this energy transformation, exploring the science behind toasting and the different types of energy involved.
The Electrical Journey: From Outlet to Element
The journey begins at your wall outlet, a source of electrical potential energy. This energy, stored in the form of moving electrons within the electrical grid, flows into your toaster via the power cord. The cord, consisting of insulated copper wires, acts as a conductor, facilitating the movement of these electrons with minimal resistance. The higher the voltage, the greater the electrical potential energy available for conversion.
Resistance Heating: The Heart of the Toaster
Once the electricity reaches the toaster, it encounters the heating element, the crucial component responsible for the transformation of electrical energy into thermal energy. This element is typically made of a high-resistance material, often nichrome (an alloy of nickel and chromium). This high resistance is key; it's what enables the conversion process.
As electrons flow through the nichrome wire, they collide repeatedly with the atoms within the material. These collisions impede the electron's flow, converting their kinetic energy (energy of motion) into heat, or thermal energy. This process is known as resistive heating, or Joule heating, and it's the fundamental principle behind how toasters work.
The higher the resistance of the nichrome wire, the greater the number of collisions and the more efficiently electrical energy is transformed into heat. This is why nichrome, with its high resistance and high melting point, is ideally suited for this application.
Beyond Resistance: Other Energy Transformations
While resistive heating is the primary mechanism, other subtle energy transformations occur within the toaster. These are often less significant in terms of overall energy conversion but contribute to the overall efficiency and performance of the appliance.
Electromagnetic Radiation: Infrared and Visible Light
As the nichrome element heats up, it emits electromagnetic radiation. A significant portion of this radiation falls within the infrared spectrum, which we experience as heat. This infrared radiation is what directly warms the bread slices, causing the carbohydrates to undergo the Maillard reaction, resulting in that characteristic toasted flavor and brown color.
The element also emits a smaller amount of visible light, which you can observe as a dull red glow when the toaster is operating. This visible light is another form of electromagnetic radiation, a byproduct of the heating process.
Conduction and Convection: Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Once the thermal energy is generated within the nichrome element, it needs to be transferred to the bread. This happens through two primary mechanisms: conduction and convection.
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact. The heat from the hot nichrome element is directly conducted to the bread slices through the metal slots in the toaster. The better the thermal conductivity of the metal, the more efficient this heat transfer.
Convection plays a role, especially within the toaster's internal cavity. The heated air within the toaster rises, creating convection currents that help distribute the heat more evenly around the bread slices. This ensures more uniform toasting.
Energy Efficiency and Losses: Where Does the Energy Go?
It's important to note that not all the electrical energy input is perfectly converted into thermal energy used for toasting. Some energy is lost through various mechanisms:
-
Radiation Losses: Some of the infrared radiation generated by the heating element escapes into the surrounding environment without reaching the bread. This is a form of energy loss, reducing the overall efficiency of the toasting process.
-
Conduction Losses: Heat is also conducted away from the toaster itself through the casing and other components. This represents another avenue for energy loss.
-
Internal Resistance: The wiring within the toaster, while designed for minimal resistance, still exhibits some resistance, generating a small amount of heat that isn't directly contributing to toasting.
The overall energy efficiency of a toaster is a function of how effectively it minimizes these energy losses and maximizes the transfer of heat to the bread. Modern toasters employ various design features to improve efficiency, such as better insulation and optimized heating element designs.
Beyond the Basics: Types of Toasters and Their Energy Efficiency
The type of toaster can also impact energy efficiency. While the underlying principle remains the same (converting electrical energy to thermal energy through resistive heating), variations in design and features can affect energy usage.
-
Slotted Toasters: These are the most common type, offering simple and straightforward toasting. Energy efficiency varies depending on the quality of the insulation and the design of the heating element.
-
Four-Slice Toasters: While allowing for simultaneous toasting of four slices, these toasters generally consume more energy than their two-slice counterparts due to their larger heating elements and increased surface area.
-
Convection Toasters: These toasters utilize forced convection, employing fans to circulate heated air more effectively around the bread. While potentially achieving faster and more even toasting, their energy efficiency can vary depending on the efficiency of the fan and heating elements.
-
Toaster Ovens: These appliances combine the functionality of a toaster and a small oven. While offering greater versatility, they generally consume significantly more energy than traditional toasters due to their larger size and increased heating requirements.
The Bigger Picture: Energy Consumption and Sustainability
Understanding the energy transformation within a toaster provides insight into its overall energy consumption. While a toaster isn't a major energy consumer in a household, mindful usage can contribute to energy conservation. Choosing energy-efficient models with good insulation and optimal heating element design can make a difference.
Furthermore, the toaster's energy usage is part of the larger picture of energy consumption in our homes and the impact on the environment. Considering the source of the electricity used to power the toaster is crucial. Using renewable energy sources reduces the environmental footprint associated with toasting your bread.
Conclusion: A Simple Appliance, Complex Science
The humble toaster, seemingly a simple appliance, reveals a fascinating world of energy transformation. From the electrical potential energy at the wall outlet to the thermal energy that browns your bread, the process involves a complex interplay of electrical and thermal phenomena. Understanding these processes not only enhances our appreciation for this everyday appliance but also promotes a deeper understanding of energy, its conversion, and its impact on our lives and the environment. By considering the energy efficiency of our toasters and choosing appliances wisely, we can contribute to a more sustainable future, one perfectly toasted slice at a time.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Longest Stage Of The Cell Cycle
Apr 08, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 18 And 12
Apr 08, 2025
-
How Many Meters In A Kilogram
Apr 08, 2025
-
How Many Acres Are In One Hectare
Apr 08, 2025
-
Words That Begin With A G
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Type Of Energy Transformed By A Toaster Into Thermal Energy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.