Triangle With 3 Lines Of Symmetry
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
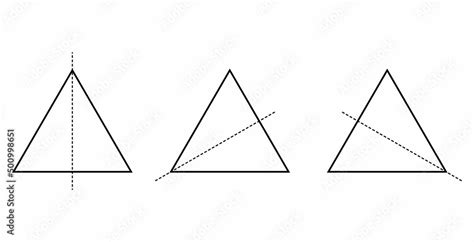
Table of Contents
The Equilateral Triangle: A Masterpiece of Symmetry
The world of geometry is replete with fascinating shapes, each with its unique properties. Among them, the equilateral triangle stands out as a paragon of symmetry, boasting a remarkable three lines of symmetry. This seemingly simple shape holds a wealth of mathematical elegance and practical applications, making it a subject worthy of in-depth exploration. This article delves into the captivating world of the equilateral triangle, examining its symmetries, properties, and significance in various fields.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before delving into the specifics of the equilateral triangle, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap.
Many shapes possess lines of symmetry, some more than others. A square, for instance, has four lines of symmetry: two that run diagonally and two that run horizontally and vertically. A circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry, as any line passing through its center will divide it into two identical halves.
The Unique Symmetry of the Equilateral Triangle
The equilateral triangle, defined as a triangle with all three sides of equal length, distinguishes itself by possessing three lines of symmetry. These lines are:
- One vertical line of symmetry: This line runs from the apex (the top vertex) to the midpoint of the opposite side (the base).
- Two diagonal lines of symmetry: These lines connect each vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
Each of these lines perfectly bisects the triangle, creating two congruent mirror images. This threefold symmetry is a defining characteristic that sets the equilateral triangle apart from other types of triangles. This perfect balance and symmetry contribute to its aesthetic appeal and its frequent use in design and art.
Mathematical Proof of Symmetry
The existence of three lines of symmetry in an equilateral triangle can be proven mathematically. Let's consider an equilateral triangle ABC, where AB = BC = CA.
-
Vertical Line of Symmetry: Draw a line from vertex A to the midpoint M of BC. AM is the altitude and median of the triangle. By the properties of an equilateral triangle, AM also bisects angle A. Therefore, triangle AMB is congruent to triangle AMC (Side-Angle-Side congruence). This proves that the line AM is a line of symmetry.
-
Diagonal Lines of Symmetry: Similarly, drawing lines from vertex B to the midpoint of AC (let's call it N) and from vertex C to the midpoint of AB (let's call it O) will create two more lines of symmetry. The triangles formed (BNC and COA, and AOB) are all congruent, demonstrating the existence of the two diagonal lines of symmetry.
Properties of an Equilateral Triangle
Beyond its captivating symmetry, the equilateral triangle boasts several other remarkable properties:
-
All angles are equal (60°): The sum of angles in any triangle is 180°. In an equilateral triangle, all three angles are equal, meaning each angle measures 60°. This constant angle makes it highly predictable and useful in various geometric constructions.
-
All sides are equal: This is the defining characteristic of an equilateral triangle. This equal-sidedness contributes to the inherent balance and symmetry of the shape.
-
Altitude, median, angle bisector, and perpendicular bisector coincide: In an equilateral triangle, the line segment from a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side acts as the altitude (height), median (midpoint connector), angle bisector, and perpendicular bisector simultaneously. This unique property further underscores the inherent symmetry and balance of the figure.
-
Inradius and circumradius relationship: The inradius (radius of the inscribed circle) and circumradius (radius of the circumscribed circle) have a specific ratio of 1:2. This means the circumradius is twice the length of the inradius.
Applications of Equilateral Triangles
The unique properties and symmetrical nature of the equilateral triangle make it incredibly versatile and useful across many fields:
1. Architecture and Design:
Equilateral triangles are frequently incorporated into architectural designs, creating visually appealing and structurally sound structures. They are used in:
- Trusses and Bridges: Their inherent strength and stability make them ideal components in truss structures and bridge designs.
- Roof structures: The triangular shape provides excellent support and load distribution, making it an efficient choice for roofing systems.
- Tessellations: Equilateral triangles are the only regular polygon that can tessellate (tile a plane) on their own, without leaving gaps. This property finds application in various tiling patterns and floor designs.
2. Art and Nature:
The equilateral triangle's aesthetic appeal is undeniable. It's frequently used in:
- Artwork and logos: Many logos and works of art feature the equilateral triangle, utilizing its symmetry and balance for visual effect.
- Nature's patterns: Naturally occurring patterns often incorporate equilateral triangles, including the arrangement of leaves on some plants and the structure of certain crystals.
3. Mathematics and Geometry:
As a fundamental geometric shape, the equilateral triangle plays a significant role in:
- Trigonometry: It serves as a basis for understanding trigonometric functions and ratios.
- Geometric constructions: It's used in various geometric constructions, such as dividing a line segment into equal parts.
- Fractal geometry: The equilateral triangle is a building block for numerous fractals, creating intricate and self-similar patterns.
4. Engineering and Science:
- Structural Engineering: The equilateral triangle's strength and stability find applications in various engineering structures.
- Physics and Mechanics: Its symmetrical properties are relevant in various physics principles, such as the analysis of forces and equilibrium.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Deeper Concepts
While the basic properties and applications of the equilateral triangle are readily understood, further exploration can reveal even more intriguing aspects:
-
Advanced Geometric Constructions: Constructing more complex geometric shapes using equilateral triangles as the foundation reveals fascinating connections within geometry.
-
Relationship to other shapes: The equilateral triangle holds specific relationships with other shapes like hexagons and other regular polygons, forming intricate patterns and tessellations.
-
Applications in Computer Graphics: The equilateral triangle's properties are utilized in computer graphics for polygon modeling, texture mapping, and other advanced techniques.
-
Advanced Mathematical proofs and theorems: Various mathematical proofs and theorems utilize the equilateral triangle as a fundamental element in demonstrating deeper concepts within geometry.
Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of the Equilateral Triangle
The equilateral triangle, with its three lines of symmetry and unique properties, stands as a testament to the beauty and power of mathematical elegance. Its applications span various fields, from architecture and design to mathematics and science. By understanding its fundamental characteristics and exploring its deeper connections within geometry, we gain a richer appreciation for this seemingly simple, yet profoundly significant, shape. Its enduring appeal lies in its perfect balance, its inherent stability, and the endless possibilities it offers for exploration and application. The equilateral triangle, more than just a geometric shape, is a symbol of symmetry, harmony, and the fundamental elegance found within the mathematical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Force Increase On An Inclined Plane
May 09, 2025
-
Interesting Words That Start With V
May 09, 2025
-
Compare And Contrast A Light Microscope And An Electron Microscope
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 6 25 Meters In Feet And Inches
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Are In 50 Millimeters
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Triangle With 3 Lines Of Symmetry . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.