There Is A Repulsive Force Between Two Charged Objects When
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
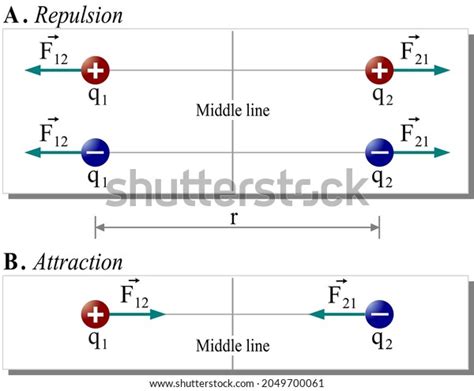
Table of Contents
There's a Repulsive Force Between Two Charged Objects When... Understanding Electrostatic Interactions
The universe is governed by fundamental forces, and among them, electromagnetism plays a crucial role in shaping our everyday experiences. From the simple act of turning on a light switch to the complex workings of electronic devices, electromagnetism is at play. A key aspect of electromagnetism is the interaction between charged objects, which can manifest as either attractive or repulsive forces. This article delves into the conditions that lead to a repulsive force between two charged objects, exploring the underlying principles and providing practical examples.
Understanding Charge and its Properties
Before diving into the repulsive force, it's essential to grasp the concept of electric charge. Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter, characterized by its ability to exert and experience electromagnetic forces. There are two types of electric charge:
- Positive charge: Typically associated with protons, the positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
- Negative charge: Typically associated with electrons, the negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus.
The fundamental principle governing the interaction between charges is Coulomb's Law, which quantifies the force between two point charges. This law states that the force is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The Repulsive Force: Like Charges Repel
The key to understanding when a repulsive force occurs lies in the nature of the charges involved. A fundamental principle of electrostatics dictates that:
Like charges repel, while unlike charges attract.
This means that:
- Two positively charged objects will repel each other.
- Two negatively charged objects will also repel each other.
This repulsive force arises from the inherent nature of the electromagnetic field surrounding charged particles. These fields interact, and when the fields are of the same polarity (both positive or both negative), they create a repulsive pressure, pushing the objects apart.
Visualizing the Repulsive Force
Imagine two positively charged balloons. If you bring them close together, you'll observe them pushing away from each other. This is a direct manifestation of the repulsive electrostatic force. The same would be true if you had two negatively charged objects, such as two electrons. Their negative charges would cause a repulsive force to push them apart.
This repulsive interaction can be visualized as a kind of "pressure" exerted by the electromagnetic fields of the charged objects. The stronger the charges and the closer they are, the greater this repulsive pressure becomes.
Coulomb's Law: The Mathematical Description
Coulomb's Law provides the quantitative framework for understanding the repulsive force between charged objects. Mathematically, it's expressed as:
F = k * |q1 * q2| / r²
Where:
- F represents the magnitude of the electrostatic force.
- k is Coulomb's constant (approximately 8.98755 × 10⁹ N⋅m²/C²).
- q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the two charges.
- r is the distance between the centers of the two charges.
The absolute value signs around q1 and q2 ensure that the force is always positive, reflecting the magnitude of the repulsion. The inverse square relationship (1/r²) highlights that the force decreases rapidly as the distance between the charges increases.
Implications of Coulomb's Law
Several crucial implications arise from Coulomb's Law in the context of repulsive forces:
-
Magnitude of Charges: The greater the magnitude of the charges, the stronger the repulsive force. Two objects with charges of 1 Coulomb each will experience a much stronger repulsion than two objects with charges of 0.1 Coulomb each at the same distance.
-
Distance between Charges: The repulsive force decreases rapidly with increasing distance. If you double the distance between the charges, the repulsive force becomes four times weaker. This inverse square relationship has far-reaching implications in many areas of physics and engineering.
-
Point Charges: Coulomb's Law is strictly accurate only for point charges – objects whose size is negligible compared to the distance between them. For larger objects, the calculation becomes more complex and often requires integration techniques to account for the distribution of charge across their surfaces.
Examples of Repulsive Forces in Everyday Life
While often unseen, repulsive forces between charged objects are prevalent in everyday life:
-
Static Cling: When you rub a balloon against your hair, it becomes charged (usually negatively). If you try to bring another similarly charged balloon close, they will repel each other. This is a common example of electrostatic repulsion.
-
Electrostatic Precipitation: This technology uses electrostatic forces to remove pollutants from industrial emissions. The pollutants are given a charge and then repelled by similarly charged plates, allowing for collection and removal.
-
Inkjet Printers: Inkjet printers utilize electrostatic forces to propel tiny droplets of ink onto the paper. The ink droplets are charged, and an electric field guides them to the precise location on the page. The repulsion between similarly charged ink droplets ensures that they remain separated and form clear, distinct dots.
-
Lightning: Although a more complex phenomenon, the repulsion between similarly charged particles within a thundercloud contributes to the build-up of static electricity that eventually leads to a lightning strike.
Repulsive Forces and Their Applications in Technology
The understanding and manipulation of repulsive forces have led to numerous technological advancements:
-
Electrostatic painting: This technique uses electrostatic repulsion to ensure even paint coverage on objects. The paint particles are charged, and the object to be painted is given the opposite charge, resulting in an even distribution of paint.
-
Xerography (photocopying): This process relies heavily on electrostatic forces. The toner particles are charged, and the electrostatic charge pattern on the drum repels or attracts the toner, creating an image on the paper.
-
Particle accelerators: These machines accelerate charged particles to extremely high energies. The repulsive forces between the particles must be carefully managed to prevent beam instability and ensure efficient acceleration.
-
Ion thrusters: Used in spacecraft propulsion, ion thrusters use the repulsion between charged ions to generate thrust. This type of propulsion system offers high efficiency but generally low thrust.
Beyond Coulomb's Law: More Complex Scenarios
While Coulomb's Law provides a foundational understanding, real-world situations can be far more complex. The following factors can influence the observed repulsive force:
-
Charge Distribution: In objects larger than point charges, the charge distribution can be uneven, leading to more complicated interactions than those described by Coulomb's Law.
-
Dielectric Materials: The presence of dielectric materials (insulators) between charged objects can reduce the strength of the electrostatic force. The dielectric constant of the material affects the strength of the interaction.
-
Induced Charges: When a charged object is brought near a neutral conductor, it can induce charges on the conductor's surface. These induced charges can influence the net repulsive or attractive forces.
Conclusion: The Significance of Repulsive Forces
The repulsive force between like charges is a fundamental aspect of electromagnetism with significant implications across various scientific disciplines and technological applications. Understanding this force is crucial for analyzing and designing systems involving charged particles, from everyday phenomena like static cling to sophisticated technologies such as particle accelerators and electrostatic painting. As our understanding of electromagnetism deepens, we can expect further innovations leveraging the power of electrostatic repulsion. The exploration and application of these principles will continue to shape the technological landscape for years to come. The seemingly simple interaction of like charges repelling each other forms the basis of numerous crucial technologies, highlighting the power of fundamental physics in driving innovation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Bones Do Shark Have
Apr 01, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 12 And 18
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Phase Is The Reverse Of Prophase
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is Tungsten A Metal Or Nonmetal
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Seconds Is 24 Hours
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about There Is A Repulsive Force Between Two Charged Objects When . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
